Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
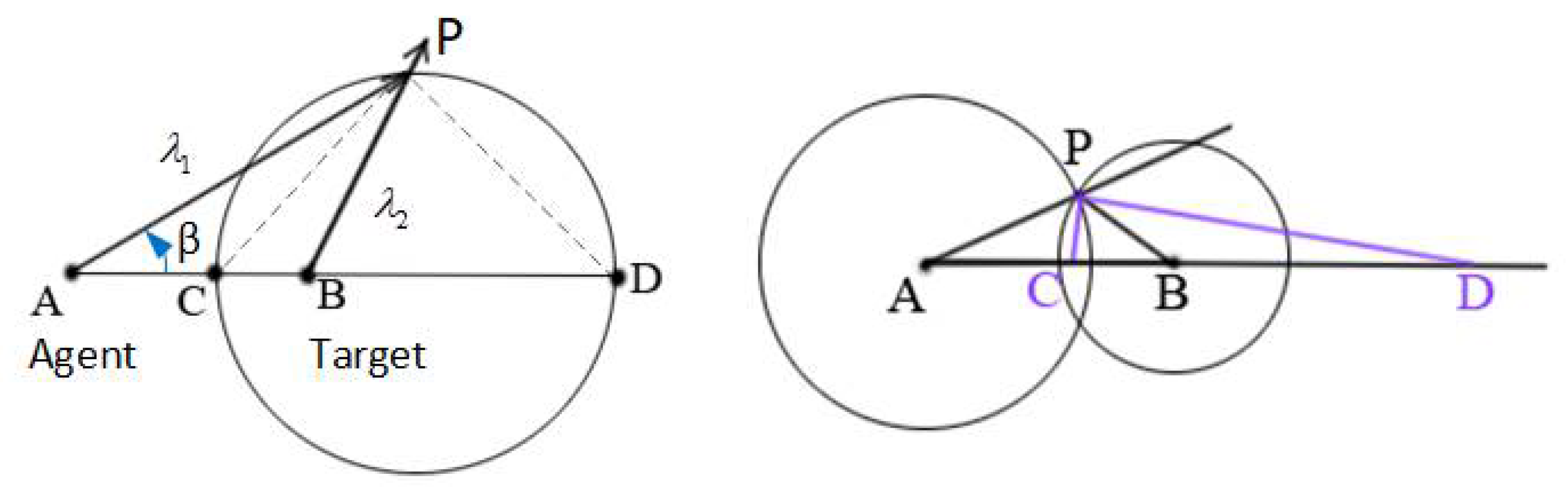
2.1. Mathematical Solutions to Terrestrial Interception Based on the Geometrical Constraints
2.2. Canonical Base of the Reference Frame for the Interception System
2.3. Harmonic Cross-Ratio Model with Constant Ratios and Proportions
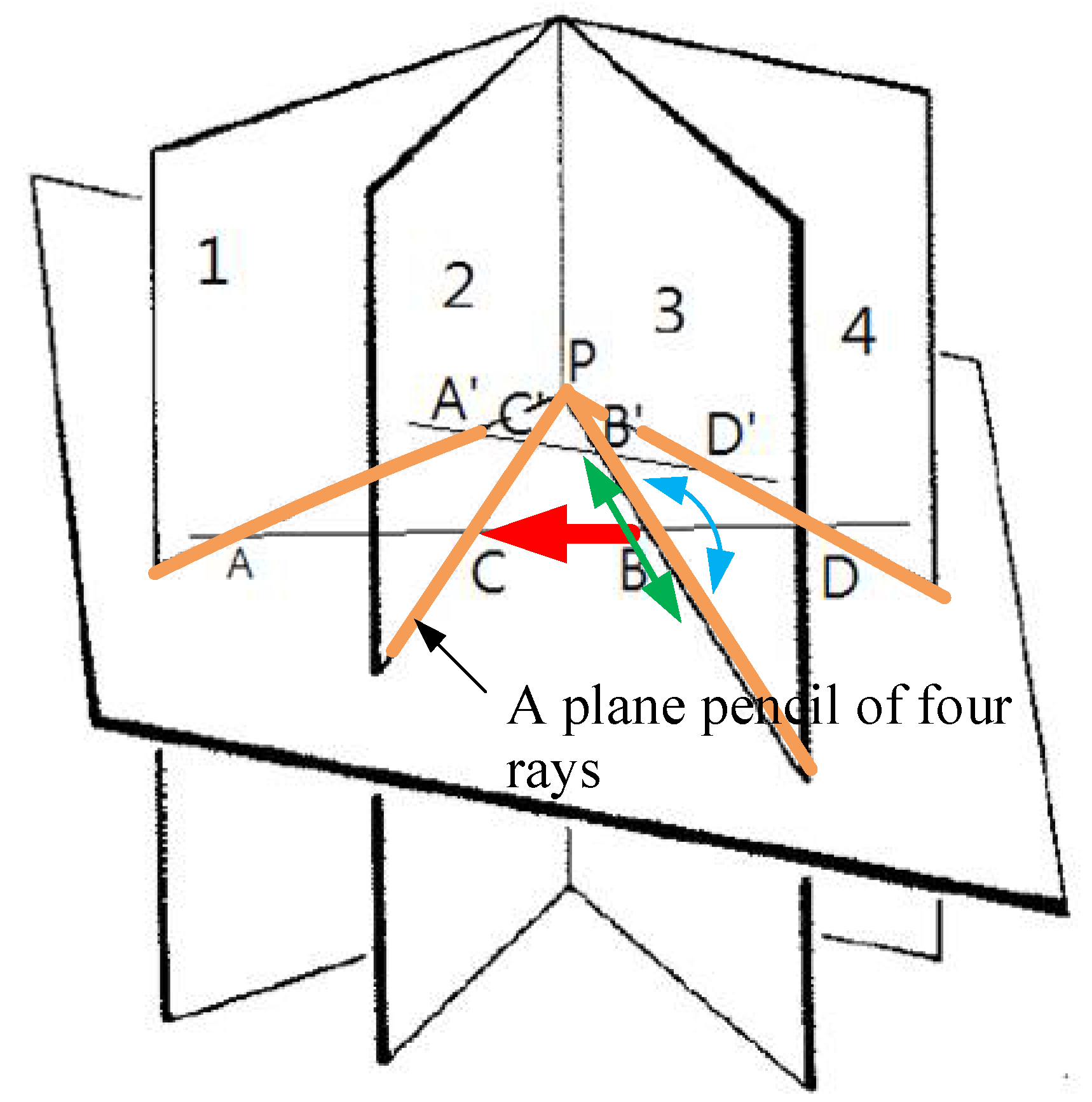
2.4. Cross-Ratios at Infinity
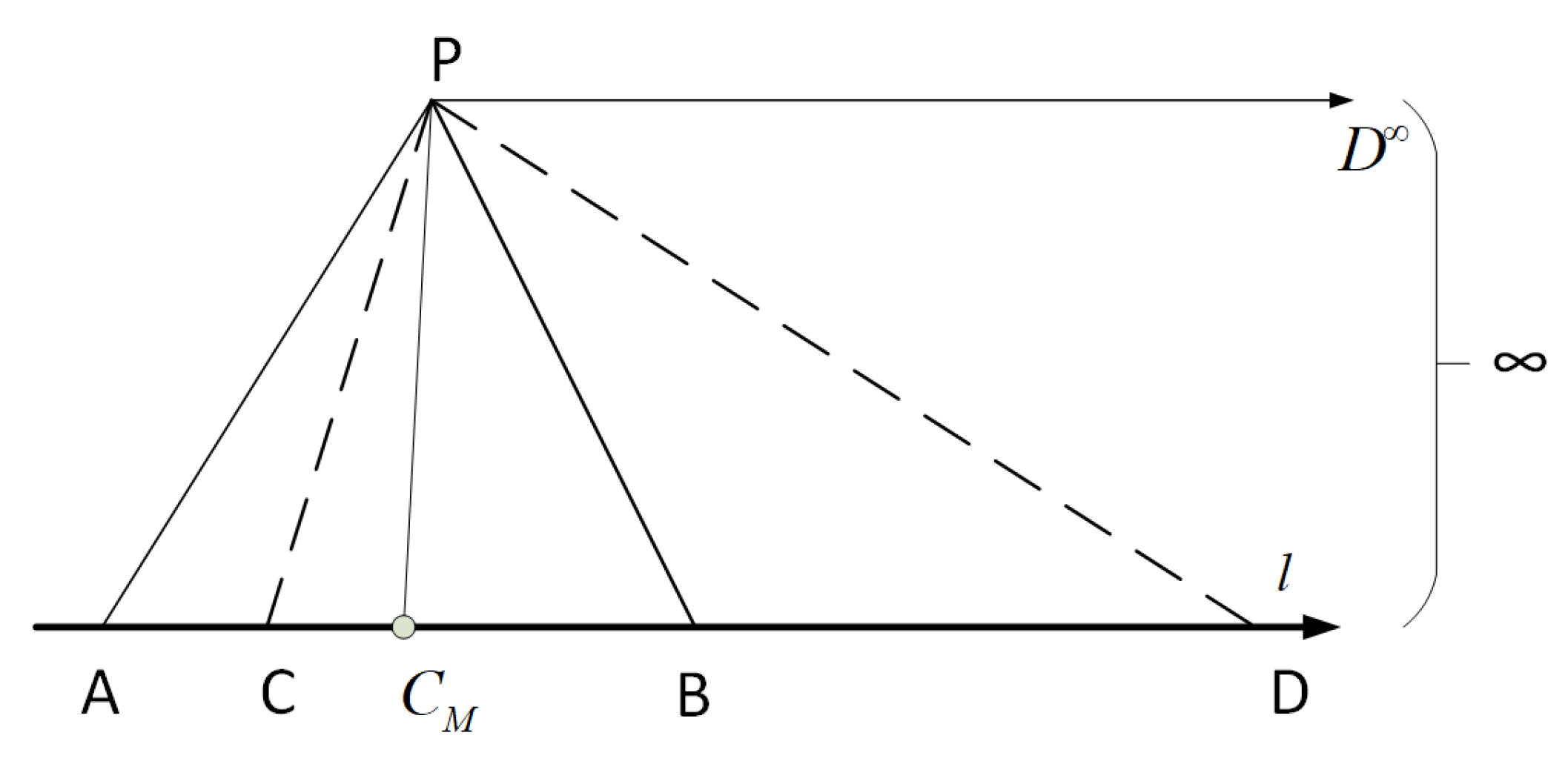
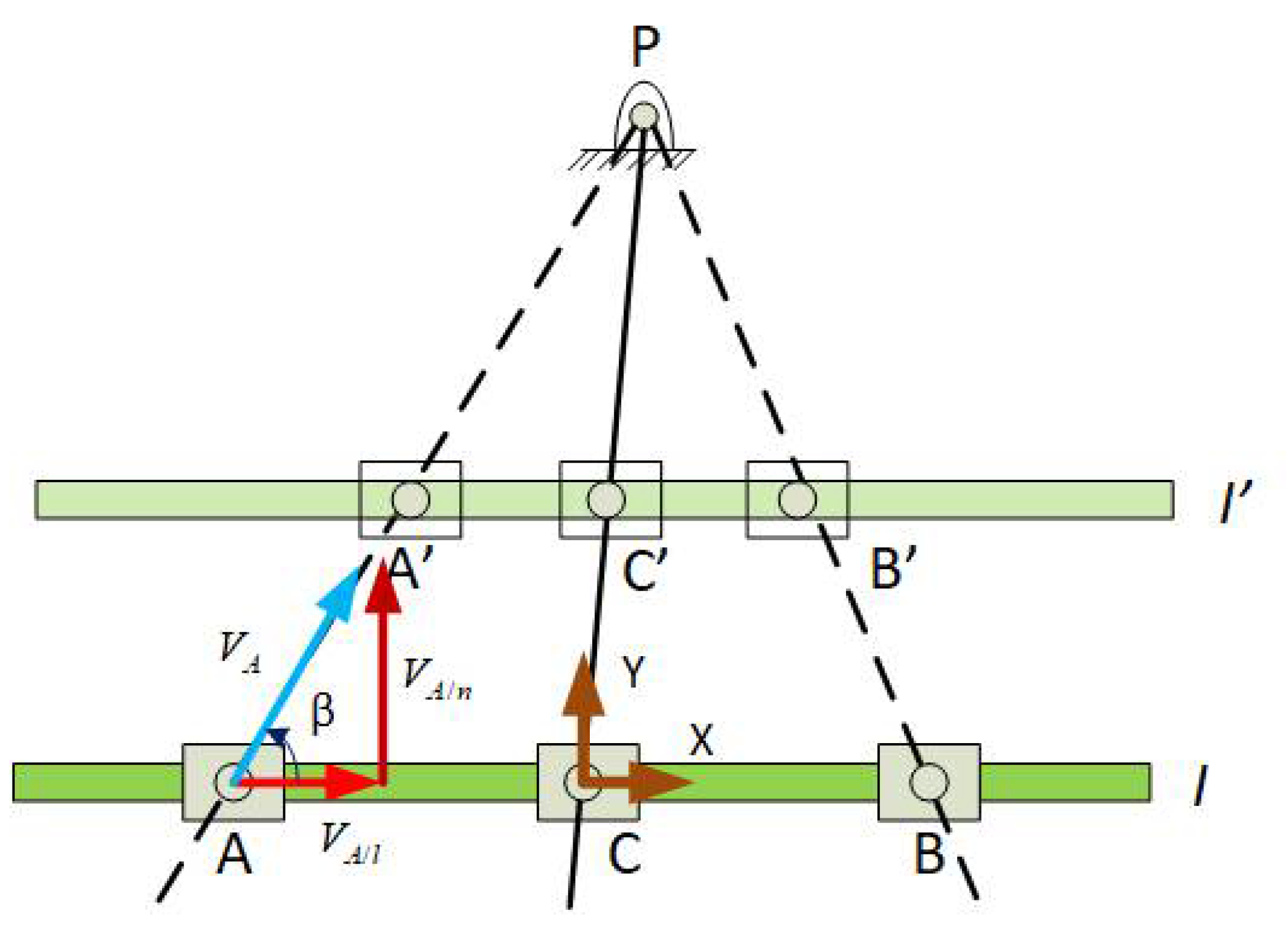
3. Results
3.1. Perception and Action Coupling in Virtual Environments
3.2. Action Shaping Perception
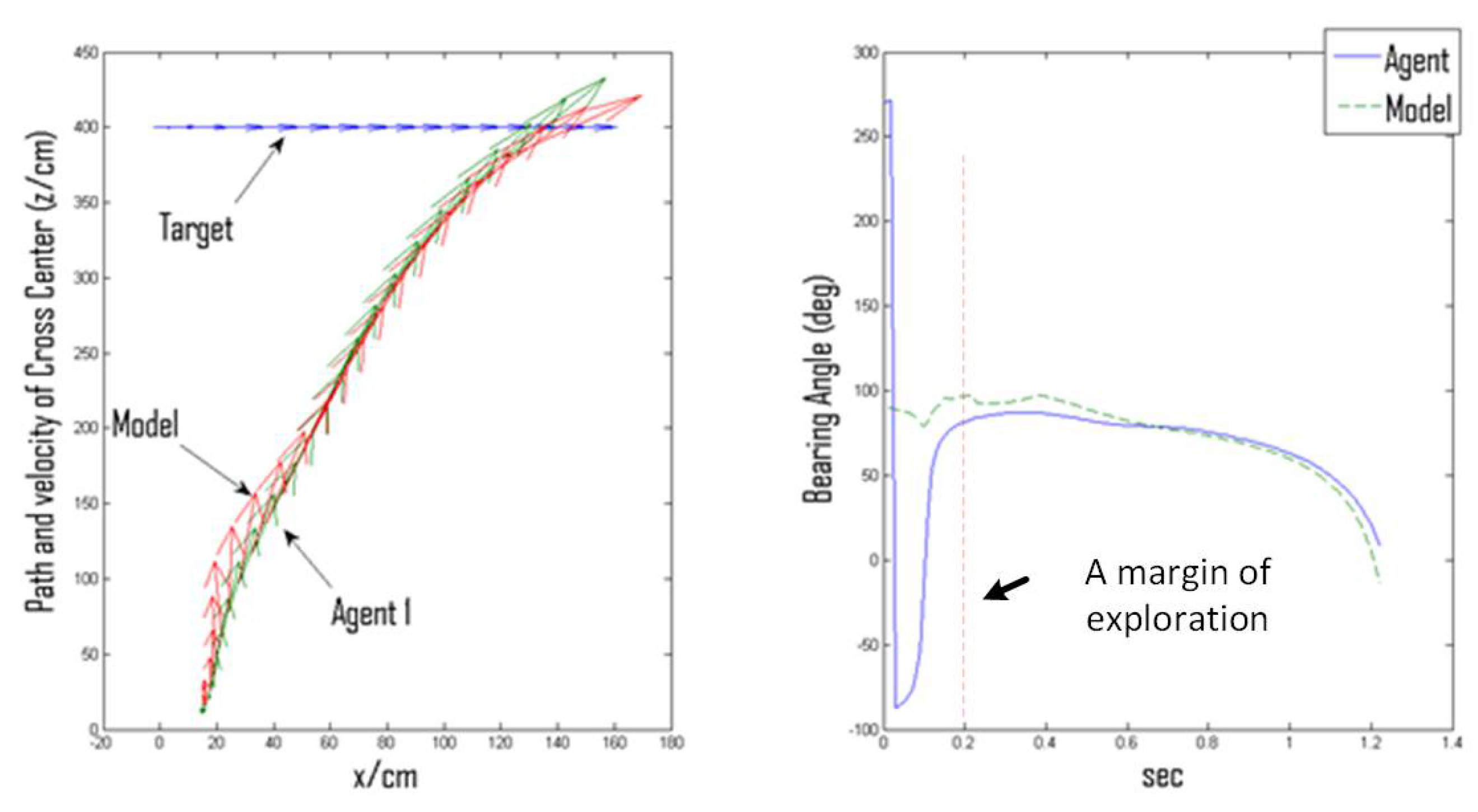
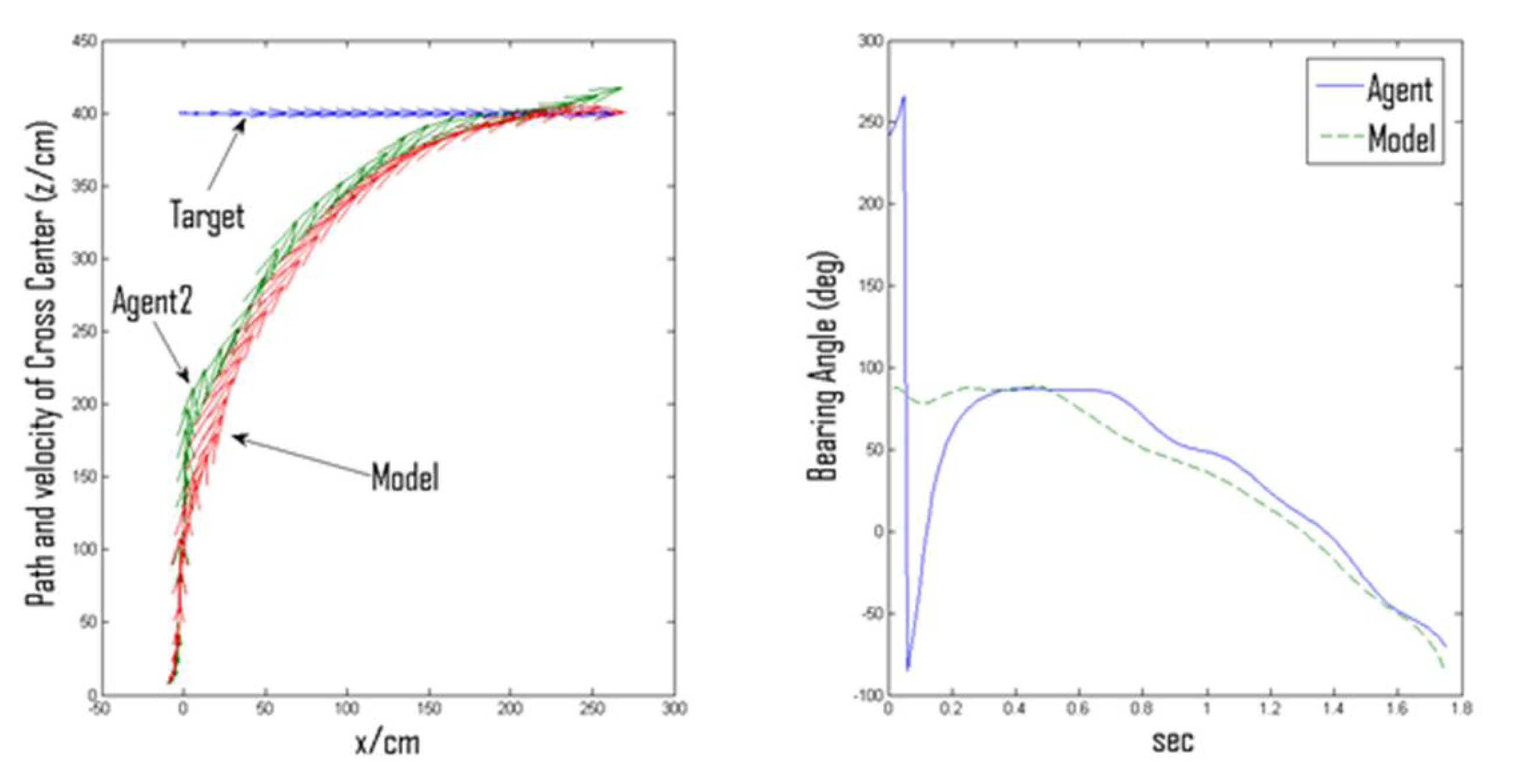
3.3. Kinematical Possibilities of Interception: Virtual vs. Actual Directional Heading
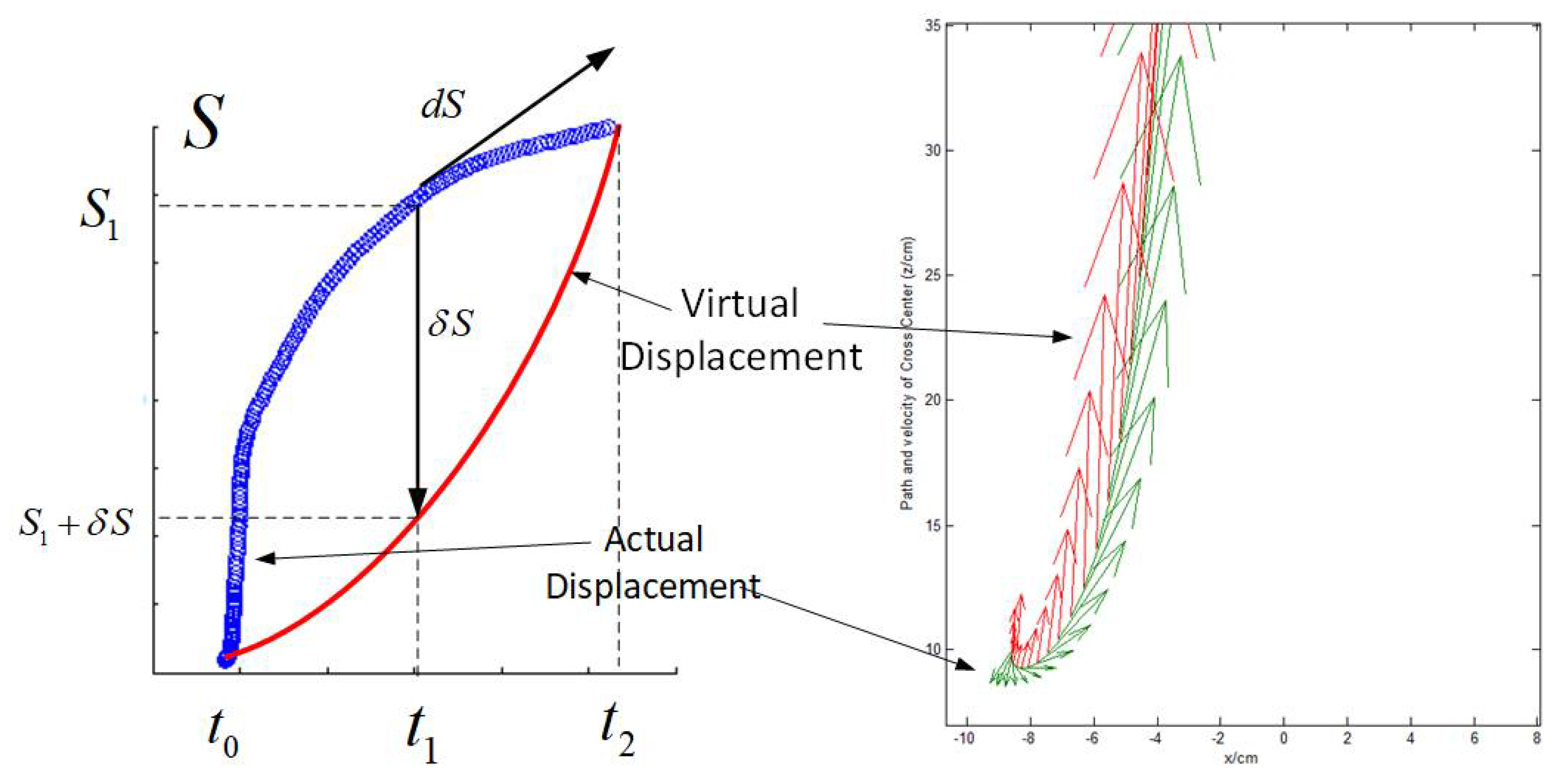
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Reed, E.S., Encountering the World: Toward an Ecological Psychology. 1996: Oxford University Press.
- Gibson, J.J., The ecological approach to visual perception. 1979: Houghton Mifflin.
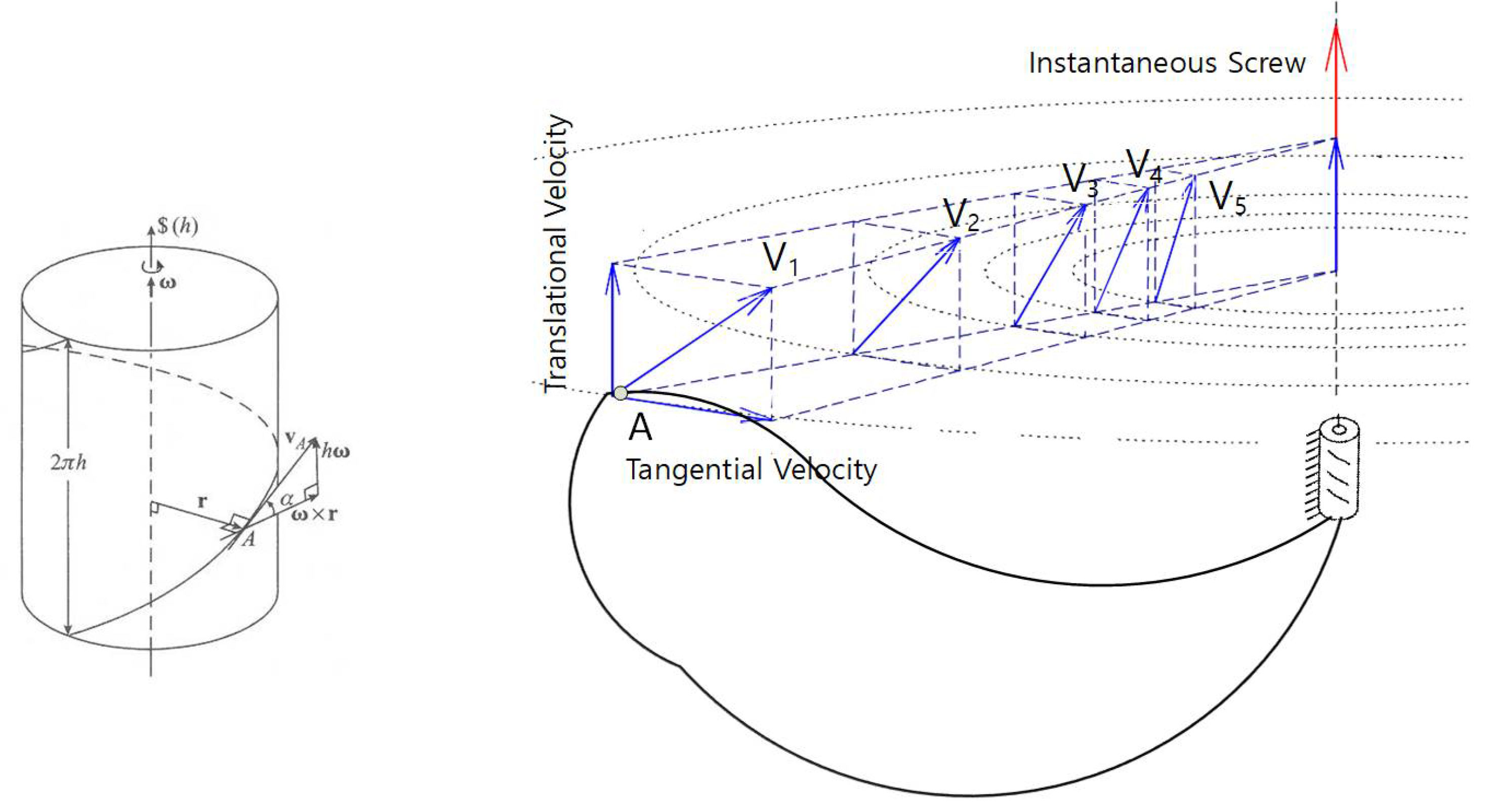
- Ball, R., A treatise on the theory of screws. 1900: Cambridge University Press.
- Ball, R.S., A Treatise on the Theory of Screws. 1998: Cambridge University Press.
- Phillips, J., Freedom in Machinery: Volume 1, Introducing Screw Theory. 1984: Cambridge University Press.
- Jessop, C.M., Treatise on the Line Complex. 1903: American Mathematical Society.
- Gibson, J.J. and L.E. Crooks, A theoretical field-analysis of automobile-driving. The American journal of psychology, 1938. 51(3): p. 453-471. [CrossRef]
- Flach, J.M. and J.G. Holden, The Reality of Experience: Gibson’s Way. Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 1998. 7(1): p. 90-95.
- Warren, W.H., et al., Optic flow is used to control human walking. Nature neuroscience, 2001. 4(2): p. 213-216.
- Gibson, J.J. and E.J. Gibson, Continuous perspective transformations and the perception of rigid motion. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1957. 54(2): p. 129-138. [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, M., et al., Intercepting Moving Objects During Self-Motion. J Mot Behav, 1999. 31(1): p. 55-67. [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, M., et al., Intercepting moving objects during self-motion: effects of environmental changes. Res Q Exerc Sport, 1999. 70(4): p. 349-60. [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.J., F. Phillips, and B.R. Fajen, Intercepting moving targets: a little foresight helps a lot. Exp Brain Res, 2009. 195(3): p. 345-60. [CrossRef]
- Fajen, B.R. and W.H. Warren, Visual guidance of intercepting a moving target on foot. Perception, 2004. 33(6): p. 689-715. [CrossRef]
- Fajen, B.R. and W.H. Warren, Behavioral dynamics of intercepting a moving target. Experimental Brain Research, 2007. 180(2): p. 303-319. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D., K. Davids, and R. Hristovski, The ecological dynamics of decision making in sport. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 2006. 7(6): p. 653-676. [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S., Catching a Baseball. American Journal of Physics, 1968. 36(10): p. 868-870.
- Courant, R., H. Robbins, and I. Stewart, What is mathematics? : an elementary approach to ideas and methods. 2nd ed. 1996, New York: Oxford University Press. 566 p.
- Zhao, H. and W.H. Warren, Intercepting a moving target: On-line or model-based control? Journal of vision, 2017. 17(5): p. 12-12.
- Stepp, N. and M.T. Turvey, On strong anticipation. Cognitive systems research, 2010. 11(2): p. 148-164.
- Wilson, M., Physics Avoidance: and other essays in conceptual strategy. 2017: Oxford University Press.
- Lange, M., The principle of virtual work, counterfactuals, and the avoidance of physics. European Journal for Philosophy of Science, 2019. 9(3): p. 33.
- Gibson, J.J., The perception of the visual world. 1974, Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. xii, 235 p.
- Blake, R., Gibson’s inspired but latent prelude to visual motion perception. Psychol Rev, 1994. 101(2): p. 324-8.
- Warren Jr, W.H., Visually Controlled Locomotion: 40 years Later. Ecological Psychology, 1998. 10(3-4): p. 177-219.
- Turvey, M.T., et al., Ecological laws of perceiving and acting: in reply to Fodor and Pylyshyn (1981). Cognition, 1981. 9(3): p. 237-304.
- Kelso, J.A.S., Dynamic Patterns: The Self-organization of Brain and Behavior. 1995: MIT Press.
- Kim, W., et al., Affordance-Based Surgical Design Methods Considering Biomechanical Artifacts. Ecological Psychology, 2020: p. 1-15.
- Seifert, L., et al., Neurobiological degeneracy: A key property for functional adaptations of perception and action to constraints. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 2016. 69: p. 159-165.
- Thelen, E., Motor development. A new synthesis. Am Psychol, 1995. 50(2): p. 79-95.
- Shaw, R.E. and M. Turvey, Ecological foundations of cognition. II: Degrees of freedom and conserved quantities in animal-environment systems. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 1999. 6(11-12): p. 111-124.
- Shaw, R.E., J.M. Kinsella-Shaw, and W.M. Mace, Affordance types and affordance tokens: Are Gibson’s affordances trustworthy? Ecological Psychology, 2019. 31(1): p. 49-75.
- Henrici, O., The Theory of Screws1. Nature, 1890. 42(1075): p. 127-132.
- Semple, J.G. and G.T. Kneebone, Algebraic Projective Geometry. 1952: Clarendon Press.
- Lanczos, C., The variational principles of mechanics. 2012: Courier Corporation.
- Courant, R. and H. Robbins, What is Mathematics? An elementary approach to ideas and methods. 1941, London, New York etc.: Oxford university press. 3 p. l., v-xix, 521 p.
- Emmer, M., The visual mind II. 2005: MIT press.
- Simpson, W.A. The cross-ratio and the perception of motion and structure. in Proc. of the ACM SIGGRAPH/SIGART interdisciplinary workshop on Motion: representation and perception. 1986.
- Griffis, M. and J.M. Rico, The nut in screw theory. Journal of Robotic Systems, 2003. 20(8): p. 437-476.
- Gibson, J.J. and E.J. Gibson, Continuous perspective transformations and the perception of rigid motion. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1957. 54(2): p. 129.
- Olberg, R.M., A.H. Worthington, and K.R. Venator, Prey pursuit and interception in dragonflies. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 2000. 186(2): p. 155-162.
- Gibson, J.J., The senses considered as perceptual systems. 1966, Boston: Houghton.
- Turvey, M.T., Ecological foundations of cognition: Invariants of perception and action, in Cognition: Conceptual and methodological issues. 1992, American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, US. p. 85-117.
- Gibson, J.J., Visually controlled locomotion and visual orientation in animals. Br J Psychol, 1958. 49(3): p. 182-94.
- Bernstein, N.A., The co-ordination and regulation of movements. 1967: Pergamon Press.
- Rheingold, H., Virtual reality: exploring the brave new technologies. 1991: Simon & Schuster Adult Publishing Group.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




