Submitted:
08 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
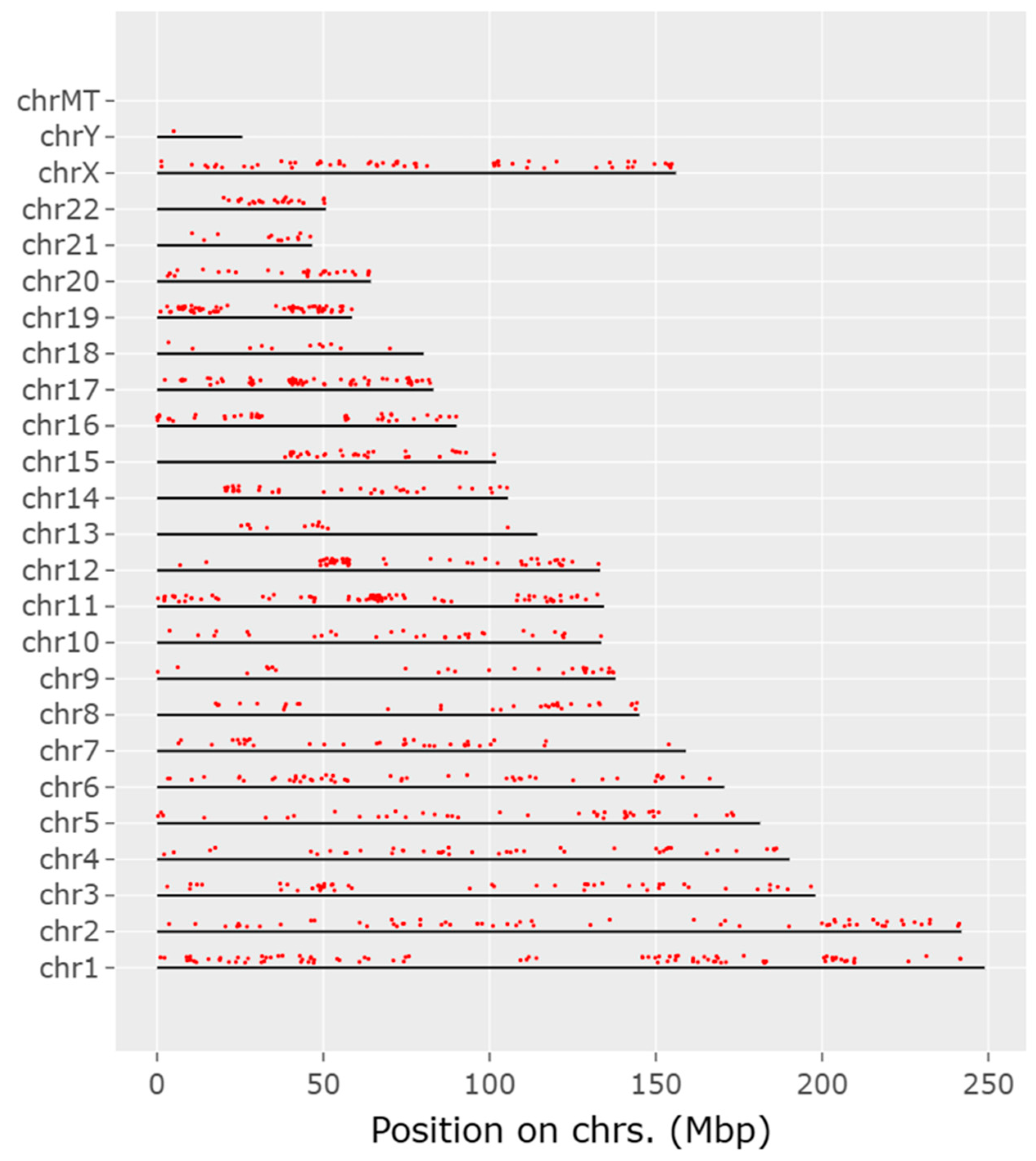
Raw data Collection & Web Scraping
Implementation with Python and Selenium
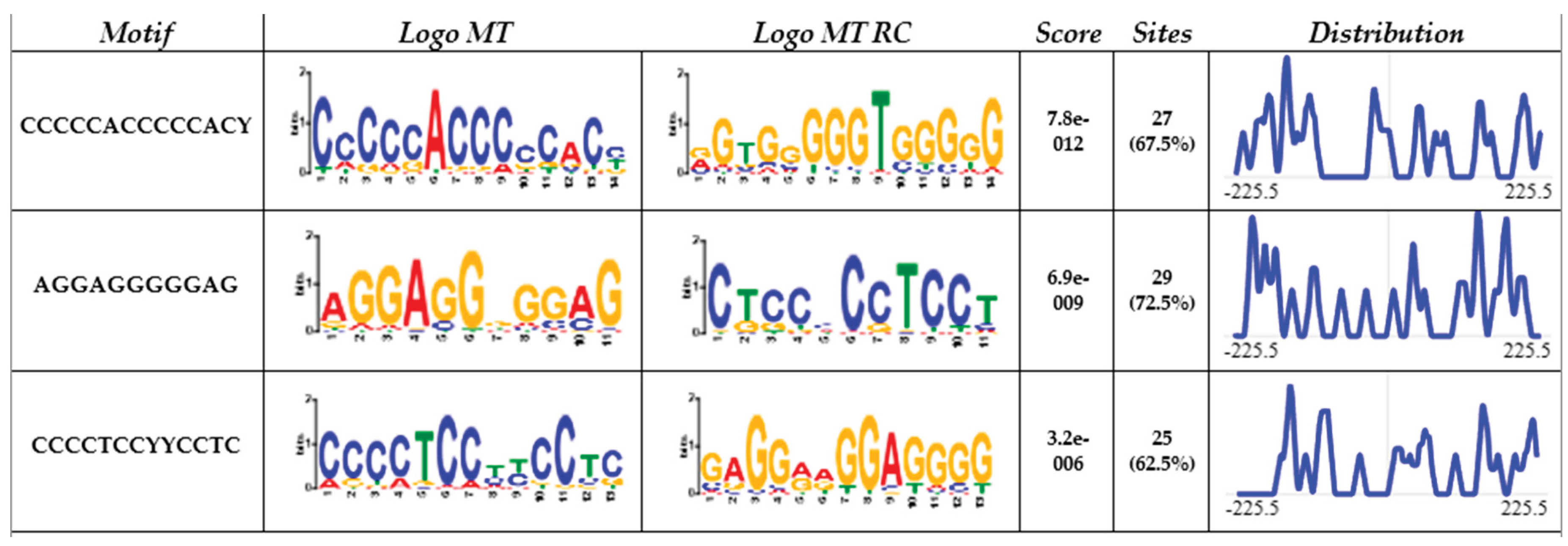
MEME
STRING
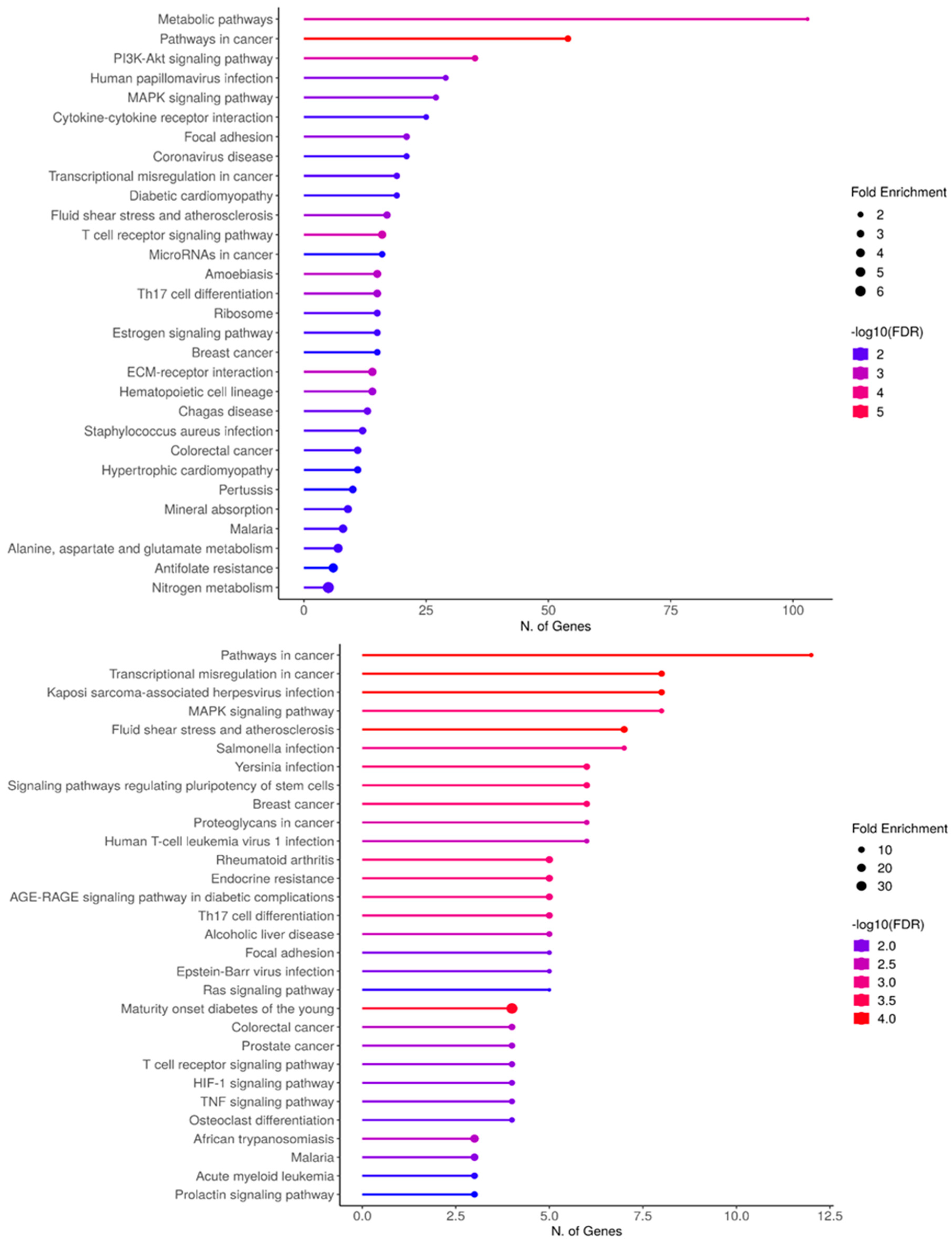
ShinyGO
Enrichr & Appyter
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davie, K.; Jacobs, J.; Atkins, M.; Potier, D.; Christiaens, V.; Halder, G.; Aerts, S. Discovery of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Regions Driving in Vivo Tumor Development by ATAC-Seq and FAIRE-Seq Open Chromatin Profiling. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1004994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lei, C.; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Tao, Y. Nuclear Functions of Mammalian MicroRNAs in Gene Regulation, Immunity and Cancer. Mol Cancer 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frietze, S.; Farnham, P.J. Transcription Factor Effector Domains. In; 2011; pp. 261–277.
- Santoyo-Suarez, M.G.; Mares-Montemayor, J.D.; Padilla-Rivas, G.R.; Delgado-Gallegos, J.L.; Quiroz-Reyes, A.G.; Roacho-Perez, J.A.; Benitez-Chao, D.F.; Garza-Ocañas, L.; Arevalo-Martinez, G.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; et al. The Involvement of Krüppel-like Factors in Cardiovascular Diseases. Life 2023, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, K.; Sakaguchi, G.; Takagi, S.; Naito, K.; Mimori, T.; Igarashi, H. Sp1 Family Proteins Recognize the U5 Repressive Element of the Long Terminal Repeat of Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type I through Binding to the CACCC Core Motif. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 12944–12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraizer, G.C.; Shimamura, R.; Zhang, X.; Saunders, G.F. PAX 8 Regulates Human WT1 Transcription through a Novel DNA Binding Site. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1997, 272, 30678–30687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavallée, G.; Andelfinger, G.; Nadeau, M.; Lefebvre, C.; Nemer, G.; Horb, M.E.; Nemer, M. The Kruppel-like Transcription Factor KLF13 Is a Novel Regulator of Heart Development. EMBO Journal 2006, 25, 5201–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhinav, P.; Zhang, G.-F.; Zhao, C.-M.; Xu, Y.-J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.-Q. A Novel KLF13 Mutation Underlying Congenital Patent Ductus Arteriosus and Ventricular Septal Defect, as Well as Bicuspid Aortic Valve. Exp Ther Med 2022, 23, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, B.; Li, T.; Zhang, E.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Sun, K. Identification and Analysis of KLF13 Variants in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. BMC Med Genet 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Wang, T.-M.; Qiao, X.-H.; Huang, R.-T.; Xue, S.; Dong, B.-B.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Q. KLF13 Loss-of-Function Variation Contributes to Familial Congenital Heart Defects. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020, 24, 11273–11285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, I.D.; Hoffman, M.; Gaignebet, L.; Lucchese, A.M.; Markopoulou, E.; Palioura, D.; Wang, C.; Bannister, T.D.; Christofidou-Solomidou, M.; Oka, S.I.; et al. KLF5 Is Induced by FOXO1 and Causes Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy; 2021; Vol. 128; ISBN 1215707142.
- Gao, C.; Qian, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-363-3p Serves as a Diagnostic Biomarker of Acute Myocardial Infarction and Regulates Vascular Endothelial Injury by Targeting KLF2. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 2020, 10, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yan, T.; Gao, Y. Silence of MiR-32-5p Promotes Endothelial Cell Viability by Targeting KLF2 and Serves as a Diagnostic Biomarker of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Diagn Pathol 2020, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinjamur, D.S.; Wade, K.J.; Mohamad, S.F.; Haar, J.L.; Sawyer, S.T.; Lloyd, J.A. Krüppel-like Transcription Factors KLF1 and KLF2 Have Unique and Coordinate Roles in Regulating Embryonic Erythroid Precursor Maturation. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, O. New Study Reveals Latest Data on Global Burden of Cardiovascular Disease Available online:. Available online: https://www.acc.org/About-ACC/Press-Releases/2023/12/11/18/48/New-Study-Reveals-Latest-Data-on-Global-Burden-of-Cardiovascular-Disease (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X. Current Knowledge of Krüppel-like Factor 5 and Vascular Remodeling: Providing Insights for Therapeutic Strategies. J Mol Cell Biol 2021, 13, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Nayak, L.; Jain, M.K. Krüppel-like Factors in Endothelial Cell Biology. Curr Opin Hematol 2017, 24, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, P.; Koroleva, M.; Zhang, S.; Si, S.; Jin, Z.G. Suberanilohydroxamic Acid as a Pharmacological Kruppel-Like Factor 2 Activator That Represses Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Qi, Y.; Du, J. Krüppel-Like Factor 4 Transcriptionally Regulates TGF-Β1 and Contributes to Cardiac Myofibroblast Differentiation. PLoS One 2013, 8, 0–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Luo, L.; Zhu, Z. De; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, Z.L.; Ma, Q.; et al. Chlorogenic Acid Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Blocking the MiR-21-Regulated TGF-Β1/Smad7 Signaling Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Duan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Tomlinson, B.; et al. Endothelial Klf2-Foxp1-TGFβ Signal Mediates the Inhibitory Effects of Simvastatin on Maladaptive Cardiac Remodeling. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.; Palioura, D.; Kyriazis, I.D.; Cimini, M.; Badolia, R.; Rajan, S.; Gao, E.; Nikolaidis, N.; Schulze, P.C.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Cardiomyocyte Krüppel-Like Factor 5 Promotes De Novo Ceramide Biosynthesis and Contributes to Eccentric Remodeling in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2021, 143, 1139–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Wai, B.; Lang, C.C.; Levin, D.; Palmer, C.N.A.; Parry, H.M.; Velkoska, E.; Harrap, S.B.; Srivastava, P.M.; Burrell, L.M. Genetic Variation in Kruppel like Factor 15 Is Associated with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Discovery and Replication Cohorts. EBioMedicine 2017, 18, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.R.; Lam, C.; Jain, M.K. Evolutionary Protection of Krüppel-Like Factors 2 and 4 in the Development of the Mature Hemovascular System. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-K.; He, P.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. SP and KLF Transcription Factors in Digestive Physiology and Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1845–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Han, M.; Wen, J.-K. Role of Krüppel-like Factor 4 in Phenotypic Switching and Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. IUBMB Life 2010, NA–NA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, L.S.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.F.; Haskins, R.M.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.A.C.; Greene, E.S.; Straub, A.C.; et al. KLF4-Dependent Phenotypic Modulation of Smooth Muscle Cells Has a Key Role in Atherosclerotic Plaque Pathogenesis. Nat Med 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, T.; Manabe, I.; Fukushima, Y.; Tobe, K.; Aizawa, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Kawai-Kowase, K.; Moriyama, N.; Imai, Y.; Kawakami, H.; et al. Krüppel-like Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor KLF5/BTEB2 Is a Target for Angiotensin II Signaling and an Essential Regulator of Cardiovascular Remodeling. Nat Med 2002, 8, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Chen, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, Y.; Tang, W.; Xia, F. Fibronectin 1 Inhibits the Apoptosis of Human Trophoblasts by Activating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Med 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, J.; Rashbass, P.; Schedl, A.; Brenner-Morton, S.; Kawakami, A.; van Heyningen, V.; Jessell, T.M.; Briscoe, J. Pax6 Controls Progenitor Cell Identity and Neuronal Fate in Response to Graded Shh Signaling. Cell 1997, 90, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoforou, N.; Chellappan, M.; Adler, A.F.; Kirkton, R.D.; Wu, T.; Addis, R.C.; Bursac, N.; Leong, K.W. Transcription Factors MYOCD, SRF, Mesp1 and SMARCD3 Enhance the Cardio-Inducing Effect of GATA4, TBX5, and MEF2C during Direct Cellular Reprogramming. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, J.D.; McDermott, J.C. MEF2 in Cardiac Hypertrophy in Response to Hypertension. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Schwartz, R.J. Recruitment of the Tinman Homolog Nkx-2.5 by Serum Response Factor Activates Cardiac Alpha-Actin Gene Transcription. Mol Cell Biol 1996, 16, 6372–6384.
- Dahlgren, A.; Zethelius, B.; Jensevik, K.; Syvänen, A.-C.; Berne, C. Variants of the TCF7L2 Gene Are Associated with Beta Cell Dysfunction and Confer an Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the ULSAM Cohort of Swedish Elderly Men. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Costa, M.J.; Rivero-Gutiérrez, B.; Ji, L.; Morgan, S.L.; Feldman, B.J. The Circadian Clock Regulates Adipogenesis by a Per3 Crosstalk Pathway to Klf15. Cell Rep 2017, 21, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Prosdocimo, D.A.; Bai, X.; Fu, C.; Zhang, R.; Campbell, F.; Liao, X.; Coller, J.; Jain, M.K. KLF15 Establishes the Landscape of Diurnal Expression in the Heart. Cell Rep 2015, 13, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butzner, M.; Leslie, D.L.; Cuffee, Y.; Hollenbeak, C.S.; Sciamanna, C.; Abraham, T. Stable Rates of Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in a Contemporary Era. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandamudi, S.; Slusser, J.; Mahoney, D.W.; Redfield, M.M.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Chen, H.H. The Prevalence of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: A Population-Based Study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Card Fail 2014, 20, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grarup, N.; Andersen, G.; Krarup, N.T.; Albrechtsen, A.; Schmitz, O.; Jørgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Association Testing of Novel Type 2 Diabetes Risk Alleles in the JAZF1, CDC123/CAMK1D, TSPAN8, THADA, ADAMTS9, and NOTCH2 Loci With Insulin Release, Insulin Sensitivity, and Obesity in a Population-Based Sample of 4,516 Glucose-Tolerant Middle-Aged Danes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, A.; Ladenvall, C.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Kravic, J.; Krus, U.; Taneera, J.; Isomaa, B.; Tuomi, T.; Renström, E.; Groop, L.; et al. Effects of Common Genetic Variants Associated With Type 2 Diabetes and Glycemic Traits on α- and β-Cell Function and Insulin Action in Humans. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; QiLi, M.; Liang, H.; Li, T.; E, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, M.; et al. Aspirin Reduces Cardiac Interstitial Fibrosis by Inhibiting Erk1/2-Serpine2 and P-Akt Signalling Pathways. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2018, 45, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intengan, H.D.; Schiffrin, E.L. Vascular Remodeling in Hypertension. Hypertension 2001, 38, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, M. Sp1 and Sp3 Transcription Factors Are Required for Trans-Activation of the Human SERCA2 Promoter in Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 2003, 60, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, Y.; Dong, Y.; Paris, M.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Schwarz, E.M.; Drissi, H. Runx2-Mediated Regulation of the Zinc Finger Osterix/Sp7 Gene. Gene 2006, 372, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, R.-N.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Wen, J.-K. Vascular Calcification Is Coupled with Phenotypic Conversion of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through Klf5-Mediated Transactivation of the Runx2 Promoter. Biosci Rep 2014, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsophonsakul, P.; Furmanik, M.; Forsythe, R.; Dweck, M.; Schurink, G.W.; Natour, E.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Jacobs, M.; Mees, B.; Schurgers, L. Role of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching and Calcification in Aortic Aneurysm Formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2019, 39, 1351–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paavola, J.; Alakoski, T.; Ulvila, J.; Kilpiö, T.; Sirén, J.; Perttunen, S.; Narumanchi, S.; Wang, H.; Lin, R.; Porvari, K.; et al. Vezf1 Regulates Cardiac Structure and Contractile Function. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Albuquerque Dias, R.; Balbinot, K.M.; da Silva Kataoka, M.S.; de Melo Alves Júnior, S.; de Jesus Viana Pinheiro, J. Expression of Stem Cell Markers SALL4, LIN28A, and KLF4 in Ameloblastoma. Diagn Pathol 2023, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiplunkar, A.R.; Lung, T.K.; Alhashem, Y.; Koppenhaver, B.A.; Salloum, F.N.; Kukreja, R.C.; Haar, J.L.; Lloyd, J.A. Krüppel-Like Factor 2 Is Required for Normal Mouse Cardiac Development. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
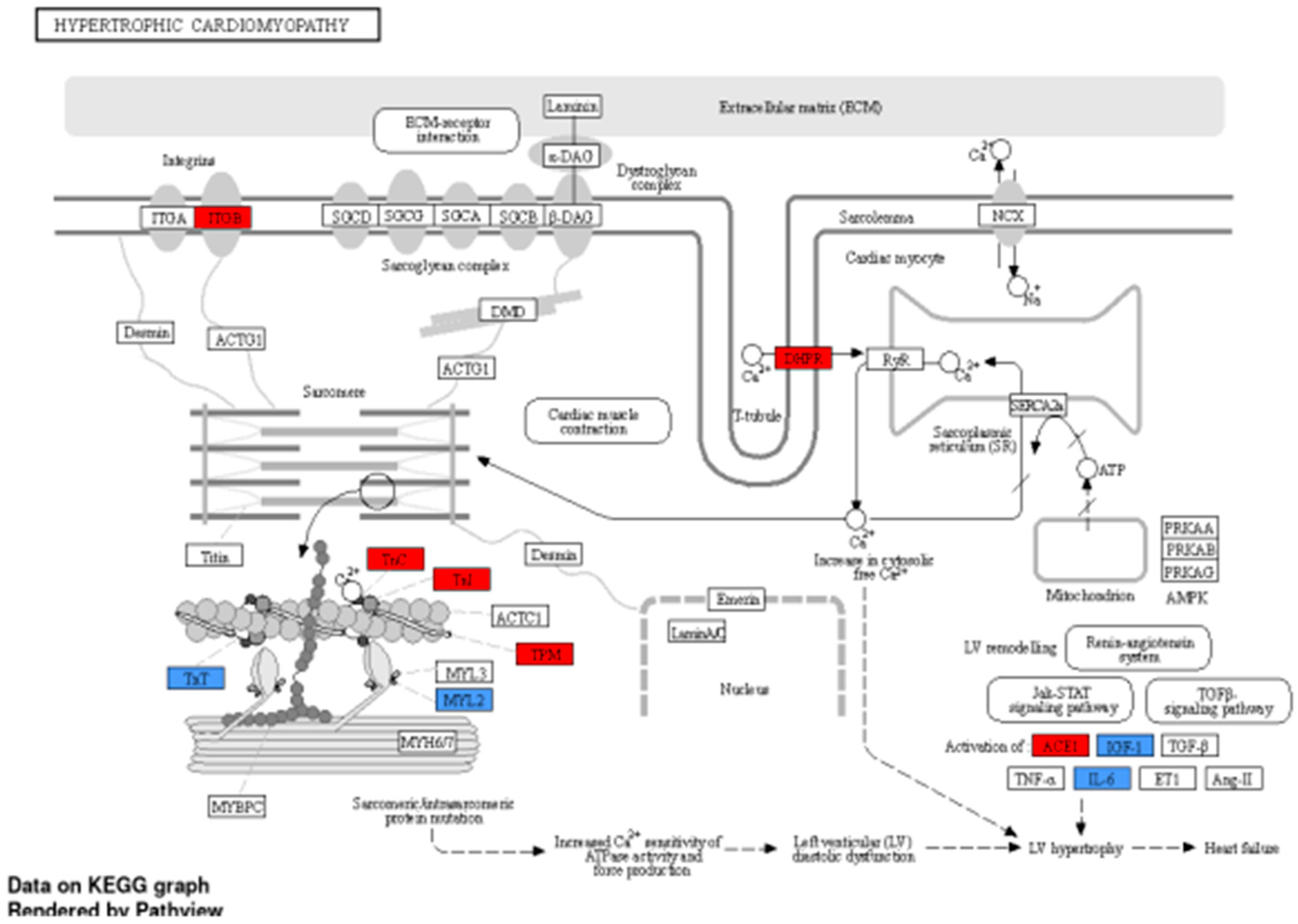
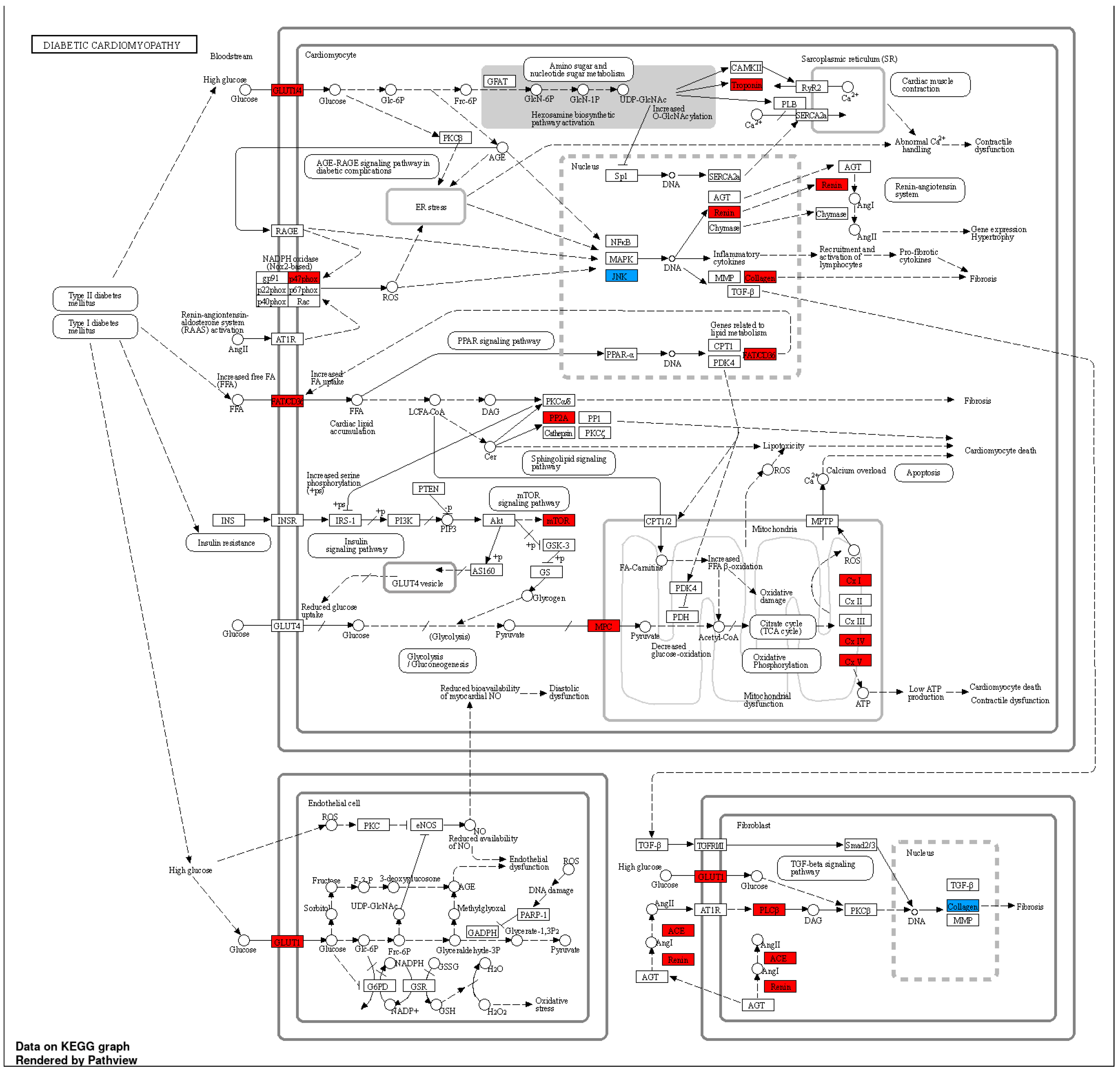
| Family member | KLF | Direct interaction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | KLF-3 | NKX2-8, NKX2-2, LLGL2 |
| 1 | KLF-8 | NKX2-8, NKX2-2 |
| 1 | KLF-12 | TFAP2A, NKX2-2, DNASE1 |
| 2 | KLF-1 | SPI1, HBZ, NKX2-8, TET2, CD44, HBB, HBE1, HBG2, GATA2, AHSP EPB42, UBC |
| 2 | KLF-2 | GZMB, TNNT2, DUSP1, CCR7, LEF1, ZAP70, CXCR4, TEK, HAS2, CD44, FOXP3, FOS, FBXW7, ICAM1, GATA2, TRPV4, CD8A, TBX3 |
| 2 | KLF-4 | SALL4, COL1A1, SPI1, TNNT2, SOX9, MYOD1, TBX3, EED, EPAS1, EPCAM, LEF1, CDH2, NODAL, GRHL3, T, IGF1, FOS, HAS2, TBX5, TUBB3, NKX2-5, DLK1, MEF2C, GATA2, FN1, PAX9, SOX15, LEFTY2, NES, TCF7L2, FLNA, DKK1, RARG, KLF-6, KDM2B, TET2, ESR1, GFAP, CXCR4, IL6, MYH11, CD24, CD44, TCF4, PAX6, PBX1 |
| 2 | KLF-5 | SOX9, TBX3, TP63, NCOR1, FBXW7, NODAL, UCP3, GATA2, MKX, SUMO1, ESR1 |
| 2 | KLF-6 | PPP1R15A, FOS, DUSP1, KLF-4, ESR1, CYP2E1, NAT1, ANGPT1 |
| 2 | KLF-7 | PROKR2, GABPB1, TBX3, LEF1, NFIA, NKX2-8 |
| 3 | KLF-9 | NKX2-8, THRA, RB1, MAPK10, TFAP2A, ACTG2 |
| 3 | KLF-10 | NKX2-8, SMAD7, NKX2-2, FOS, FOXP3 |
| 3 | KLF-11 | HNF1A, NKX2-2, FOXP3, |
| 3 | KLF-13 | HBB, HBE1, TBX5 |
| 3 | KLF-14 | HHEX, TCF7L2, FHL2, CAMK1D, JAZF1 |
| 3 | KLF-16 | - |
| - | KLF-15 | NR3C1, NFIA, ARNTL, GATA2, MKX, NKX2-8 |
| - | KLF-17 | TG, NODAL, CD44, TBX3, SLC5A5 |
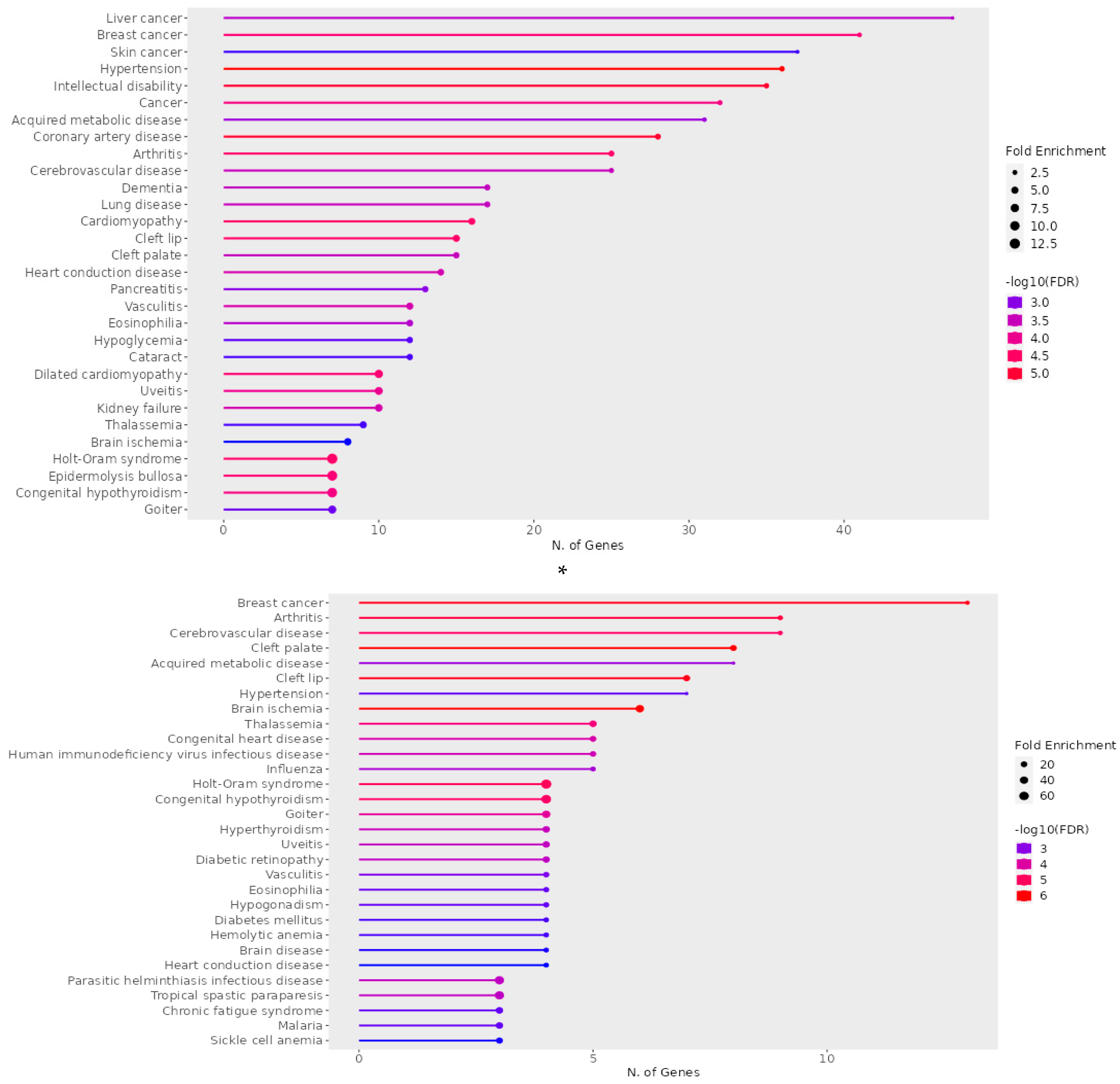
| A) Disease |
q - value | p–value | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holt-Oram syndrome | 2.91E-06 | 0.001117367 | TFAP2B, SALL4, GJA5, TBX6, TBX5, NKX2-5, TBX3 |
| Hypertension | 6.45E-06 | 0.00148591 | ENPEP, NCF1, CUL3, NPR3, KLK4, UMOD, ADM, CACNA1D, DBH, AAAS, NR3C1, ICAM1, ADD2, GJA5, NPY, TNNI3, GGT1, DUOX2, KL, ACE, ANGPT1, CYP4F2, CAV1, ATP6AP2, MTHFR, IGF1, FOS, RHOA, SELP, IL6, TH, NEDD4, SCNN1B, CYP11B1, TRPV4, REN, ANG |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | 8.98E-06 | 0.001549478 | BAG3, LAMA4, TNNC1, TNNT2, ANKRD1, LDB3, TNNI3, DSG2, CRYAB, VCL |
| Coronary artery disease | 9.42E-06 | 0.001549478 | SLC22A4, KLK4, ADM, TNFRSF11B, LDB3, AAAS, MPO, CX3CL1, THBS4, ICAM1, XIRP1, TNNI3, CD36, GGT1, LDLR, SCAI, ACE, ANGPT1, APOA2, MTHFR, APOC3, IGF1, SELP, FABP3, IL6, TNNT1, TNNT2, REN, CD68 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.0015946 | 0.04946049 | NTRK2, PRKCH, ACE, ANGPT1, CYP4F2, F11, KLK4, MTHFR, CXCR4, ADM, IGF1, FOS, MPO, RHOA, ICAM1, GFAP, SELP, IL6, TNNT1, TNNT2, REN, TNNI3, CD68, NES |
| Cardiomyopathy | 1.33E-05 | 0.001700831 | TNNC1, LAMA4, PSEN1, TBX5, MTO1, JPH2, BAG3, GJA5, MYL2, TNNT2, DSG2, TNNI3, CTNNA3, FPGT-TNNI3K, CRYAB, VCL |
| Heart conduction disease | 0.000268757 | 0.013461245 | CAV1, IL5RA, DPT, CXCR4, MTHFR, TBX5, SLC4A4, DKK1, ARHGAP24, SFRP2, NFIA, CLDN14, TRPM7, BMPR1B |
|
B) Disease |
q - value | p-value | Genes |
| Holt-Oram syndrome | 3.30E-07 | 2.16E-05 | SALL4, TBX5, NKX2-5, TBX3 |
| Hypertension | 0.00045705 | 0.006255711 | NR3C1, ICAM1, ANGPT1, IGF1, FOS, IL6, TRPV4 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.000426195 | 0.006255711 | UCP3, HNF1A, FOXP3 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 3.12E-05 | 0.000720179 | IL6, ANGPT1, IGF1, ICAM1 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.25E-06 | 6.14E-05 | IL6, ANGPT1, TNNT2, CXCR4, FOS, IGF1, NES, GFAP, ICAM1 |
| Congenital heart disease | 1.14E-05 | 0.000405807 | MEF2C, NKX2-5, TBX5, LEFTY2, NODAL |
| Heart conduction disease | 0.000629384 | 0.007274938 | CXCR4, TBX5, DKK1, NFIA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





