1. Introduction
Fratercula arctica, commonly called atlantic puffin or simply puffin, is a species of seabird belonging to the order
Charadriiformes and family
Alcidae. Its scientific name is related to the aspect of its black and white plumage gives it (from the Latin
fratercula; friar) and its distribution, fundamentally throughout the North Atlantic Ocean [
1,
2]. These seabirds are medium-sized birds that spend most of their lives in pelagic and offshore habitats, as they only come ashore during the reproductive period to nest on cliffs and rocky areas [
1,
3,
4,
5]. Males have larger body dimensions than females and are heavier, but their colors are similar (more vivid in the male during mating season). This seabird has a monogamous mating system, reaching sexual maturity around five years of age (range 3 to 6 years) and incubating one egg per clutch [
3,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. It feeds mainly on fish, including variable amounts of polychaetes and crustacean [
14,
15]. It is the only species of the three that constitute the genus
Fratercula (along with the horned puffin (
Fratercula corniculata) and the tufted puffin (
Fratercula cirrhata) that is included in the IUCN list of threatened species, being classified as vulnerable [
1]. Among the threats these animals face are entrapment in fishing nets [
16,
17], pollution [
7], predation by introduced species [
18,
19,
20], or reduced food availability [
21]. Another factor that has shown a tremendous negative impact on puffin populations is climate change, characterized by strong and increasingly common sea storms that can lead to massive strandings [
22,
23,
24,
25].
Puffins are essential indicators of the state of marine ecosystems and their changes over time due to their position in the trophic chains because they can act as bioaccumulator organisms [
26,
27,
28,
29]. Therefore, they play a helpful role in the transfer of phosphorus and nitrogen from oceanic waters to the continents [
30]. In addition to its biological importance, this charismatic species from the North Atlantic Ocean has become an ecotouristic attraction, and many companies in North America and Europe have developed this type of activity near puffin colonies [
3]. For all these reasons, private and governmental associations allocate part of their funds to puffin conservation projects [
31,
32].
It is considered that birds have a level of brain expansion close to that of mammals. Despite this, researchs into the neuroanatomy of this taxonomic group have been scarce. However, the irruption of modern imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) have enabled the development of this doctrine [
33].
In avian medicine, one of the more used imaging diagnostic tools has been conventional radiography, which provides valuable information on musculoskeletal and respiratory processes and alterations of the coelomic cavity (gas, effusions or masses). However, it is of little use in the head due to the structure overlapping and low resolution [
34,
35]. In this case, MRI and cross-sectional imaging modalities could provide adequate anatomical and pathological information, avoiding the main drawbacks of radiography [
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. It should be noted that, as in human medicine, MRI is the technique of choice for the study of the nervous system [
34], which has already been used in the study of the avian nervous system [
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. Nonetheless, to the authors’ knowledge, no research has been carried out on the nervous system of the Atlantic puffin. Therefore, this study aimed to describe the head of this bird using anatomical cross sections and MRI, so the results obtained could serve as a basis not only for future research on the puffin, but also on other birds or phylogenetically related animals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
We performed this study with 20 Atlantic puffins with a weight ranging between 0.185 and 0.310 kg, and size ranging between 16 cm and 24 cm (measured from beak to tail). The animals used in the study died due to natural causes and were provided by the Consejeria de Área de Medio Ambiente, Clima, Energía y Conocimiento of the Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria, as part of the investigation to determine the possible causes of the massive stranding of these animals. Moreover, the person in charge gave the authorization to include them in this study.
2.2. MRI Technique
The twenty puffins were imaged at Los Tarahales Veterinary Hospital (Las Palmas, Canary Islands, Spain). Magnetic resonance images were obtained with a Canon Vantage Elan 1.5 T equipment, using T1W sequences in a transversal plane (TR: 634 ms, TE: 10, FOV: 1809 × 829, thickness 2 mm, matrix 192 × 160), T2W sequences in a transversal plane (TR: 4769 ms, TE: 120, FOV: 1809 × 829, thickness 2 mm, matrix 192 × 224), T2W sequences in the dorsal plane (TR: 5271 ms, TE: 120, FOV: 1809 × 829, thickness 2.5 mm, matrix 240 × 192), T2W sequences in the sagittal plane (TR: 4450 ms, TE: 120, FOV: 1809 × 829, thickness 2.9 mm, matrix 224 × 224); enhanced spin-echo sequences were performed in the dorsal, transverse and sagittal planes. MRI images had a thickness of 2.7–3.5 mm.
2.3. Anatomical sections
After scanning the animals, seven of the twenty juvenile puffins were positioned in dorsal decubitus inside expanded polystyrene containers and frozen at -80 °C for 72 hours. Subsequently, serial sections of half centimeter thick were made using an electric band saw to obtain sequential transverse, sagittal and dorsal anatomical cross sections. These slices were immediately cleaned with water, numbered and photographed on both sides.
2.4. Anatomic evaluation
Those anatomical cross section that better matched with the MR images were selected to facilitate the identification of relevant structures of the Atlantic puffin head. In addition, it was necessary to consult text books, relevant references on bird osteology and anatomy, as well as bone preparations from other seabird specimens [
33,
34,
43,
44,
45,
46].
3. Results
In this study, we present a total of 10 figures, which correspond to anatomical sections and T2W MR images. T2W MR images were used because they exhibited higher resolution and contrast.
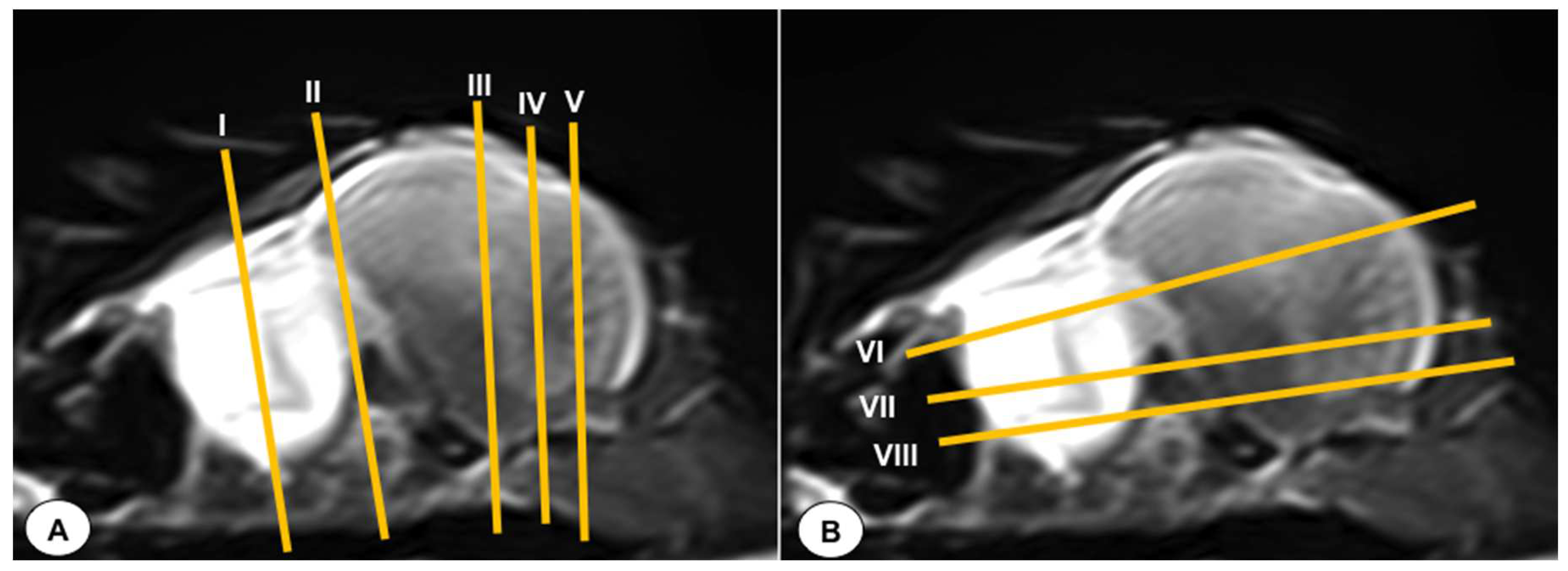
Figure 1 is composed of a transverse (A) and a dorsal (B) images, displaying the cross-section levels that are depicted by lines (II-VIII), which approximately matched the anatomical sections (
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9). These figures are displayed in two images: (A) anatomical cross section and (B) T2W MR image. In addition,
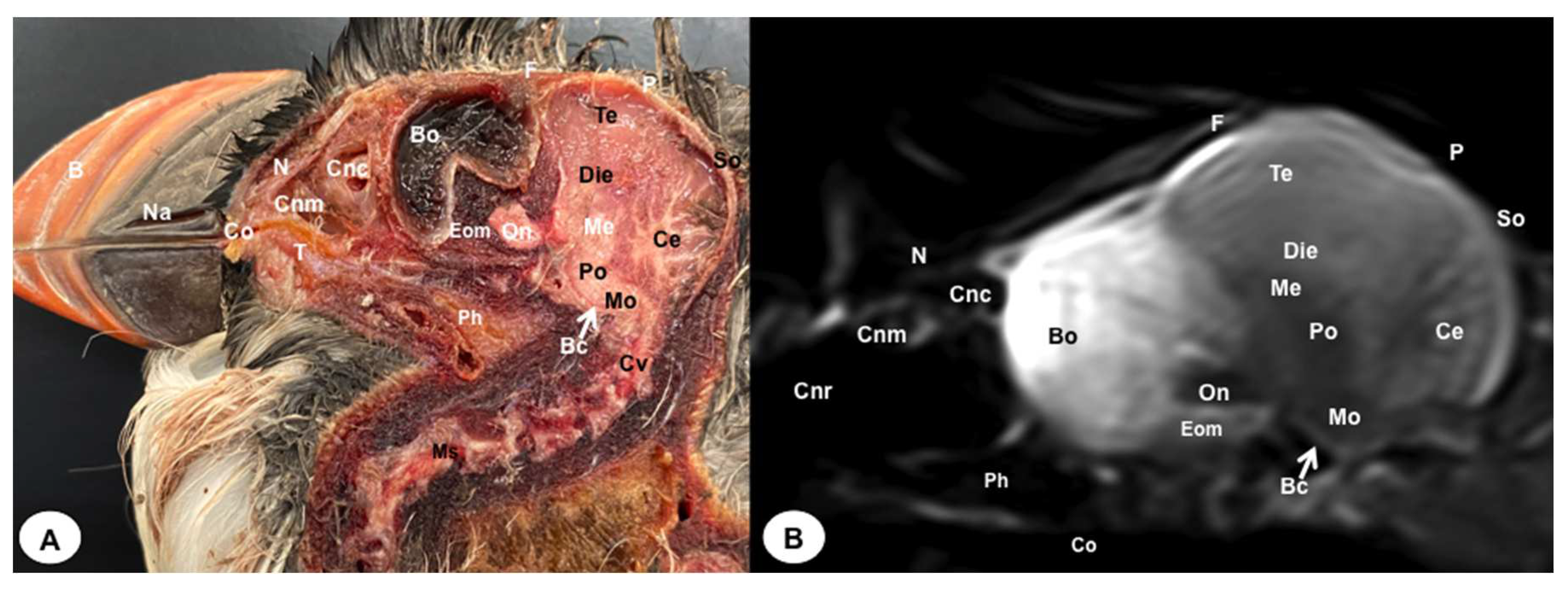
Figure 10 shows a sagittal anatomical section and the corresponding T2W image, identifying the main structures that compose the head of the Atlantic puffin, especially those related to the central nervous system.
3.1. Anatomical sections
The anatomical sections presented in this study were quite helpful in identifying different structures belonging to the central nervous system and its associated structures, which were labelled following the
Nomina Anatomica Avium. Therefore, we observed the avian brain with the telencephalic hemispheres containing the lateral ventricles (see
Figure 4A and
Figure 7A). Both hemispheres were separated by the
fissura longitudinalis cerebri (
Figure 6A and
Figure 7A). In addition, transverse cross sections were quite helpful in distinguishing a slightly caudolateral disposed rostral groove, the vallecula telencephali, which was presented on the dorsal surface of each hemisphere, as well as a little pointed olfactory bulb situated at the rostral end of each hemisphere (see
Figure 2A,
Figure 3A and
Figure 7A). The diencephalon was identified as a rostral continuation to the mesencephalon and represents the rostral limit of the brain stem (
Figure 10A). The dorsal and sagittal anatomical sections allowed the visualisation of some components of the hypothalamus, such as the optic chiasm and the optic nerve penetrating the sclera (see Figures 8A–10A). Besides, these sections allowed us the identification of other components of the Atlantic puffin brain, such as the dorsal part of the mesencephalon, as well as the large unpaired median corpus cerebelli, the internal medullary body with an internal white substance and the little paired cerebellar hemispheres (Figures 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A 8A, 9A and 10A). Moreover, these sections allowed the identification of the ventral part of the rhombencephalon, including the pons and the medulla oblongata, which did not present an obvious demarcation (see Figures 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A and 10A).
In addition, dorsal, transverse, and sagittal anatomical sections yielded fundamental insights regarding the avian eyeball, which exhibits a relatively substantial size in proportion to the cranial volume and a lateral positioning characteristic of avian anatomy, assuming a globose morphology with slight medial flattening, as depicted in
Figure 2A. Furthermore, the delineation of various ocular components, including the cornea, sclera, retina, vitreous chamber,
pecten oculi, and lens, was achieved with precision (see Figures 2A, 3A, 7A, 8A, 9A and 10A). Concurrently, our examination unveiled associated structures about the eyeball, encompassing the interorbital septum, extraocular muscles, and the infraorbital sinus that provides structural support to the eyeball, as illustrated in Figures 2A, 3A, 7A, 8A, 9A and 10A. Moreover, these sections provided essential information about the skull shape and different bony structures comprising the skull, including the nasal, the frontal, the parietal, the pterygoid, and the otic and occipital bones (see Figures 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A and 10A).
Regarding the nasal cavity, it was found to be bilaterally situated on either side of the median nasal septum. The nares were dorsally positioned at the base of the avian beak, as depicted in
Figure 10A. Within the nasal cavity, three nasal conchae were discerned in a rostrocaudal sequence: the rostral nasal concha, middle nasal concha, and caudal nasal concha, with particular emphasis on the enhanced development of the middle concha relative to the others (see Figures 7A, 8A and 10A). Moreover, the dorsal, sagittal and transverse sections were essential to distinguish the roof of the oral cavity and the pharynx (see Figures 2A, 3A, 9A and 10A). Thus, we could observe how the roof was covered by a non-glandular keratinised mucosa forming the transverse ridges (
rugae palatinae), which were covered by numerous papillae (see
Figure 9A).
3.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
No discernible anatomical distinctions were evident in the examined juvenile puffins. T2-weighted magnetic resonance (T2W MR) images demonstrated a precise alignment with the cranial structures observed in the cadaveric cross sections, furnishing comprehensive insights into the central nervous system (CNS) and its associated structures. Consequently, various constituents of the puffin head’s CNS, the
bulbus oculi, and their related elements were adequately differentiated. Thus, in the transverse and dorsal planes, the two telencephalic hemispheres were homogeneous, displaying regions of moderate and hypointense signals corresponding to the cerebral hemispheres and lateral ventricles, respectively (see Figures 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B and 10B). Notably, these two planes facilitated the identification of the olfactory bulb, which was a small rostrally tapering structure with moderate and homogeneous signal intensity (see Figures 2B, 3B and 7B). The hyperpallium, distinguished by its curved dorsal contour and moderate signal intensity, was another distinct structure identified (see
Figure 3B). Conversely, the diencephalon, another forebrain component, displayed limited differentiation from the adjacent mesencephalon, manifesting moderate to low-intensity signals (see
Figure 10B). Additionally, prominent features of the mesencephalon, such as the optic lobe, were exclusively discerned in the dorsal T2W MR images, showcasing analogous signal characteristics (see Figures 4B, 8B and 9B). Other essential components of the CNS, including the pons, and the medulla oblongata, were identifiable in the transverse, dorsal and sagittal planes, characterized by low-intensity signals (see Figures 4B, 5B, 6B, 8B, 9B and 10B). Adjacent to the brain stem, the
corpus cerebelli and the small paired cerebellar hemispheres exhibited poorly defined regions of hypo-and moderate intense signal (see Figures 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B, 8B, 9B and 10B).
Regarding the bulbus oculi, the vitreous chamber consistently exhibited hyperintense signals across all planes employed (see Figures 2B, 3B, 7B, 8B, 9B and 10B). However, the cornea, sclera, lens, scleral skeleton, and pecten oculi displayed a hypointense signal in the T2W MR images (see Figures 2B, 3B, 7B, 8B and 9B). The optic nerve showed an accurate visualization using MRI, presenting a hypointense signal and was surrounded by hyperintense cerebrospinal fluid (see Figures 9B and 10B). Furthermore, the oral cavity, the pharynx and the trachea were visualized with low-intensity signals in the T2W images (see Figures 2B, 3B, 4B and 5B). Moreover, diverse muscles of the head, including the musculus pterygoideus pars ventralis, musculus tracheolateralis, musculus rectus capitus (musculus rectus dorsalis+ musculus rectus ventralis+ musculus rectus lateralis) and musculus constrictor colli were displayed with intermediate intensity signal in the T2W MR images (see Figures 2B, 6B, 8B and 9B). In addition, various skull bones, including the nasal, the frontal, the parietal, the pterygoid, and the otic and occipital bones could be identified in the T2W MR images (see Figures 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B, 8B, 9B and 10B).
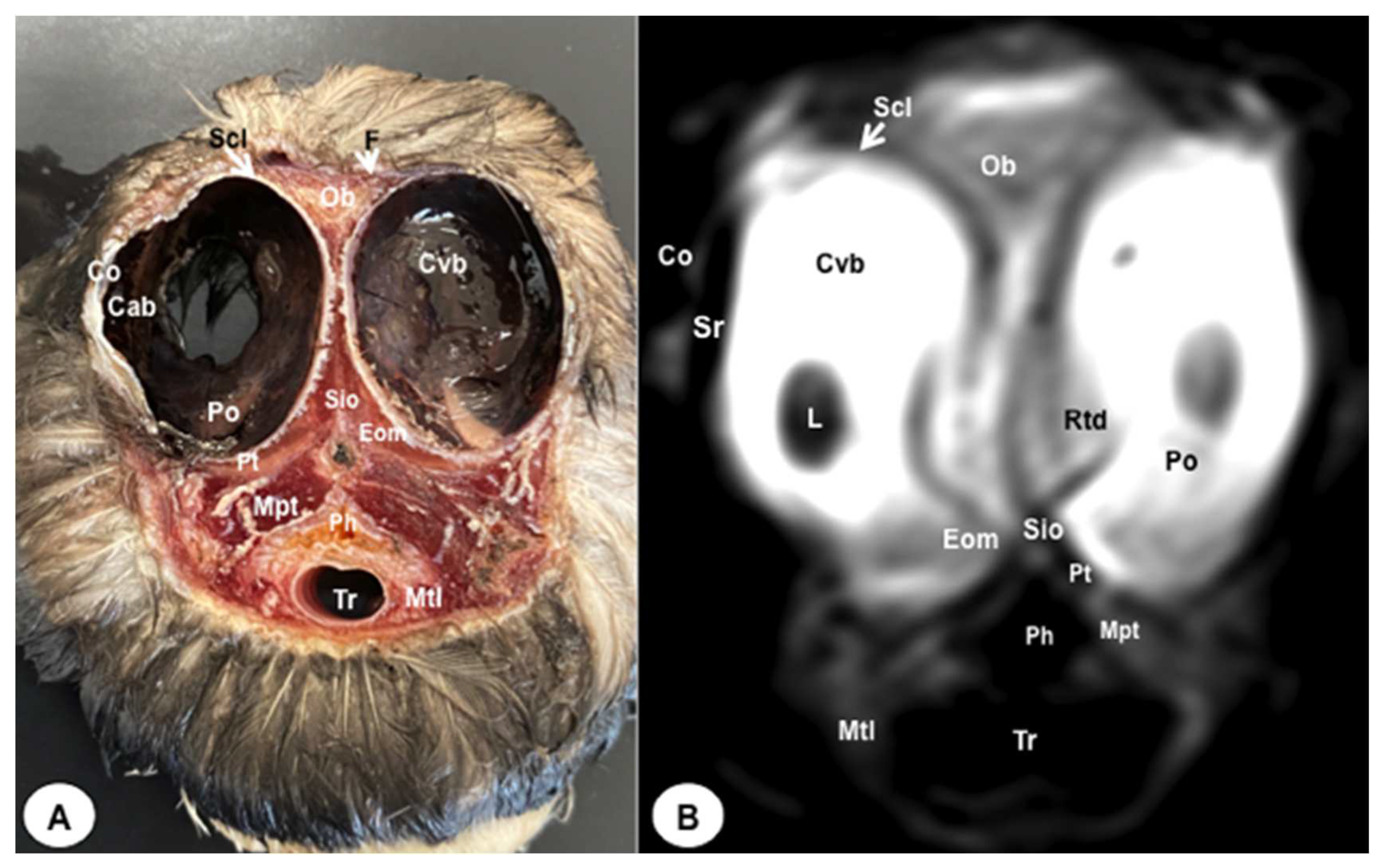
Figure 2.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the
bulbus oculi corresponding to line I in
Figure 1. Scl: sclera; Sr: sclerotic ring; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Co: cornea; Cab:
camera anterior bulbi: Po:
pecten oculi;
Rtd: retinal detachment; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Eom: extraocular muscle; Ob: olfactory bulb; F:
Os frontale; Ph: pharinx; Tr: trachea; Pt:
Os pterygoideus; Mpt:
Musculus pterygoideus pars ventralis; Mtl:
Musculus tracheolateralis.
Figure 2.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the
bulbus oculi corresponding to line I in
Figure 1. Scl: sclera; Sr: sclerotic ring; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Co: cornea; Cab:
camera anterior bulbi: Po:
pecten oculi;
Rtd: retinal detachment; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Eom: extraocular muscle; Ob: olfactory bulb; F:
Os frontale; Ph: pharinx; Tr: trachea; Pt:
Os pterygoideus; Mpt:
Musculus pterygoideus pars ventralis; Mtl:
Musculus tracheolateralis.
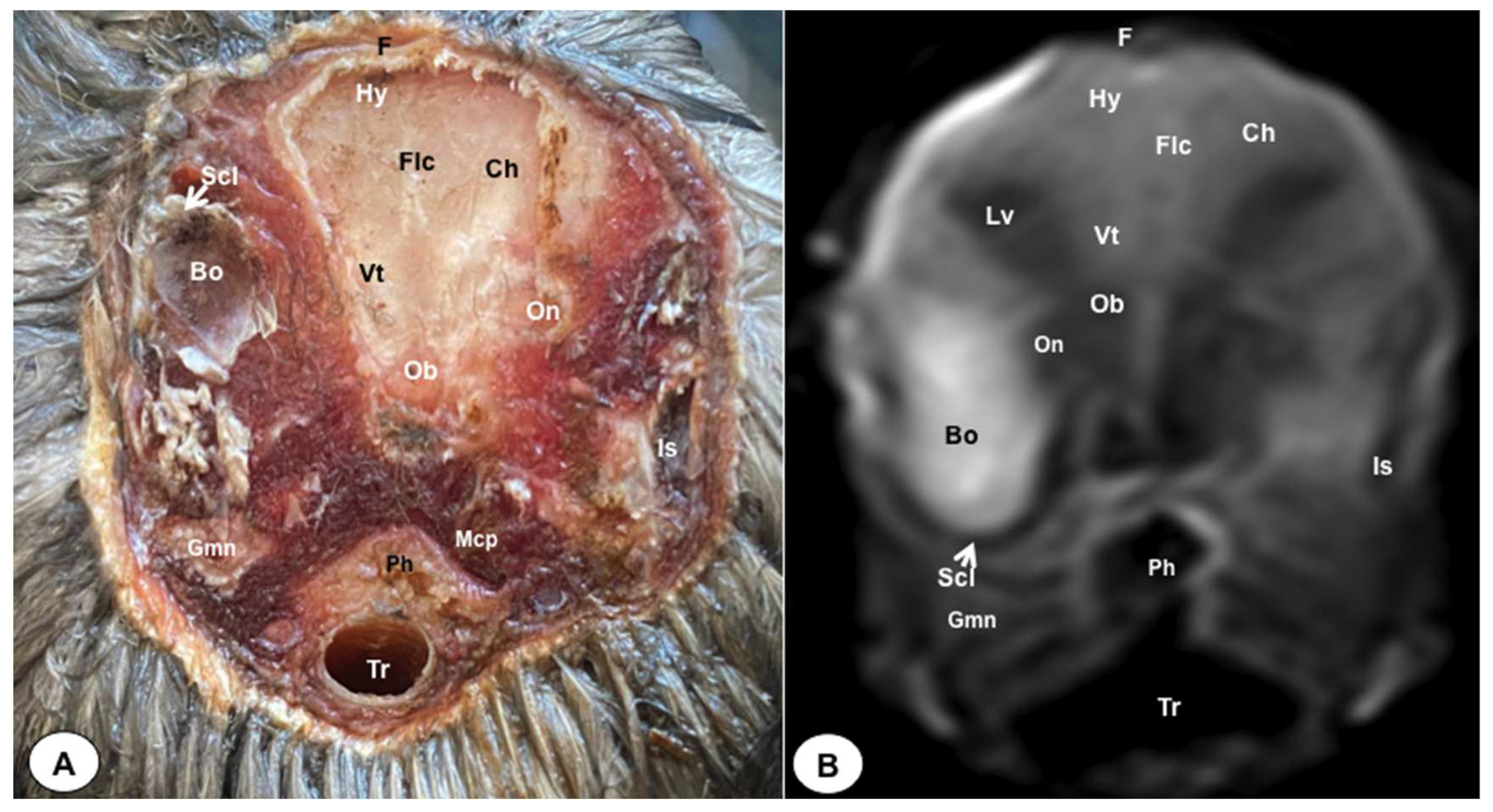
Figure 3.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the olfatory bulb corresponding to line II in
Figure 1. F:
Os frontale; Hy:
hyperpallium; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Lv: lateral ventricles; Vt:
Vallecula telencephali; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ob: olfatory bulb; On: optic nerve; Scl: sclera; Bo:
bulbus oculi; Is:
Sinus infraorbitalis; Gmn:
Glandula membranae nictitantis; Ph: pharynx; Mcp:
Musculus constrictor pharyngis; Tr: trachea.
Figure 3.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the olfatory bulb corresponding to line II in
Figure 1. F:
Os frontale; Hy:
hyperpallium; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Lv: lateral ventricles; Vt:
Vallecula telencephali; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ob: olfatory bulb; On: optic nerve; Scl: sclera; Bo:
bulbus oculi; Is:
Sinus infraorbitalis; Gmn:
Glandula membranae nictitantis; Ph: pharynx; Mcp:
Musculus constrictor pharyngis; Tr: trachea.
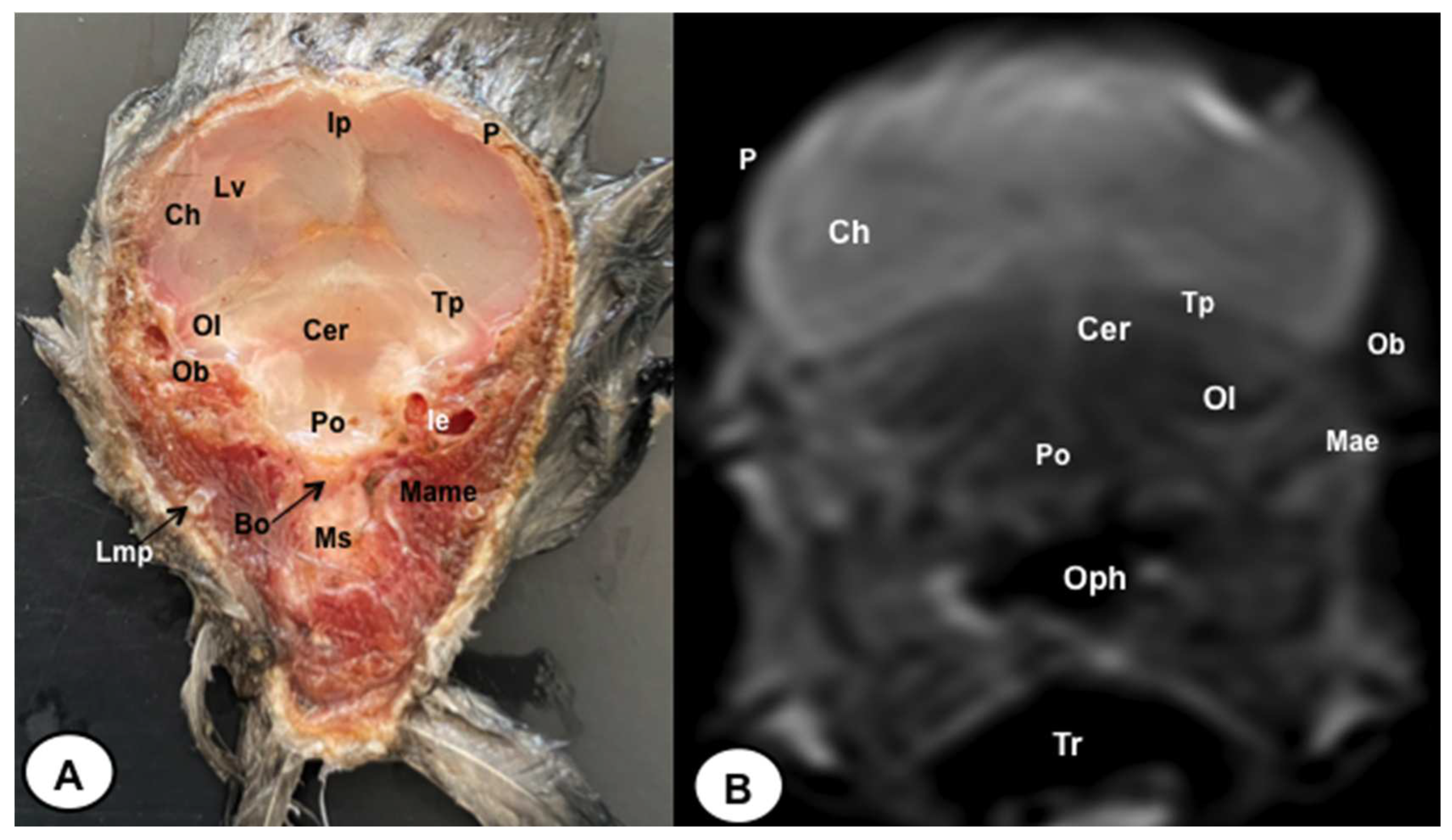
Figure 4.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic lobe corresponding to line III in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Ip: interparietal bone; Lv: lateral ventricle; Tp: tentorial process; Bo:
Os basioccipitale; Ob: otic bones
; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Ol: optic lobe; Cer:
cerebellum (body); Po: pons; Ms:
medulla spinalis; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Ie: inner ear; Lmp: Lateral mandibular process; Mame:
Musculus adductor mandibulae externus; Oph: oropharynx; Tr: trachea.
Figure 4.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic lobe corresponding to line III in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Ip: interparietal bone; Lv: lateral ventricle; Tp: tentorial process; Bo:
Os basioccipitale; Ob: otic bones
; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Ol: optic lobe; Cer:
cerebellum (body); Po: pons; Ms:
medulla spinalis; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Ie: inner ear; Lmp: Lateral mandibular process; Mame:
Musculus adductor mandibulae externus; Oph: oropharynx; Tr: trachea.
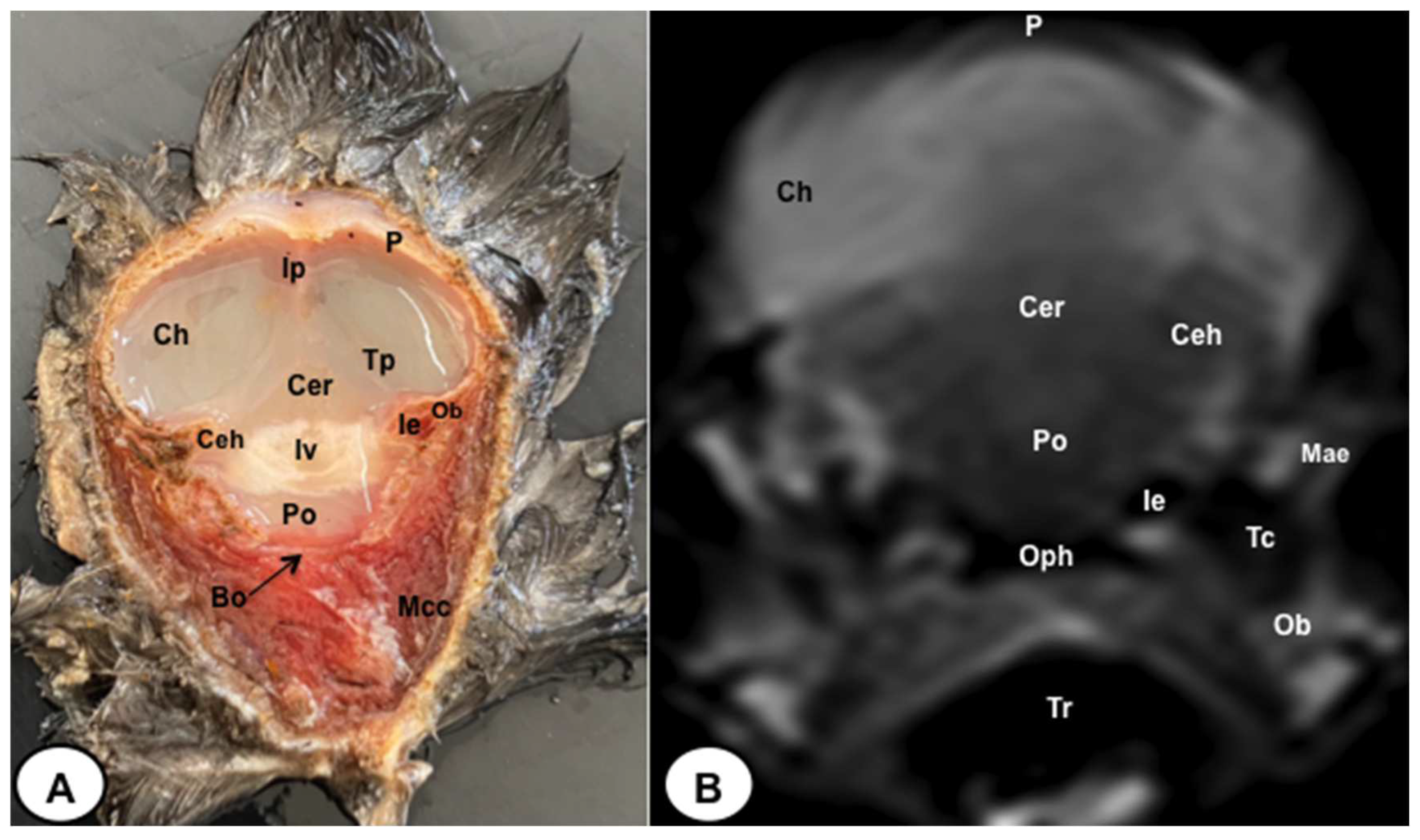
Figure 5.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the pons corresponding to line IV in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Ip: interparietal bone; Tp: tentorial process; Bo:
Os basioccipitale; Ob: otic bones
; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Ceh: cerebellar hemisphere; Cer:
cerebellum (body); IV: fourth ventricle; Po: pons; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Ie: inner ear; Mcc:
Musculus cucularis capitis; Oph: oropharynx; Tr: trachea.
Figure 5.
Transverse cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the pons corresponding to line IV in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Ip: interparietal bone; Tp: tentorial process; Bo:
Os basioccipitale; Ob: otic bones
; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Ceh: cerebellar hemisphere; Cer:
cerebellum (body); IV: fourth ventricle; Po: pons; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Ie: inner ear; Mcc:
Musculus cucularis capitis; Oph: oropharynx; Tr: trachea.
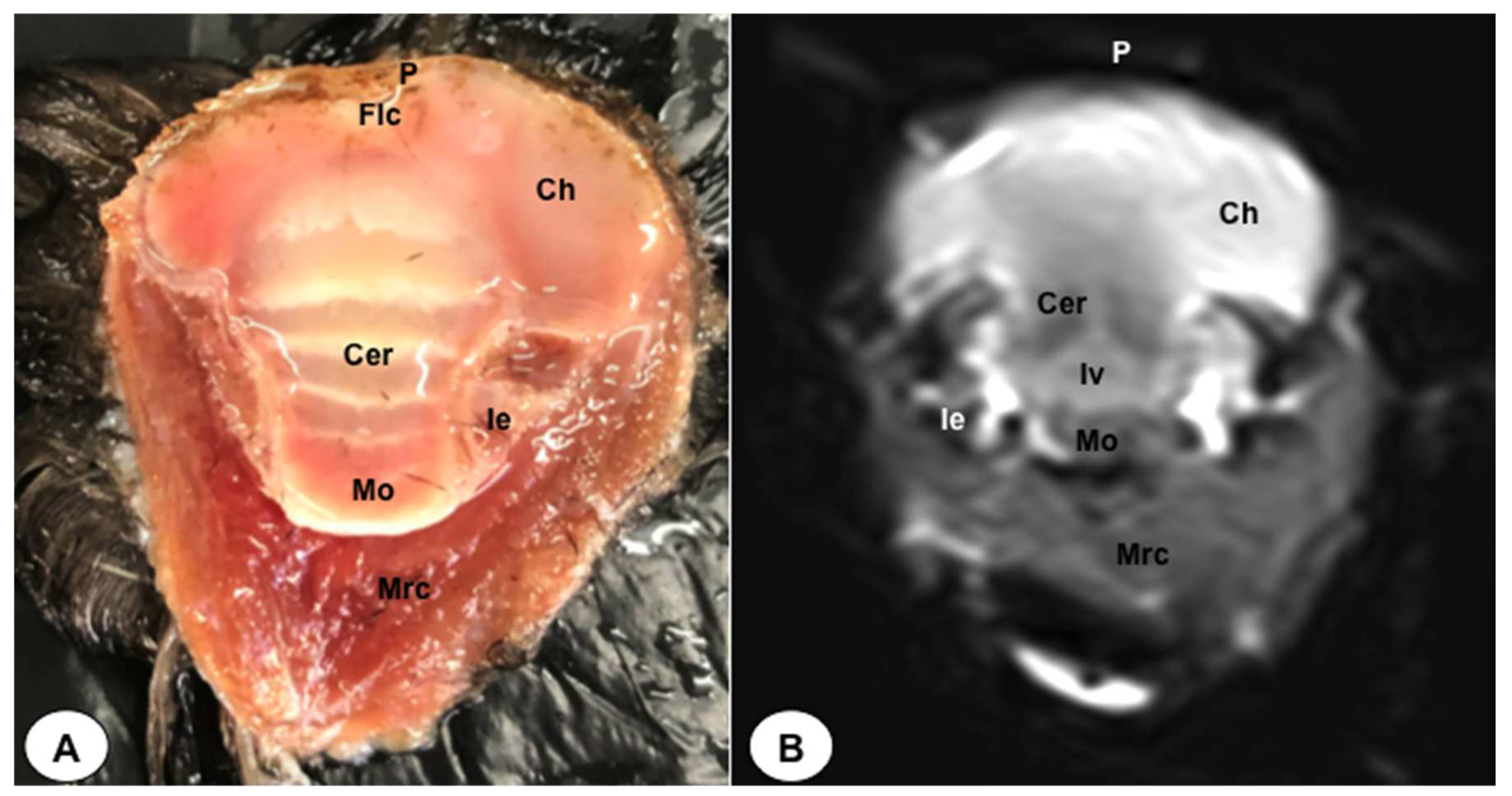
Figure 6.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the
medulla oblongata corresponding to line V in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Cer:
cerebellum (body); Mo:
Medulla oblongata; Ie: inner ear. Mrc:
Musculus rectus capitus (Musculus rectus dorsalis+ Musculus rectus ventralis+ Musculus rectus lateralis).
Figure 6.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the
medulla oblongata corresponding to line V in
Figure 1. P:
Os parietale; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ch: cerebral hemisphere; Cer:
cerebellum (body); Mo:
Medulla oblongata; Ie: inner ear. Mrc:
Musculus rectus capitus (Musculus rectus dorsalis+ Musculus rectus ventralis+ Musculus rectus lateralis).
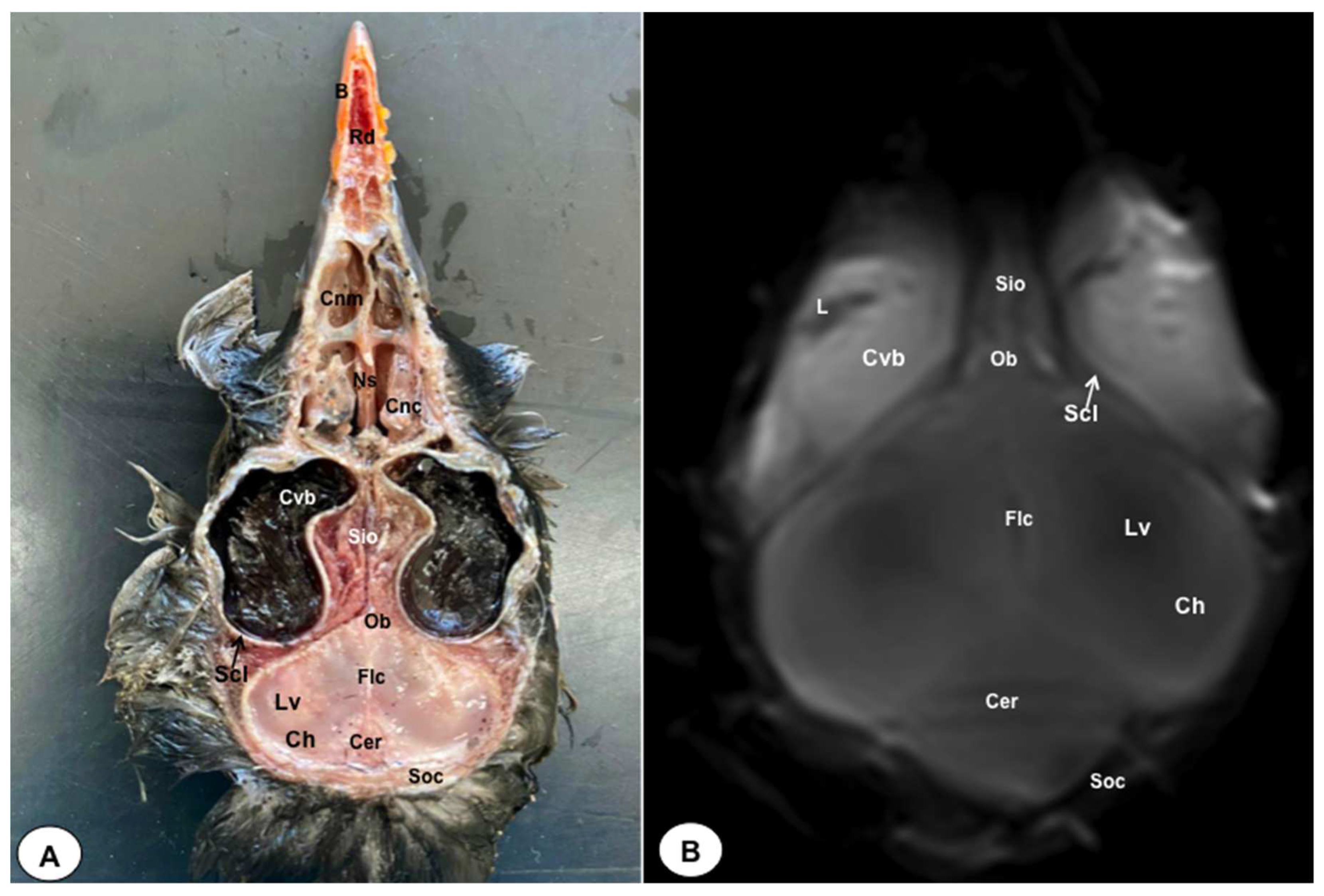
Figure 7.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the nasal cavity corresponding to line VI in
Figure 1. B: beak; Rd: rostral diverticulum; Cnm:
Concha nasalis media; Cnc:
concha nasalis caudalis; Ns: nasal septum; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Ob: olfatory bulb; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ch: cerebral hemisphere: Lv: lateral ventricle; Cer:
cerebellum; Scl: sclera; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale.
Figure 7.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the nasal cavity corresponding to line VI in
Figure 1. B: beak; Rd: rostral diverticulum; Cnm:
Concha nasalis media; Cnc:
concha nasalis caudalis; Ns: nasal septum; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Ob: olfatory bulb; Flc:
fissura longitudinalis cerebri; Ch: cerebral hemisphere: Lv: lateral ventricle; Cer:
cerebellum; Scl: sclera; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale.
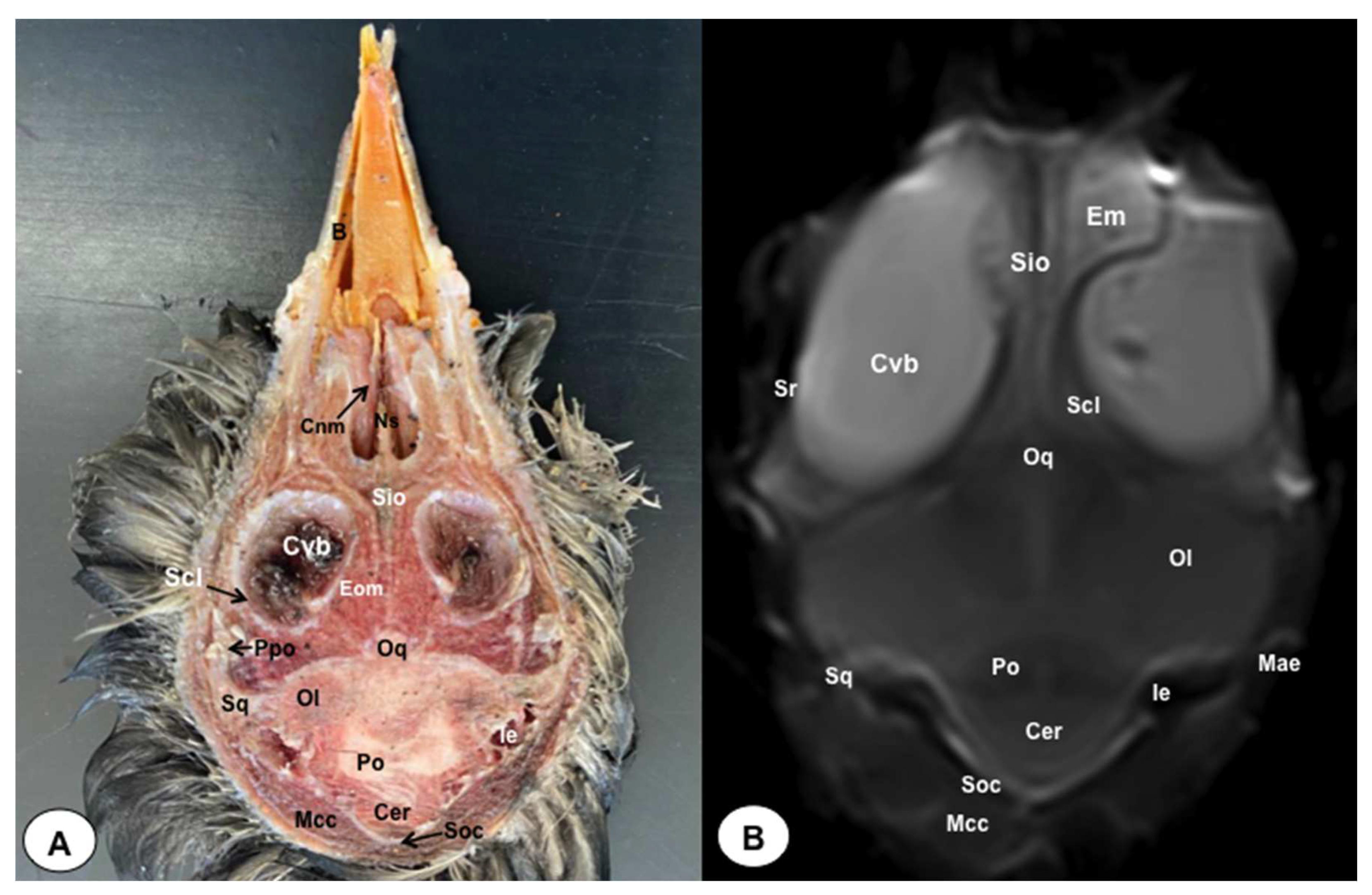
Figure 8.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of optic lobes corresponding to line VII in
Figure 1. Sr: sclerotic ring; Scl: sclera; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Eom: extraocular muscles; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Po: pons; Ol: optic lobe; Oq:
chiasma opticum; Ce:
cerebellum; Ie: inner ear; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Sq:
Os squamosum; Ppo:
Processus postorbitalis; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale; Mcc:
Musculus constrictor colli; Em:
Musculus ethmomandibularis; Ns: Nasal septum; Cnm:
Concha nasalis media; B: Beak.
Figure 8.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of optic lobes corresponding to line VII in
Figure 1. Sr: sclerotic ring; Scl: sclera; Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Eom: extraocular muscles; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; Po: pons; Ol: optic lobe; Oq:
chiasma opticum; Ce:
cerebellum; Ie: inner ear; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Sq:
Os squamosum; Ppo:
Processus postorbitalis; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale; Mcc:
Musculus constrictor colli; Em:
Musculus ethmomandibularis; Ns: Nasal septum; Cnm:
Concha nasalis media; B: Beak.
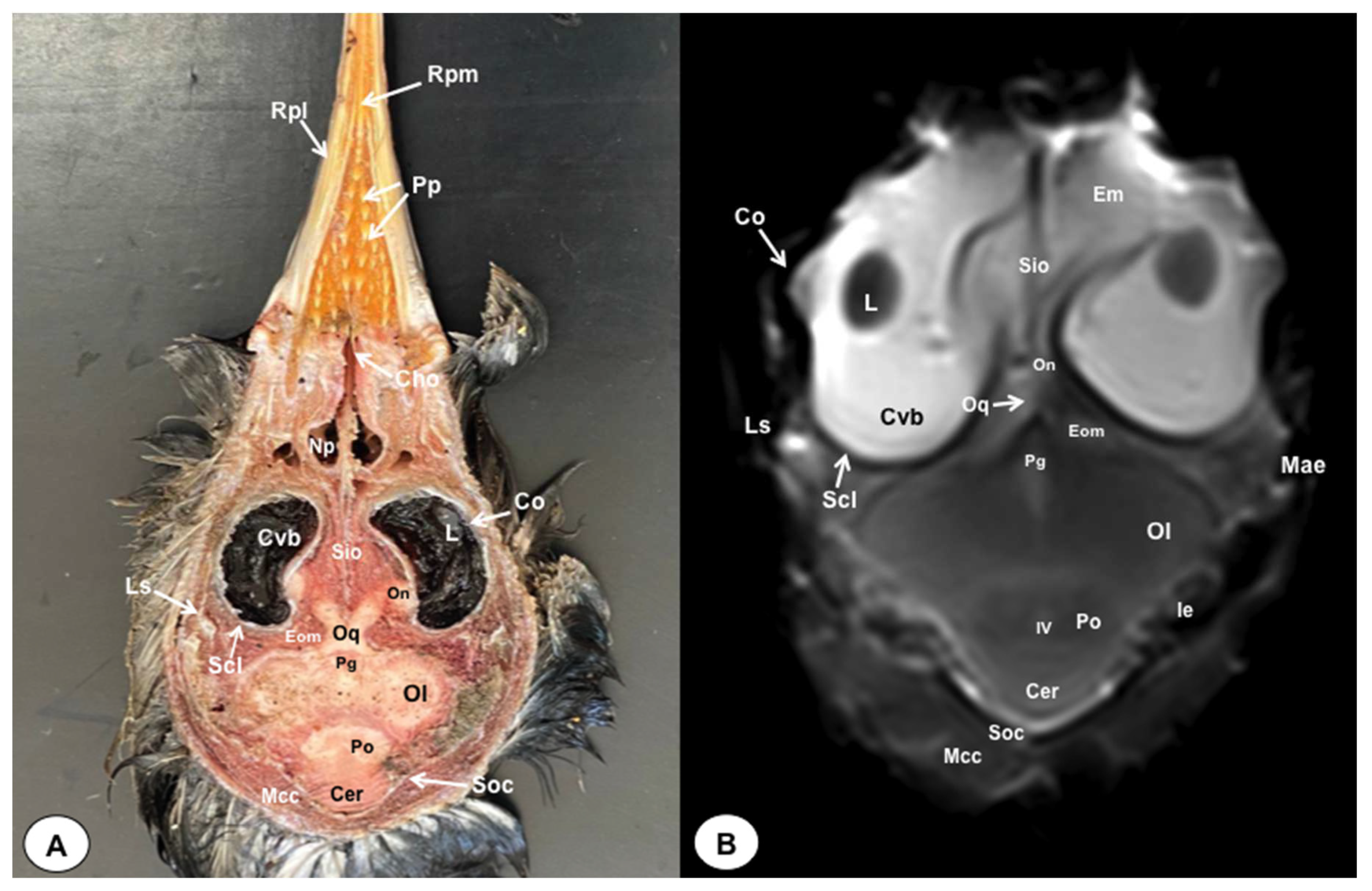
Figure 9.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic chiasm corresponding to line VIII in
Figure 1. Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; On: optic nerve; Oq:
chiasma opticum; Co: cornea; L: lens; Scl: sclera; Eom: extraocular muscle
; Ls:
Os laterosphenoidale; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale; Po
: pons; Cer:
cerebellum; Ol: optic lobe; Pg: pituitary gland; IV: fourth ventricle; Ie: Inner ear; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Mcc:
Musculus constrictor colli; Np: nasopharynx; Em:
Musculus ethmomandibularis; Cho:
Choanas; Pp:
Papillae palatinae; Rpl:
Ruga palatina lateralis; Rpm:
Ruga palatina mediana.
Figure 9.
Dorsal cross-section (
A) and T2W MR (
B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic chiasm corresponding to line VIII in
Figure 1. Cvb:
camera vitrea bulbi; Sio:
septum interorbitalis; On: optic nerve; Oq:
chiasma opticum; Co: cornea; L: lens; Scl: sclera; Eom: extraocular muscle
; Ls:
Os laterosphenoidale; Soc:
Os supraoccipitale; Po
: pons; Cer:
cerebellum; Ol: optic lobe; Pg: pituitary gland; IV: fourth ventricle; Ie: Inner ear; Mae:
Meatus acusticus externus; Mcc:
Musculus constrictor colli; Np: nasopharynx; Em:
Musculus ethmomandibularis; Cho:
Choanas; Pp:
Papillae palatinae; Rpl:
Ruga palatina lateralis; Rpm:
Ruga palatina mediana.
Figure 10.
Sagittal cross-section (A) and T2W MR (B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic nerve. B: beak; Na: naris; Co: cavum oris; N: Os nasale; T: tongue; Cnm: Concha nasalis media; Cnc: concha nasalis caudalis: Bo: bulbus oculi: On: optic nerve; Ph: pharinx; F: Os frontale; Te: telencephalon; Die: diencephalon; Ce: cerebellum; Me: mesencephalon; Eom: extraocular muscles; Po: pons; Mo: medulla oblongata; Ms: medulla spinalis; Bc: basis cranii; P; os parietale; So: Os supraoccipitale. Cv: Cervical vertebra.
Figure 10.
Sagittal cross-section (A) and T2W MR (B) images of the atlantic puffin head at the level of the optic nerve. B: beak; Na: naris; Co: cavum oris; N: Os nasale; T: tongue; Cnm: Concha nasalis media; Cnc: concha nasalis caudalis: Bo: bulbus oculi: On: optic nerve; Ph: pharinx; F: Os frontale; Te: telencephalon; Die: diencephalon; Ce: cerebellum; Me: mesencephalon; Eom: extraocular muscles; Po: pons; Mo: medulla oblongata; Ms: medulla spinalis; Bc: basis cranii; P; os parietale; So: Os supraoccipitale. Cv: Cervical vertebra.
4. Discussion
Atlantic puffins can reach latitudes close to the Canary Islands, but their presence on its coasts is uncommon [
1]. In our study, the birds that were stranded massively were juvenile specimens. It constituted a limiting factor encountered during the execution of this study, as the small size of the head (less than 5 cm from beak to occipital bone) hindered the acquisition of CNS images, and particularly those images of the rostral aspect of the head affecting the beak. Some authors have reported that utilization of various coil types can enhance the signal-to-noise ratio and contrast, both in 1.5 T [
47] and higher field intensity equipment [
48]. This observation should be considered in future similar studies to improve image resolution. In addition, potential tissue changes associated with post-mortem phenomena should be taken into consideration, as they could also negatively impact the obtained image. However, conducting this type of in vivo study typically involves the use of anaesthesia, thereby posing a higher risk to the animals undergoing this procedure [
49,
50]. In our study, the use of anatomical cross sections in different planes allowed the depiction of the normal anatomy of the Atlantic puffin brain and its associated structures with excellent detail, complementing the employ of MRI and enabling the acquisition of valuable anatomical information despite the aforementioned limitations.
In our study, we used advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging, to examine the head of the Atlantic puffin. To the best of the author’s knowledge, this is the first description of the head of this species using a high field strength magnet (1.5 T). This technique has already provided essential information in the assessment of the anatomical knowledge of the head and associated structures in other wildlife species, such as reptiles [
51,
52], rodents [
53,
54], terrestrial mammals [
55,
56], as well as different avian species, including red kite (
Milvus milvus), common buzzard (
Buteo buteo), and common kestrel (
Falco tinnunculus) [
34], domestic pigeon (
Columba livia domestica) [
42] or African grey parrot (
Psittacus erithacus) [
40] among others. In contrast to conventional imaging procedures, MRI can be used to obtain images via various anatomic planes without repositioning of specimens [
51,
57,
58,
59]. This technique constitutes a high-value tool to evaluate the central nervous system (CNS) and its associated structures because it provides adequate differentiation between the cranial bones and soft tissue structures compared with other modern imaging techniques. Thus, in this study, we use sagittal, transverse and dorsal MRI planes, which were quite helpful in identifying different components of the CNS and soft tissue structures. Nonetheless, it is important to highlight that images could not be accurately interpreted without a thorough knowledge of the tomographic or planimetric anatomy of the subject species.
As previously mentioned in other species, high field strength magnet was adequate to visualize the avian brain [
34]. Hence, we could visualize the telencephalon and the telencephalic hemispheres that were lissencephalic, the olfactory bulb, as well as a dorsal eminence corresponding to the hyperpallium, whose curved dorsal contour was better visualized in the T2W MR images. The identification of this specific structure in this species, and the dimensions of the sclerotic ring [
60] suggested its strong visual specialization that could be related to the bird’s feeding patterns. In contrast to the anatomical cross sections, the dorsal and transverse T2W MR images were quite helpful in distinguishing the lateral ventricles, which were located in the medial and occipital regions of the cerebral hemispheres until projected laterally towards the olfactory bulb. However, studies performed on birds with higher resolution equipment did not clearly label the extension of the lateral ventricles [
34]. Therefore, we assumed this finding could be attributed to postmortem changes affecting the ventricular system.
In relation to the mesencephalon, the optic lobes were discernible in both transverse and dorsal cross-sectional views, as well as in corresponding T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images. These structures were situated in lateral proximity to the telencephalon, and their differentiation from the telencephalic hemispheres was evident due to the presence of the tentorial process, which resulted in a distinct demarcation between these regions. Notably, these lobes exhibited substantial volume, primarily attributed to their processing of a significant portion of visual information [
46,
61].
Similar to terrestrial mammals, the cerebellum of the Atlantic puffin lies above the midsection of the mesencephalon, the pons, and the medulla oblongata, with no discernible clear demarcations between these regions. Examination through transverse cross-sections and T2-weighted MR images revealed the presence of two small cerebellar hemispheres and a larger unpaired central structure. These cerebellar structures were separated by transverse fissures, facilitating a distinct separation between them. Furthermore, these fissures exhibited a marked differentiation between the gray and white matter within the cerebellum.
The T2W MR images combined with anatomical cross sections allowed adequate differentiation of soft tissue structures. Therefore, different ocular components, including the lens, the vitreous chamber, the anterior chamber, the optic nerve and the sclera, were distinguished. Thus, they appeared with high signal intensity in T2-weighted MR images. However, other formations, such as the
pecten oculi showed low signal intensity and low resolution because we used cadaveric specimens, and the intravenous contrast use was not feasible. In vivo studies involving such substances [
59] have demonstrated their utility in visualizing these structures in greater detail since its connective tissue scaffold, enclosing a compacted capillary network.
Despite the low resolution of the bony structures, the skull showed a dome shape, with large orbits separated by a thin interorbital septum and modification of the facial bones to form the beak. The skull bones visualized did not show important pneumatization as happens in other non-aquatic species. This lower pneumatization of the skull of the puffin [
43] could be related to their living and eating habits, since as we have mentioned, they are excellent divers and therefore, the pneumatization of the skull could be a problem when diving in oceanic waters. In addition to these findings, the ethmoidal labyrinth was not described, probably due to the poor development of the sense of smell, also related to the small rostrally tapering olfactory bulb.
5. Conclusions
This study presents an initial characterization of the cranial anatomy of the Atlantic puffin utilizing transverse, sagittal, and dorsal magnetic resonance imaging in conjunction with anatomical cross-sections. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has demonstrated its suitability as a tool, providing comprehensive anatomical insights into the various components comprising the puffin’s cranial region. Despite the high economic cost associated with this equipment, its availability in routine clinical settings remains challenging. Nevertheless, MRI offers valuable information that may serve as a reference in research investigations and clinical evaluations of neurological disorders in seabirds. Subsequent investigations involving adult puffins are essential to facilitate a comparative analysis of cephalic anatomical structures and to explore potential age-related variations in these structures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R.J., M.F. and M.E.; methodology, M.E., H.A.N., A.M. and M.F.; investigation, J.R.J., M.F., D.S. and M.E.; resources, A.M. and H.A.N. writing—original draft preparation, J.R.J. and M.F.; writing—review and editing, J.R.J., M.F., A.M., D.S. and M.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
In this study, we did not need ethical approval since the puffins were coming to our hospital to rule out by CT any cause of stranding. From these studies, we obtained the information presented in our paper. As happens in domestic mammals, just informed consent from the owner allowed us to carry out this study. Therefore, El Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria was informed that all animal identity information obtained from this study was treated as confidential to the extent permitted by law and only used for research or teaching purposes.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from El Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
In loving memory of Alvaro Domingo Rodriguez Garcia. We also thank Concepción Mingot, Carmen Mingot, Emilia Mingot, Nicolas Aquino, Ayesh Mohamad, Nicolasa Rodríguez, Marisa Mohamad and Jamal Jaber for their support and constructive comments. Moreover, we also thank to the Consejeria de Área de Medio Ambiente, Clima, Energía y Conocimiento of the Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria to provide the animals of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Jobling, J.A. A Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, U.K, 1991; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Lowther, P.E.; Diamond, A.W.; Kress, S.W.; Robertson, G.J.; Russell, K. The birds of North America; The Birds of North America, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.; Daunt, F.; Newell, M.; Phillips, R.; Wanless, S. Wintering areas of adult Atlantic Puffins Fratercula arctica from a North Sea colony as revealed by geolocation technology. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleship, D.N.; Kirwan, G.M.; Christie, D.A.; de Juana, E. Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.K.; Burnham, J.L.; Johnson, J.A. Morphological measurements on Atlantic puffin Fratercula arctica naumanni in high Arctic Greenland. Polar Res. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.P.; Wanless, S. The puffin; Poyser Monographs; Bloomsbury Publishing: London. U.K, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, J. Fratercula arctica. Available online: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Fratercula_arctica/ (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- Breton, A.; Diamond, A.; Kress, S. Encounter, survival and movement probabilities from an Atlantic puffin (Fratercula arctica) metapopulation. Ecol. Monogr. 2006, 76, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.; Tycho, A.; Nills, C. Ocean climate prior to breeding affects the duration of the nestling period in the Atlantic puffin. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodway, M. Relationship between wing length and body mass in atlantic puffin chicks. J. Field Ornithol. 1997, 14, 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Cramp, S. The birds of the Western Palearctic, Full ed.; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, U.K, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Boag, D.; Alexander, M.The Puffin; Blandford Press: London, U.K., 1995.
- Harris, M. P.; Hislop, J. R. G. The food of young Puffins Fratercula arctica. J. Zool. 1978, 185, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.; Jensen, J. K.; Kampp, K. Winter diet of Atlantic puffins (Fratercula arctica) in the northeast Atlantic. Col. Waterbirds 1992, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, M. L.; Camphuysen, C. J.; Cooper, J.; Garthe, S.; Montevecchi, W. A.; Blaber, S. J. M. The impacts of fishing on marine birds. J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, E.; Mackey, M. Megafauna bycatch in drift nets for albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) in the NE Atlantic. Fish. Res. 2007, 86, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.T. Atlantic Puffin Fratercula arctica chick growth in relation to food load composition. Seabird 2015, 28, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempniewicz, L.; Jensen, J.K. Puffin harvesting and survival at Nólsoy, The Faeroes. Ornis Svec. 2007, 17, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P. I. .; Newton, S.F.; Ratcliffe, N.; Dunn, T.E. Seabird populations of Britain and Ireland, 1st ed.; Christopher Helm: London, U.K, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Breton, A.R.; Diamond, A.W. Annual survival of adult Atlantic Puffins Fratercula arctica is positively correlated with Herring Clupea harengus availability. Ibis 2014, 156, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.; Anker-Nilssen, T.; Stenseth, N. C. Trophic interactions under climate fluctuations: the Atlantic puffin as an example. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2003, 270, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvik, H.; Erikstad, K.E.; Barrett, R.T.; Yoccoz, N.G. The effect of climate on adult survival in five species of North Atlantic seabirds. J Anim Ecol. 2005, 74, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J. M.; Richmond, T. T. C.; Yohe, G. W. Extreme Weather. In: Highlights of Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment. U.S. Global Change Research Program, 2014.
- Harris, M.; Elkins, N. An unprecedented wreck of Puffins in eastern Scotland in March and April 2013. Scott. Birds 2013, 33, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, C.; Meyers, R. Anatomy and histochemistry of flight muscles of wing-propelled diving bird, the Atlantic puffin, Fratercula arctica. J. Morphol. 2000, 244, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, E.; Burger, J. Biology of Marine Birds, 1st ed.; CRC Press: New Jersey, U.S.A, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, K.; Jensen, J.; Kampp, K. Winter diet of Atlantic puffins (Fratercula arctica) in the northeast Atlantic. Col. Waterbirds 1992, 15, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, S. Morphologic and genetic variation among breeding colonies of the Atlantic puffin. The Auk 1991, 108, 755–763. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, X.L.; De La Peña-Lastra, S.; Pérez-Alberti, A.; Osorio Ferreira, T.; Huerta-Díaz, M.A. Seabird colonies as important global drivers in the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.K Government. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/englands-treasured-island-seabird-populations-to-be-protected-with-new-government-funding (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- The National Audubon Society. Project Puffin. Available online: https://projectpuffin.audubon.org/about (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Smith, N.A.; Balanoff, A.M.; Ksepka, D.T. Symposium on ‘Evolving approaches for studying the anatomy of the avian brain’: introduction. J Anat. 2016, 229, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stańczyk, E. K.; Velasco Gallego, M. L.; Nowak, M.; Hatt, J. M.; Kircher, P. R.; Carrera, I. 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging anatomy of the central nervous system, eye, and inner ear in birds of prey. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2018, 59, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, F.V. Orthopedic diagnostic imaging in exotic pets. Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2019, 22, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauber, E.; Holmes, S.; DeGhetto, D.L.; Finch, N. Magnetic resonance imaging is superior to radiography in evaluating spinal cord trauma in three bald eagles (Haliaeetus leucocephalus). J Avian Med Surg 2007, 21, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernick, M.B.; Dennler, M.; Beckmann, K.; Schybli, M.; Albini, S.; Hoop, R.K.; Steffen, F.; Kircher, P.; Hatt, J.M. Peripheral nerve sheath tumor in a subadult golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos). J Avian Med Surg. 2014, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delk, K.W.; Mejia-Fava, J.; Jiménez, D.A.; Kent, M.; Myrna, K.; Mayer, J.; Divers, S. Diagnostic imaging of peripheral vestibular disease in a Chinese goose (Anser cygnoides). J Avian Med Surg. 2014, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Francisco, O.N.; Feeney, D.; Armién, A.G.; Wuenschmann, A.; Redig, P.T. Correlation of brain magnetic resonance imaging of spontaneously lead poisoned bald eagles (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) with histological lesions: A pilot study. Res Vet Sci. 2016, 105, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, G.J.; Lester, N.V.; Stevenson, R.; Silver, X.S. High field strength (4.7T) magnetic resonance imaging of hydrocephalus in an African Grey parrot (Psittacus erithacus). Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2003, 44, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirak, D.; Janacek, J.; Kear, B. P. A combined MR and CT study for precise quantitative analysis of the avian brain. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnano, A.; Shiroma, J.T.; Heard, D.J.; Johnson, R.D.; Schiering, M.R.; Mladinich, M.S. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and coelomic cavity of the domestic pigeon (Columba livia domestica). Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 1996, 37, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faillace, A. C. L.; Vieira, K. R. A.; Santana, M. I. S. Computed tomographic and gross anatomy of the head of the blue-fronted Amazon parrot (Amazona aestiva). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2021, 50, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumel, J. J.; Anthony, S.; King, J. E.; James, E. Handbook of Avian Anatomy: Nomina Anatomica Avium, 2nd ed.; Nutttall Ortinithological Club: Cambridge, Massachusetts, U.S.A, 1993; pp. 318–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hadden, P. W.; Ober, W. C. , Gerneke; D. A., Thomas, D.; Scadeng, M.; McGhee, C. N. J.; Zhang, J. Micro-CT guided illustration of the head anatomy of penguins (Aves: Sphenisciformes: Spheniscidae). J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, H. E., Korbel, R., Liebich, H. G.; Klupiec, C. Avian anatomy: Textbook and colour atlas, 2nd ed; 5m Books Ltd.: Sheffield, U.K., 2016.
- Yoshioka, H.; Ueno, T.; Tanaka, T.; Shindo, M.; Itai, Y. High-resolution MR imaging of triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC): Comparison of microscopy coils and a conventional small surface coil. Skeletal Radiol. 2003, 32, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittersohl, B.; Huang, T.; Schneider, E.; Blazar, P.; Winalski, C.; Lang, P.; Yoshioka, H. High-resolution MRI of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) at 3T: Comparison of surface coil and volume coil. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson, H. L.; Monticelli, P.; Cuff, A. R.; Michel, K. B.; d’Ovidio, D.; Adami, C. Anesthesia and anesthetic-related complications of 8 elegant-crested tinamous (Eudromia elegans) undergoing experimental surgery. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2020, 34, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M. S.; Adami, C. Psittacine Sedation and Anesthesia. Vet. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 25, 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- González Rodríguez, E.; Encinoso Quintana, M.; Morales Bordon, D.; Garcés, J.G.; Artiles Nuez, H.; Jaber, J.R. Anatomical Description of Rhinoceros Iguana (Cyclura cornuta cornuta) Head by Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Gross-Sections. Animals 2023, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arencibia, A. , Hidalgo, M. R., Vázquez, J. M., Contreras, S., Ramírez, G.; Orós, J. Sectional anatomic and magnetic resonance imaging features of the head of juvenile loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, V. Diagnostic Imaging of Dental Disease in Pet Rabbits and Rodents. Veter Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2016, 19, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Bordon, D.; Encinoso, M.; Arencibia, A.; Jaber, J.R. Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Animals 2023, 13, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber Mohamad, J. R., Encinoso Quintana, M. Ó., Morales, D., Artiles Vizcaíno, A., Santana, M., Blanco Sucino, D.; Arencibia Espinosa, A. Anatomic study of the normal Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris) brain and associated structures using low field magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Anat. 2016.
- Arencibia, A. , Matos, J., Encinoso, M., Gil, F., Artiles, A., Martínez-Gomariz, F.; Vázquez, J. M. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging study of a normal tarsal joint in a Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyneken, J. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging anatomy of reptiles. In: Mader DR, ed. Reptile medicine and surgery. 2nd ed. St Louis: Saunders Elsevier, 2006; 1088–1096.
- Valente, A. L. S.; Cuenca, R.; Zamora, M. A.; Parga, M. L.; Lavin, S.; Alegre, F.; Marco, I. Sectional anatomic and magnetic resonance imaging features of coelomic structures of loggerhead sea turtles. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y. D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z. S.; Zhou, S. K. MRI contrast agents: Classification and application. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumero-Hernández, M.; Encinoso, M.; Ramírez, A.S.; Morales, I.; Suárez Pérez, A.; Jaber, J.R. A Cadaveric Study Using Computed Tomography for Measuring the Ocular Bulb and Scleral Skeleton of the Atlantic Puffin (Aves, Alcidae, Fratercula arctica) Animals 2023, 13, 2418.
- Evans HE. Avian anatomy. In: Lovette IJ, Fitzpatrick JW, eds.Hand-book of Bird Biology. 3rd ed. Chester, West Suisses: Wiley & Sons; 2016: 219.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).