Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Interpretation of the Four-Force Densities in Flat Spacetime
2.2. Classical and Quantum Interpretation for Continuous Media in Flat Spacetime
2.3. Classical and Quantum Interpretation for Point-like Particles in Flat Spacetime
2.4. Generalization to Other Fields
- fundamental interactions (body forces) related to
- related to gravity (against gravity)
- secondary interactions (radiation reaction forces) related to
3. Discussion
3.1. Dark Sector and Perspectives for Unification of Interactions
3.2. Quantum Gravity
3.3. Quantization
4. Conclusion
5. Statements
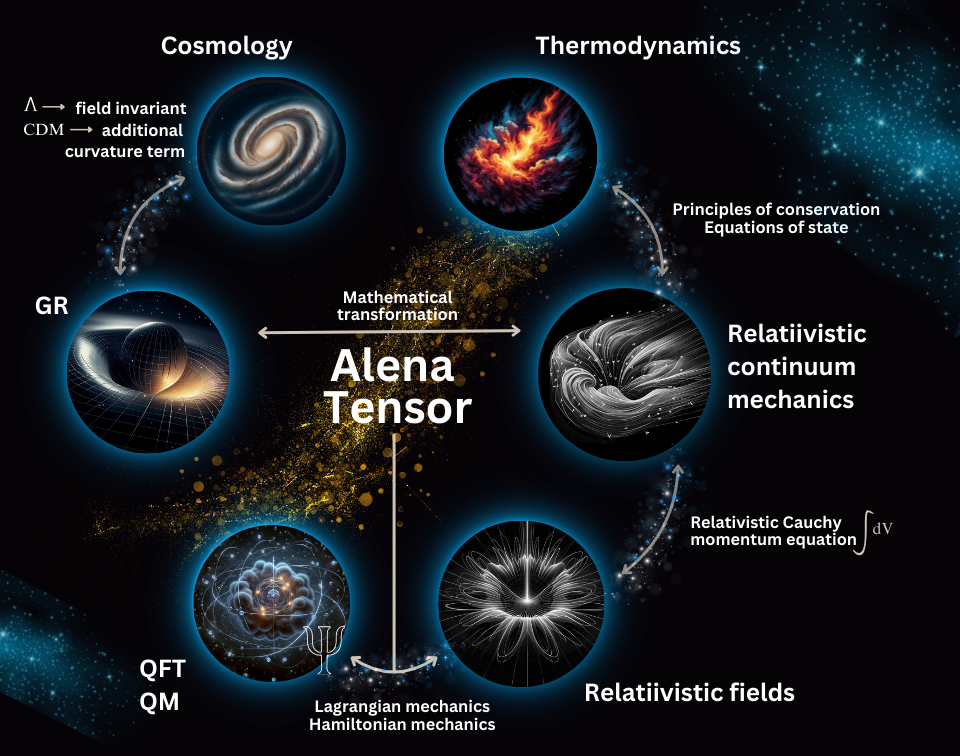
Appendix A. Summary of Conclusions from Previous Publications about Alena Tensor
Appendix A.1. Alena Tensor and Main Definitions
- is a metric tensor by which the spacetime of a physical system is considered,
- ,
- where is rest mass density and is Lorentz gamma factor,
- is four-momentum density in the system, in accordance with the postulate raised in the description to eq. (11) from publication [14],
- is the metric tensor of curved spacetime in which all motion takes place along geodesics and it is related to the field tensor, which will be explained next,
- is related to the invariant of the field tensor, which will be explained next.
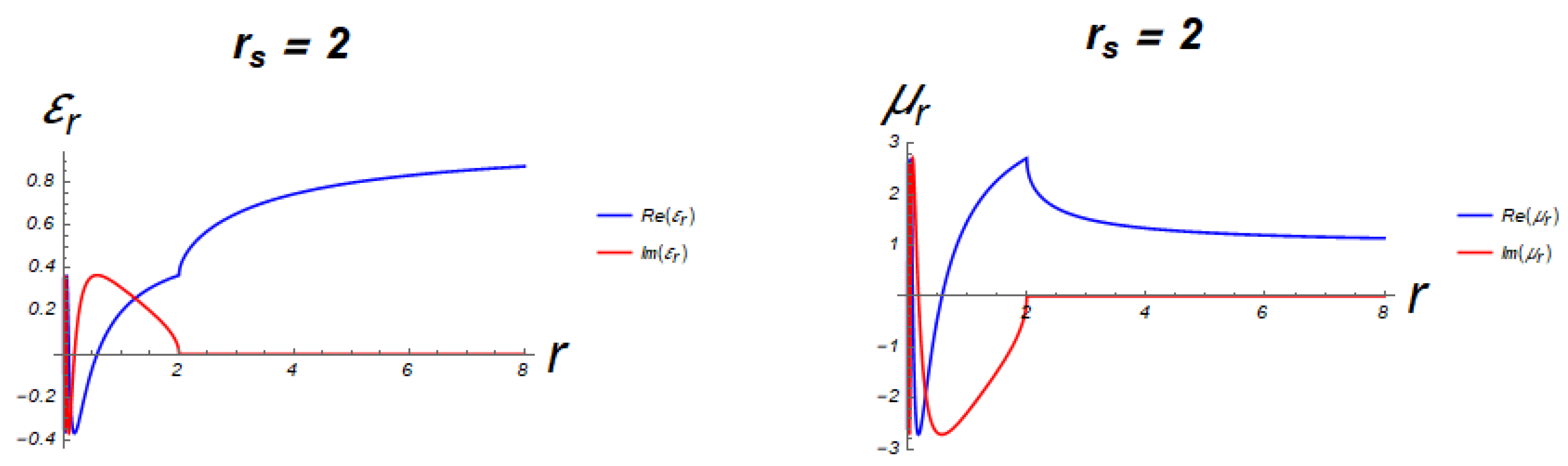
Appendix A.2. Behavior of the System in Curved Spacetime
Appendix A.3. Behavior of the System in Flat Minkowski Spacetime
Appendix A.4. Dynamics of Point-like Particles in Flat Spacetime
References
- Böhmer, C.G.; Downes, R.J. From continuum mechanics to general relativity. International Journal of Modern Physics D 2014, 23, 1442015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, V.I.; Olmo, G.J.; Orazi, E.; Rubiera-García, D. Mapping nonlinear gravity into General Relativity with nonlinear electrodynamics. The European Physical Journal. C, Particles and Fields 2018, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalyt-Margolin, A. The Quantum Field Theory Boundaries Applicability and Black Holes Thermodynamics. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 2021, 60, 1858–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, E.; Marins, A. The dark sector cosmology. International Journal of Modern Physics D 2020, 29, 2030014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenner, H. On the History of Unified Field Theories. Living Rev. Relativ. 2004, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halverson, J.; Sung, B. Faking gauge coupling unification in string theory. Physical Review D 2022, 105, 126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, A. Searches for supersymmetry at the Large Hadron Collider. Reviews in Physics 2019, 4, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, P. An approach to Grand Unification. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2021, Vol. 2081, p. 012010.
- Mahanta, M. A dualistic approach to gravitation. Annalen der Physik 1984, 496, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, N.G. The classical-quantum duality of nature including gravity. International Journal of Modern Physics D 2019, 28, 1950055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmer, D. Introducing the ISE Methodology: A Powerful New Tool for Topological Redescription, 2023, [arXiv:physics.hist-ph/2303.04130].
- Beach, R.J. The geometrization of Maxwell’s equations and the emergence of gravity and antimatter. Annals of Physics 2024, 465, 169661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torromé, R.G. Maximal acceleration geometries and spacetime curvature bounds. International Journal of Geometric Methods in Modern Physics 2020, 17, 2050060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogonowski, P. Proposed method of combining continuum mechanics with Einstein Field Equations. International Journal of Modern Physics D 2023, 2350010, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogonowski, P. Developed method: interactions and their quantum picture. Frontiers in Physics 2023, 11, 1264925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonyi, J. The Abraham–Lorentz force and electrodynamics at the classical electron radius. International Journal of Modern Physics A 2019, 34, 1950077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.L.; Marciano, W.J. Lepton dipole moments; Vol. 20, World Scientific, 2010.
- Masood, S.; Mein, H. Magnetic Moment of Leptons. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.08569, arXiv:1901.08569 2019.
- Wen, M.; Keitel, C.H.; Bauke, H. Spin-one-half particles in strong electromagnetic fields: Spin effects and radiation reaction. Physical Review A 2017, 95, 042102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Bauke, H.; Keitel, C.H. Identifying the Stern-Gerlach force of classical electron dynamics. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 31624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruelle, N.; Uzan, J.P. Relativity in Modern Physics; Oxford University Press, 2018.
- Sharif, M.; Shahzadi, M. Particle dynamics near Kerr-MOG black hole. The European Physical Journal C 2017, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, K.; Witt, D. Designer de Sitter spacetimes. Canadian Journal of Physics 2008, 86, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.N.; Sato, M. High-harmonic generation by electric polarization, spin current, and magnetization. Physical Review B 2019, 100, 214424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonano, C.A.; Zich, R.E.; Mussetta, M. Definition for polarization P and magnetization M fully consistent with Maxwell’s equations. Progress In Electromagnetics Research B 2015, 64, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M. The connection between polarization calculus and four-dimensional rotations, 2013, [arXiv:physics.optics/1303.1836].
- Bașkal, S.; Kim, Y. Lorentz group in ray and polarization optics. In Mathematical Optics; CRC Press, 2018; pp. 303–340.
- Böhmer, C.G.; Jensko, E. A New 2D Formulation of Modified General Relativity. Fortschritte der Physik, 2300. [Google Scholar]
- Capozziello, S.; Mazumdar, A.; Meluccio, G. Can nonlocal gravity really explain dark energy? Physics of the Dark Universe 2024, 45, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.W.; Kumar, S.; Safdi, B.R.; Soreq, Y. Dark Grand Unification in the axiverse: decaying axion dark matter and spontaneous baryogenesis. Journal of High Energy Physics 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Sharma, M.K.; Sur, S. On the Quantum Origin of a Dark Universe. Physical Sciences Forum 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, Y. Quantum foam, gravitational thermodynamics, and the dark sector. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2016, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.J.E.; Ratra, B. The Cosmological Constant and Dark Energy. Reviews of Modern Physics 2002, 75, 559–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, P. General relativity and the accelerated expansion of the universe. Resonance 2012, 17, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlip, S. Hiding the cosmological constant. Physical review letters 2019, 123, 131302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A. Harmonic E / B decomposition for CMB polarization maps. Physical Review D 2003, 68, 083509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, I.L.; Sola, J.; Espana-Bonet, C.; Ruiz-Lapuente, P. Variable cosmological constant as a Planck scale effect. Physics Letters B 2003, 574, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvali, G.; Vilenkin, A. Field theory models for variable cosmological constant. Physical Review D 2001, 64, 063509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Visinelli, L.; Yang, W.; Melchiorri, A.; Mota, D.F.; Riess, A.G.; Silk, J. In the realm of the Hubble tension—a review of solutions. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2021, 38, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, R.J.; Dai, C. Solutions to axion electromagnetodynamics and new search strategies of sub-μeV axion. Journal of High Energy Physics 2022, 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yang, B.; Yoon, H.; Ahn, M.; Park, H.B.; Min, B.; Kim, D.; Yoo, J. Searching for Invisible Axion Dark Matter with an 18 T Magnet Haloscope. Physical review letters 2022, 128 24, 241805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.; Aloni, D.; Schmaltz, M.; Sivarajan, E.N.; Weiner, N. A Step in understanding the S 8 tension. Physical Review D 2023, 108, 023520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Yu, Z.; Brandt, W.; Tak, H.; Yang, G.; Ni, Q. Mapping the Growth of Supermassive Black Holes as a Function of Galaxy Stellar Mass and Redshift. The Astrophysical Journal 2024, 964, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, M.; Merritt, D. The final parsec problem. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings. American Institute of Physics, 2003, Vol. 686, pp. 201–210.
- Test of lepton universality in beauty-quark decays. Nature Physics 2022, 18, 277–282. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Jaramillo, F.; Hohm, O.; Plefka, J. Double field theory as the double copy of Yang-Mills theory. Physical Review D 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Spallucci, E.; Smailagic, A. Double copy of spontaneously broken Abelian gauge theory. Physics Letters B 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easson, D.A.; Manton, T.; Svesko, A. Sources in the Weyl Double Copy. Physical review letters 2021, 127 27, 271101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangzhou, G. Exploration of the unification of fields. Physics Essays 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davighi, J.; Tooby-Smith, J. Electroweak flavour unification. Journal of High Energy Physics 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfatti, J. Unification of Einstein’s Gravity with Quantum Chromodynamics. Bulletin of the American Physical Society 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lisi, A.; Smolin, L.; Speziale, S. Unification of gravity, gauge fields and Higgs bosons. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical 2010, 43, 445401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madore, J. The Geometry of the Higgs Field. International Journal of Geometric Methods in Modern Physics 2008, 05, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, P.H.; Heller, U.M. The U(1) Higgs model in an external electromagnetic field. Nuclear Physics 1988, 309, 625–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, N. Higgs boson decay into two photons in an electromagnetic background field. Physical Review D 2014, 90, 016010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leder, E. Symmetry, Symmetry Breaking, and the Current View of the Dirac Monopole. 2020.
- Quigg, C. Spontaneous symmetry breaking as a basis of particle mass. Reports on Progress in Physics 2007, 70, 1019–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, K.; Percacci, R. Gravity and unification: a review. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2018, 35, 143001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, T. Canonical quantum gravity, constructive QFT, and renormalisation. Frontiers in Physics 2020, 8, 548232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Bianchi, E. A short review of loop quantum gravity. Reports on Progress in Physics 2021, 84, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, F.; Del Zotto, M.; García Etxebarria, I.; Hosseini, S.S. Higher form symmetries and M-theory. Journal of High Energy Physics 2020, 2020, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loll, R. Quantum gravity from causal dynamical triangulations: a review. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2019, 37, 013002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.G.; Carrilho, P.; Clifton, T.; Mulryne, D.J. The 4D Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet theory of gravity: a review. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2022, 39, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.S.; Quach, J.Q.; Faizal, M. Time Fisher information associated with fluctuations in quantum geometry. Europhysics Letters 2021, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, H.I. Discretization and degeometrization: A new relational quantum physics and an alternate path to quantum gravity. Physics Essays 2021, 34, 429–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augousti, A.; Gawełczyk, M.; Siwek, A.; Radosz, A. Touching ghosts: observing free fall from an infalling frame of reference into a Schwarzschild black hole. European journal of physics 2011, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, D. Scattering times of quantum particles from the gravitational potential and equivalence principle violation. Physical Review A 2022, 106, 022215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailas, T. “Time”-covariant Schrödinger equation and the canonical quantization of the Reissner–Nordström black hole. Quantum Reports 2020, 2, 414–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. Generalized Unruh effect: A potential resolution to the black hole information paradox. Physical Review D 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kolobov, V.I.; Golubkov, K.; de Nova, J.R.M.; Steinhauer, J. Observation of stationary spontaneous Hawking radiation and the time evolution of an analogue black hole. Nature Physics, 2021; 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, S.M. Spacetime and geometry; Cambridge University Press: London, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alcubierre, M.; Lobo, F.S. Warp drive basics. Wormholes, Warp Drives and Energy Conditions 2017, pp. 257–279.
- Lundblad, N.; Aveline, D.C.; Balaž, A.; Bentine, E.; Bigelow, N.P.; Boegel, P.; Efremov, M.A.; Gaaloul, N.; Meister, M.; Olshanii, M.; et al. Perspective on quantum bubbles in microgravity. Quantum Science and Technology 2023, 8, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, Y. Undecidable problems in quantum field theory. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 2023, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noce, C.; Romano, A. Undecidability and Quantum Mechanics. Encyclopedia 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diósi, L. Planck length challenges non-relativistic quantum mechanics of large masses. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2019, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, J.; Napolitano, J. Modern Quantum Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: London, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ogonowski, P.; Skindzier, P. Maxwell-like picture of General Relativity and its Planck limit, 2013, [arXiv:physics.gen-ph/1301.2758].
- Bergstedt, V. Spacetime as a Hamiltonian Orbit and Geroch’s Theorem on the Existence of Fermions, 2020.
- Helfer, A.D. Do black holes radiate? Reports on Progress in Physics 2003, 66, 943–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brout, R.; Massar, S.; Parentani, R.; Spindel, P. Hawking radiation without trans-Planckian frequencies. Physical Review D 1995, 52, 4559–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, J.; Longo Micchi, L.F.; Afshordi, N. GW190521: Search for echoes due to stimulated Hawking radiation from black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 044047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, S.; Luo, L.; Cai, R.G. Simulating quantum field theory in curved spacetime with quantum many-body systems. Physical Review Research 2020, 2, 023107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, S.; Cianci, R.; Corradini, O.; Flachi, A.; Vignolo, S.; Vitagliano, V. Avenues of Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime, Genova, 14-16 Sep 2022. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2023, Vol. 2531, p. 011001.
- Bertone, G.; Hooper, D. History of dark matter. Reviews of Modern Physics 2018, 90, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, K.S.; Joy, A.D.; Kedari, S.R.; Nuñez, D.E.; Reddy, J.; Wongwises, S. A Nonlinear Constitutive Theory for Deviatoric Cauchy Stress Tensor for Incrompressible Viscous Fluids. 2017.
- Goraj, R. Transformation of the Navier-Stokes Equation to the Cauchy Momentum Equation Using a Novel Mathematical Notation. Applied Mathematics-a Journal of Chinese Universities Series B 2016, 07, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romatschke, P.; Romatschke, U. Relativistic fluid dynamics in and out of equilibrium: and applications to relativistic nuclear collisions; Cambridge University Press: London, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bredberg, I.; Keeler, C.; Lysov, V.; Strominger, A. From navier-stokes to einstein. Journal of High Energy Physics 2012, 2012, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasukov, V. Cosmological and Quantum Solutions of the Navier–Stokes Equations. Russian Physics Journal 2019, 62, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoff, S. Lagrangian theory for perfect fluids. arXiv preprint gr-qc/0303015 2003.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




