Submitted:
30 May 2024
Posted:
31 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
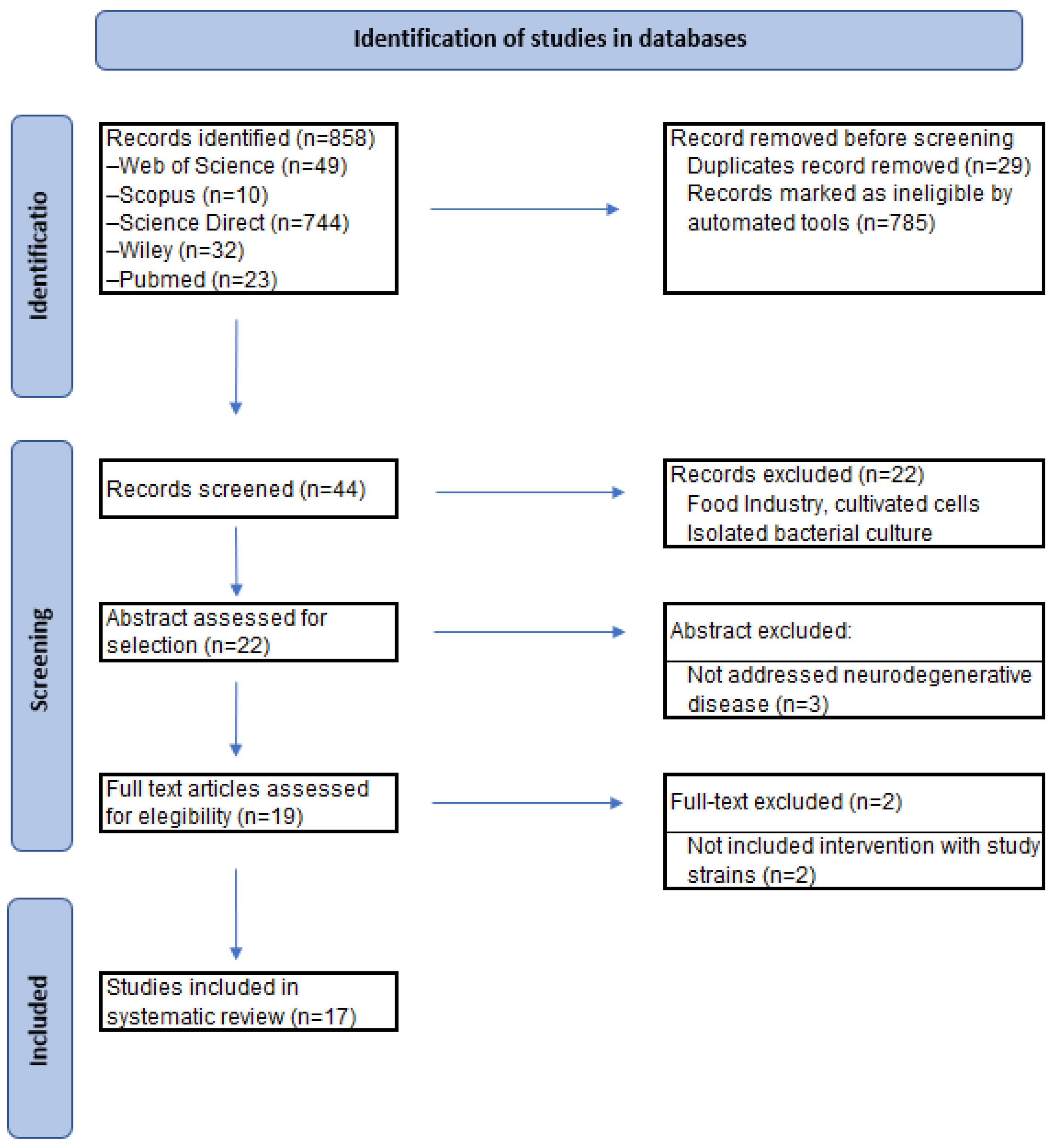
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
- ▪
- Type of study (human or animal model).
- ▪
- Type of probiotic used (Bifidobacterium infantis or Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis or Bifidobacterium breve, alone, in conjunction or in combination).
- ▪
- Neurodegenerative pathology addressed in the research.
- ▪
- Population (description).
- ▪
- Methodology of the research carried out.
- ▪
- Intervention (dose administered, time).
- ▪
- Results obtained after the intervention with Bifidobacterium infantis or Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis or Bifidobacterium breve.
| Probiotics | Population | Methodology | Intervention | Results | References | ||
| Alzheimer’s Disease | |||||||
| HUMAN STUDIES | Mixture probiotic: Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis BLI-02, Bifidobacterium breve Bv-889, and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CP-9 | 40 patients | Probiotic vs Sham | Probiotic (1 × 1010 CFU/capsule for 12 weeks) | BDNF levels in the treatment group increased significantly from a baseline value of 7115.1 ± 4461.9 pg/mL to an endpoint of 9678.5 ± 6652.9 pg/mL, with ** p = 0.005; The fold change of cortisol decrease was significantly larger in treatment group as compared with the active control group (119.4% vs. 94.3%, *p = 0.039) | (63) | 10.3390/nu16010016 |
| MCI (Mild Cognitive Impairment) | |||||||
| Bifidobacterium breve A1 | 117 patients | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve A1 (2 capsules daily > 1×1010 CFU) for 12 weeks | Significant difference between B. breve A1 and placebo groups in subscale ‘immediate memory’ of RBANS and MMSE total score (#p < 0.05 between the treatment and placebo groups at baseline; †p < 0.05 between the treatment and placebo groups at 12-weeks examination); No significant intergroup difference was observed in terms of changes in scores from the baseline scores | (59) | 10.3920/BM2018.0170 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 | 115 patients | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 (A1) (2×1010 CFU) daily for 24 weeks | A significant intergroup difference was observed in the changes from baseline of GM (gray matter atrophy in the whole brain) extent score (p = 0.013) | (60) | 10.3233/JAD-220148 | |
| Lactobacillus plantarum BioF-228, Lactococcus lactis BioF-224, Bifidobacterium lactis CP-9, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Bv-77, Lactobacillus johnsonii MH-68, Lactobacillus paracasei MP137, Lactobacillus salivarius AP-32, Lactobacillus acidophilus TYCA06, Lactococcus lactis LY-66, Bifidobacterium lactis HNO19, Lactobacillus rhamnosus HNO01, Lactobacillus paracasei GL-156, Bifidobacterium animalis BB-115, Lactobacillus casei CS-773, Lactobacillus reuteri TSR332, Lactobacillus fermentum TSF331, Bifidobacterium infantis BLI-02, and Lactobacillus plantarum CN2018 | 42 patients | Probiotic vs Sham | Mixture probiotic (>2*1010 CFU/g) probiotics daily for 12 weeks | Cognitive function and sleep quality were improved. Mini-Mental State Examination-MMSE (24.75 ± 2.47); Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale-MoCA (22,05 ± 2,14 vs 20,10 ± 1,45); Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index-PSQI (5,35 ± 2,78 vs 8,40 ± 1,76, p < 0,001) | (61) | 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.03.006 | |
| Oxidative stress | |||||||
| VSL#3® - Bifidobacterium infantis DSM 24737, Bifidobacterium longum DSM 24736, Bifidobacterium breve DSM 24732, Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM 24735, Lactobacillus delbrückii ssp. bulgaricus DSM 24734, Lactobacillus paracasei DSM 24733, Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 24730, and Streptococcus thermophilus DSM 24731 | 62 patients | Probiotic vs Sham | VSL#3® supplementation (2 capsules daily) for 56 days | Arm B did not significantly affect cholesterol or glucose, however it reduced ESR (p =0.05) and was associated with significant increases in serum folate (p=0.007) and serum vitamin B12 (p=0.001), and a decrease in plasma homocysteine (p < 0.001). Both diet alone and diet plus VSL#3® were associated with an increase in glutathione-S-transferase activity | (62) | 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.09.023 | |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | |||||||
| ANIMAL STUDIES | Bifidobacterium breve A1 | Male 10-week-old ddY mice | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve A1 (1×109 CFU in 0.2 ml, starting 2 days before Aβ injection) daily for 10 days | B. breve A1 prevents Aβ-induced cognitive dysfunction; suppresses Aβ-induced changes in gene expression in the hippocampus; B. breve A1 and acetate partially ameliorate behavioral deficits (p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 vs. control (sham). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. Aβ (+)) | (66) | 10.1038/s41598-017-13368-2 |
| Mixture probiotic: Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Bifidobacterium infantis | 50 male Wistar rats | Probiotic vs Sham | Mixture probiotic 2 g (1010 CFU) daily for 10 weeks | Aβ-treated group had longer time latency in comparison with the control and sham groups in MWM training phase (p < 0.001). Administration of probiotics promoted spatial memory and learning in comparison with Aβ-treated group (p < 0.01). Administration of probiotics mixture demonstrated a significant decrement in MDA level in comparison with Aβ-treated group (p < 0.001) | (67) | 10.29252/ibj.24.4.220 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve-five strains (B. breve NMG, B. breve MY, B. breve CCFM1025, B. breve XY, and B. breve WX) | 63 male C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old) | Individual 5 strains of Bifidobacterium breve | Bifidobacterium breve-5 strains (B. breve NMG, B. breve MY, B. breve CCFM1025, B. breve XY, and B. breve WX) (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily for 6 weeks | B. breve NMG and CCFM1025 administration led to significant improvements in alternation behavior and increases in total arm entries. However, the administration of the other three B. breve strains failed to improve working memory; CCFM1025, XY, and WX to Aβ1-42-treated mice significantly reduced the hippocampal accumulation of Aβ1-42 (Control vs. model: # p < 0.05 by unpaired student’s t-test; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA for all groups) | (68) | 10.3390/nu13051602 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 | 40 C57BL/6J mice (2-month-old) | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) five times/week for four months | Significant decrease in soluble Aβ1-42 levels in the hippocampal extracts of probiotic mice vs to those of mice that received Sham; p-Akt and p-GSK-3β protein levels were significantly increased in the hippocampus of the probiotic group vs Sham group (* p < 0.05); B. breve MCC1274 significantly increased the protein levels of SYT and syntaxin, and showed a tendency to increase the protein levels of SYP and PSD-95 in hippocampal extracts (** p < 0.01) | (69) | 10.3390/nu14122543 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve A1 | 52 App knock-in (KI) mice (AppNL-G-F)-3-month-old | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve A1 (1×109 CFU in 0.2 ml, starting 2 days before Aβ injection) daily for 10 days | Memory impairment: the probiotic group had a significantly increased exploration time for the novel object compared with the familiar object; the discrimination index (DI) was higher in the probiotics group vs Sham group; B. breve MCC1274 supplementation suppresses Aβ fibril formation; significantly upregulated ADAM10 and PS1 in the hippocampus, whereas AβPP and BACE1 levels did not change (p < 0.05) | (70) | 10.3233/JAD-215025 | |
| Vitalon Probiotics (VP) powder: Bacillus natto, Bacillus coagulans, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve | 9–15 mice/group- APP transgenic mouse line J20 & Wild-type (WT) littermate mice (control) | Prebiotic vs Synbiotic | 3.6 g/kg/day prebiotics (WT/P and APP/P)-2.5% inulin; or 4.1 g/kg/day synbiotics (WT/S and APP/S)-Vitalon, intragastrically for 2 months | The level of Aβ1-42 was significantly decreased in APP/S mice compared with APP/C mice; synbiotic treatment significantly reduced TNF-α levels (*p < .05; ***p < .001; ****p < .0001) | (71) | 10.1002/iub.2589 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 | 40 Male adult C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old) | Probiotic + EE vs Protiobic | Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) + daily for 6 weeks vs Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily for 6 weeks | EE + B. breve CCFM1025 showed improved working memory in the Y-maze; accumulation of hippocampal Aβ1-42 was significantly decreased in the EE-treated groups, with the EE + B. breve CCFM1025 (Control vs. Model: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001) | (72) | 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1013664 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 | 24 Male adult C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old) | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 (5 × 109 CFU/mL) vs Veh-sterile 10% skimmed milk | The levels of L-tyrosine and tryptophan in the model group were restored by Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 treatment (p < 0.05); compared with the control mice, 36 metabolites were statistically altered in the hippocampal tissues of the model mice (p < 0.05) vs CCFM1025; CCFM1025 restored the level of the serum metabolite phenylalanine and L-glutamine levels in the hippocampus (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01) | (73) | 10.3390/nu14040735 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 | Male mice (16-week-old) | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily for 12 weeks | Treatment with B. breve HNXY26M4 led to dramatically lower levels of Aβ1−42 than those in APP/PS1 mice; B. breve HNXY26M4 Supplementation Ameliorates Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Damage, and Synaptic Impairment in the Brains of APP/PS1 Mice; the levels of acetate and butyrate were increased in samples from B. breve HNXY26M4-treated mice, and a more substantial increase in acetate relative to butyrate (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001) | (74) | 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00652 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 | 40 Male adult C57BL/6J mice (8 weeks old) | Probiotic+EE vs Protiobic | Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily + EE vs Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily for 6 weeks | Mice that received only EE (ADEE) or EE combined with B. breve treatment (AD+BBEE) had significantly lower concentrations of Aβ1-42 in the hippocampus than ADSE mice (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) | (75) | 10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250084 | |
| Parkinson’s Disease | |||||||
| Bifidobacterium breve A1-MCC1274 | 156 Male C57BL/6 mice (7–8 weeks old) | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 (A1) (1 × 109 CFU/mL) daily for 4 days | B. breve A1 prevented the reduction of spine density in PD mice and maintained it at the same level as that in control mice (* p < 0.01 vs. Control + Saline and † p < 0.05: between MPTP + Saline and MPTP + B. breve A1); B. breve A1 did not show any significant effects on hippocampal cAMP levels in PD and control mice (* p < 0.01 vs. Control + Saline) | (64) | 10.3390/biomedicines9020167 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1067 | 40 Male C57BL/6 mice (6 weeks old) | Probiotic vs Sham | Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1067 (109 CFU/200 μL saline) daily on days 8-41 | B. breve CCFM1067 improves MPTP-induced motor impairments: Both L-DOPA and B. breve CCFM1067 therapies substantially reduced MPTP-induced motor impairments in the PT (F (2,21) = 56.94, p < 0.0001), NBT (F (2,21) = 33.72, p < 0.0001), and RTR (F (2,18) = 21.99, p < 0.0001); B. breve CCFM1067 reduced the increase in striatal TNF-α (F (2,9) = 91.49, p < 0.0001), IL-1β (F (2,9) = 29.53, p < 0.0001), and IL-6 (F (2,9) = 24.61, p = 0.0002) | (65) | 10.3390/nu14214678 | |
3. Results
3.1. Human Studies
3.1.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.1.2. Mild Cognitive Impairment
3.1.3. Oxidative Stress
3.2. Animal Studies
3.2.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.2.2. Parkinson’s Disease
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Research
6. Practical Applications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9(7), a028035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Chang, H.Y.; Sang, T.K. Neuronal cell death mechanisms in major neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19(10), 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litke, R.; Garcharna, L.C.; Jiwani, S.; Neugroschl, J. Modifiable risk factors in Alzheimer disease and related dementias: a review. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43(6), 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Neurodegenerative diseases: from molecular basis to therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 21–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, J.M. The evolution of free radicals and oxidative stress. Am. J. Med. 2000, 108(8), 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative stress: a key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24(8), 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39(1), 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, Y.; Yarjanli, Z.; Pakniya, F.; Bidram, E.; Łos, M.J.; Eshraghi, M.; Klionsky, D.J.; Ghavami, S.; Zarrabi, A. Targeting autophagy, oxidative stress, and ER stress for neurodegenerative disease treatment. J. Control Release 2022, 345, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An overview of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(11), 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Bancher, C.; Eckert, A.; Förstl, H.; Frölich, L.; Hort, J.; Korczyn, A.D.; Kressig, R.W.; Levin, O.; Palomo, M.S.M. Management of mild cognitive impairment (MCI): the need for national and international guidelines. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21(8), 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, C.; Barone, P.; Trojano, L.; Santangelo, G. Prevalence and clinical aspects of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35(1), 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongsiriyanyong, S.; Limpawattana, P. Mild cognitive impairment in clinical practice: a review article. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 2018, 33(8), 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, J.; Swirski, M.; Clynes, J.; Harding, S.; Leng, Y.; Coulthard, E. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to enhance sleep in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J Sleep Res. 2021, 30(4), e13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Discov. Med. 2023, 35(178), 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive review on Alzheimer’s disease: causes and treatment. Molecules 2020, 25(24), 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Brion, J.P.; Stygelbout, V.; Suain, V.; Authelet, M.; Dedecker, R.; Chanut, A.; Lacor, P.; Lavaur, J.; Sazdovitch, V.; et al. Clathrin adaptor CALM/PICALM is associated with neurofibrillary tangles and is cleaved in Alzheimer’s brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125(6), 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.J. Astrocyte regulation of synaptic behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Strooper, B.; Karran, E. The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 2016, 164(4), 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulshof, L.A.; van Nuijs, D.; Hol, E.M.; Middeldorp, J. The role of astrocytes in synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 899251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, J.; Savage, J.C.; Tremblay, M.È. Synaptic loss in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanistic insights provided by two-photon in vivo imaging of transgenic mouse models. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 592607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, J.; Grant, S.G. Synapse pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 139, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet 2016, 388(10043), 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meoni, S.; Cury, R.G.; Moro, E. New players in basal ganglia dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2020, 252, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.F.; Cardoso, T.; Nolbrant, S.; Mattsson, B.; Hoban, D.B.; Jarl, U.; Wahlestedt, J.N.; Grealish, S.; Björklund, A.; Parmar, M. hESC-derived dopaminergic transplants integrate into basal ganglia circuitry in a preclinical model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep. 2019, 28(13), 3462–3473.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, H.N.; Esteves, A.R.; Empadinhas, N.; Cardoso, S.M. Parkinson’s disease: a multisystem disorder. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39(1), 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacabelos, R. Parkinson’s disease: from pathogenesis to pharmacogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18(3), 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisman, G.; Braun-Benjamin, O.; Melillo, R. Cognitive-motor interactions of the basal ganglia in development. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Pandya, D.N. Disconnection syndromes of basal ganglia, thalamus, and cerebrocerebellar systems. Cortex 2008, 44, 1037–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Microbiota-brain-gut axis and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17(12), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 2016, 167(6), 1469–1480.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. The gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58(1), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uceda, S.; Echeverry-Alzate, V.; Reiriz-Rojas, M.; Martínez-Miguel, E.; Pérez-Curiel, A.; Gómez-Senent, S.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I. Gut microbial metabolome and dysbiosis in neurodegenerative diseases: psychobiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation as a therapeutic approach—A comprehensive narrative review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(17), 13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Januszewski, S.; Czuczwar, S.J. Gut microbiota and pro/prebiotics in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging 2020, 12(6), 5539–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, S.D.; Zhang, Y.R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yu, J.T. Investigating casual associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and neurodegenerative diseases: a mendelian randomization study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 87(1), 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Maqbool, J.; Sajid, F.; Hussain, G.; Sun, T. Human gut microbiota and its association with pathogenesis and treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Reynolds, R.; Tan, E.K.; Pettersson, S. The role of gut dysbiosis in Parkinson’s disease: mechanistic insights and therapeutic options. Brain 2021, 144(9), 2571–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.L. Gut microbiota and dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for pathogenesis and treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57(12), 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, E.; Tsuji, H.; Asahara, T.; Takahashi, T.; Teraishi, T.; Yoshida, S.; Koga, N.; Hattori, K.; Ota, M.; Kunugi, H. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus counts in the gut microbiota of patients with bipolar disorder and healthy controls. Front. Psychiatry. 2019, 9, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.; do Carmo, M.; Melo, B.; Alves, M.; dos Santos, C.; Monteiro, S.; Bomfim, M.R.Q.; Fernandes, E.S.; Monteiro-Neto, V. In vitro antimicrobial activity and probiotic potential of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus against species of Clostridium. Nutrients 2019, 11(2), 448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, G.; Dargahi, L.; Peymani, A.; Mirzanejad, Y.; Alizadeh, S.A.; Naserpour, T.; Nassiri-Asl, M. The effects of probiotic formulation pretreatment (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) on a lipopolysaccharide rat model. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38(3), 209–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, G.; Dargahi, L.; Naserpour, T.; Mirzanejad, Y.; Alizadeh, S.A.; Peymani, A.; Nassiri-Asl, M. Probiotic mixture of Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175 attenuates hippocampal apoptosis induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Int. Microbiol. 2019, 22(3), 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. The potential of proteins, hydrolysates and peptides as growth factors for Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium: current research and future perspectives. Food Funct. 2020, 11(3), 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Rong, N.; Yang, Y.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y.; Siwu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Z. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus improve inflammatory bowel disease in zebrafish of different ages by regulating the intestinal mucosal barrier and microbiota. Life Sci. 2023, 324, 121699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batta, V.K.; Rao, S.C.; Patole, S.K. Bifidobacterium infantis as a probiotic in preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94(6), 1887–1905. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dylag, K.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Surmiak, M.; Szmyd, J.; Brzozowski, T. Probiotics in the mechanism of protection against gut inflammation and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzi Cionci, N.; Baffoni, L.; Gaggìa, F.; Di Gioia, D. Therapeutic microbiology: the role of Bifidobacterium breve as food supplement for the prevention/treatment of paediatric diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10(11), 1723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bao, X.Q.; Shang, M.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, D. Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome 2021, 9(1), 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Ling, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, T.; Yang, C.; Ye, S.; Ye, K.; Wei, D.; Song, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, J. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9(1), 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrik, K.E.W.; Ooijevaar, R.E.; de Jong, P.R.C.; Laman, J.D.; van Oosten, B.W.; van Hilten, J.J.; Ducarmon, Q.R.; Keller, J.J.; Kuijper, E.J.; Contarino, M.F. Fecal microbiota transplantation in neurological disorders. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Dhalaria, R.; Guleria, S.; Cimler, R.; Sharma, R.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Valko, M.; Nepovimova, E.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Singh, R.; et al. Anti-oxidant potential of plants and probiotic spp. in alleviating oxidative stress induced by H2O2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morella, I.; Negro, M.; Dossena, M.; Brambilla, R.; D’Antona, G. Gut-muscle-brain axis: molecular mechanisms in neurodegenerative disorders and potential therapeutic efficacy of probiotic supplementation coupled with exercise. Neuropharmacology 2023, 240, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.F.; Cheng, Y.F.; You, S.T.; Kuo, W.C.; Huang, C.W.; Chiou, J.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Hsieh-Li, H.M.; Wang, S.; Tsai, Y.C. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 alleviates neurodegenerative progression in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallikarjuna, N.; Praveen, K.; Yellamma, K. Role of Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC1325 in membrane-bound transport ATPases system in Alzheimer’s disease-induced rat brain. BioImpacts 2016, 6(4), 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Gogoi, O.; Berardi, S.; Scarpona, S.; Angeletti, M.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. Gut microbiota manipulation through probiotics oral administration restores glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 87, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4(1), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Reiriz, M.; Uceda, S.; Echeverry-Alzate, V. Lactiplantibacillus (Lactobacillus) plantarum as a complementary treatment to improve symptomatology in neurodegenerative disease: a systematic review of open access literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(5), 3010. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kuhara, T.; Oki, M.; Xiao, J.Z. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve A1 on the cognitive function of older adults with memory complaints: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10(5), 511–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asaoka, D.; Xiao, J.; Takeda, T.; Yanagisawa, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Endo, N.; Higa, M.; Kasanuki, K.; et al. Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in improving cognitive function and preventing brain atrophy in older patients with suspected mild cognitive impairment: Results of a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 88(1), 75–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Li, R.; Lin, L.; Li, M. Probiotic intervention benefits multiple neural behaviors in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 51, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, L.; Pinto, A.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Ostan, R.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S.; Hrelia, S.; Hrelia, P.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, et al. Impact of personalized diet and probiotic supplementation on inflammation, nutritional parameters and intestinal microbiota – The “RISTOMED project”: Randomized controlled trial in healthy older people. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34(4), 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Tsai, S.Y.; Kuo, Y.W.; Lin, J.H.; Ho, H.H.; Chen, J.F.; Hsia, K.C.; Sun, Y. Efficacy of probiotic supplements on brain-derived neurotrophic factor, inflammatory biomarkers, oxidative stress and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer’s dementia: a 12-week randomized, double-blind active-controlled study. Nutrients 2023, 16(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Furuoka, H.; Kaya, M.; Kuhara, T. Oral administration of probiotic Bifidobacterium breve improves facilitation of hippocampal memory extinction via restoration of aberrant higher induction of neuropsin in an MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9(2), 167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chu, C.; Yu, L.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Tian, F. Neuroprotective effects of Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1067 in MPTP-induced mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Nutrients 2022, 14(21), 4678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Sugahara, H.; Shimada, K.; Mitsuyama, E.; Kuhara, T.; Yasuoka, A.; Kondo, T.; Abe, K.; Xiao, J.Z. Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7(1), 13510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehrabadi, S.; Sadr, S.S. Assessment of probiotics mixture on memory function, inflammation markers, and oxidative stress in an Alzheimer’s disease model of rats. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 24(4), 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. Administration of Bifidobacterium breve improves the brain function of Aβ1-42-treated mice via the modulation of the gut microbiome. Nutrients 2021, 13(5), 1602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Zhou, C.; Jung, C.G.; Michikawa, M. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 mitigates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in wild-type mice. Nutrients 2022, 14(12), 2543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Zhou, C.; Ohno, K.; Kuhara, T.; Taslima, F.; Abdullah, M.; Jung, C.G.; Michikawa, M. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve prevents memory impairment through the reduction of both amyloid-β production and microglia activation in APP knock-in mouse. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85(4), 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.; Cheng, I.H. The beneficial effect of synbiotics consumption on Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via reducing local and systemic inflammation. IUBMB Life 2022, 74(8), 748–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium breve intervention combined with environmental enrichment alleviates cognitive impairment by regulating the gut microbiota and microbial metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Integrative metabolomic characterization reveals the mediating effect of Bifidobacterium breve on amino acid metabolism in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 2022, 14(4), 735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 attenuates cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation by regulating the gut–brain axis in APP/PS1 mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71(11), 4646–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Environmental enrichment in combination with Bifidobacterium breve HNXY26M4 intervention amplifies neuroprotective benefits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by modulating glutamine metabolism of the gut microbiome. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13(2), 982–92. [Google Scholar]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.K. The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Zhu, X.; Si, J. Angelica polysaccharide ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease rat through activating BDNF/TrkB/CREB pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245(1), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pláteník, J.; Fišar, Z.; Buchal, R.; Jirák, R.; Kitzlerová, E.; Zvěřová, M.; Raboch, J. GSK3β, CREB, and BDNF in peripheral blood of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 50, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimgampalle, M. Anti-Alzheimer properties of probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 1325 in Alzheimer’s disease induced albino rats. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11(8), KC01–KC05. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, C. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30(2), 271–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Cha, L.; Sim, M.; Jung, S.; Chun, W.Y.; Baik, H.W.; Shin, D.M. Probiotic supplementation improves cognitive function and mood with changes in gut microbiota in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76(1), 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheimer, H.; Birkmayer, W.; Hornykiewicz, O.; Jellinger, K.; Seitelberger, F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J. Neurol. Sci. 1973, 20(4), 415–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, P.; Knight, W.; Guo, Y.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Morris, J.C.; Xu, J. The interactions of dopamine and oxidative damage in the striatum of patients with neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152(2), 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Fang, J.; Ding, H.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; et al. CircSV2b participates in oxidative stress regulation through miR-5107-5p-Foxk1-Akt1 axis in Parkinson’s disease. Redox Biol. 2022, 56, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Burke, R.E. The WldS mutation delays anterograde, but not retrograde, axonal degeneration of the dopaminergic nigro-striatal pathway in vivo. J. Neurochem. 2010, 113(3), 683–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hornykiewicz, O. Dopamine miracle: from brain homogenate to dopamine replacement. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troshev, D.; Berezhnoy, D.; Kulikova, O.; Abaimov, D.; Muzychuk, O.; Nalobin, D.; Stvolinsky, S.; Fedorova, T. The dynamics of nigrostriatal system damage and neurobehavioral changes in the rotenone rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 173, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghyselinck, J.; Verstrepen, L.; Moens, F.; Van Den Abbeele, P.; Bruggeman, A.; Said, J.; Smith, B.; Barker, L.A.; Jordan, C.; Leta, V.; et al. Influence of probiotic bacteria on gut microbiota composition and gut wall function in an in-vitro model in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeiasl, Z.; Salami, M.; Sepehri, G. The effects of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains on memory and learning behavior, long-term potentiation (LTP), and some biochemical parameters in β-amyloid-induced rat’s model of Alzheimer’s disease. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24(3), 265–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.J.; Chen, J.L.; Liao, J.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Chieu, M.W.; Ke, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Hsieh-Li, H.M. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 prevents cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease mice by modulating propionic acid levels, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta activity, and gliosis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.W.; Tsai, Y.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, M.F.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, W.H.; Fang, T.J. Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 promotes longevity, memory retention, and reduces brain oxidation stress in SAMP8 mice. Nutrients 2021, 13(8), 2860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaydi, A.I.; Lew, L.C.; Hor, Y.Y.; Jaafar, M.H.; Chuah, L.O.; Yap, K.P.; Azlan, A.; Azzam, G.; Liong, M.T. Lactobacillus plantarum DR7 improved brain health in aging rats via the serotonin, inflammatory and apoptosis pathways. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11(8), 753–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Katsumata, N.; Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Odamaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, K.; Kaneko, T. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in improving cognitive functions of older adults with suspected mild cognitive impairment: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77(1), 139–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yu, D.; Xue, L.; Li, H.; Du, J. Probiotics modulate the microbiota–gut–brain axis and improve memory deficits in aged SAMP8 mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10(3), 475–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill-Bates, D.A. The antioxidant glutathione. Vitam. Horm. 2023, 121, 109–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domingues, I.; Gravato, C. Oxidative stress assessment in zebrafish larvae. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1797, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hellou, J.; Ross, N.W.; Moon, T.W. Glutathione, glutathione s-transferase, and glutathione conjugates, complementary markers of oxidative stress in aquatic biota. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19(6), 2007–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Kuo, Y.W.; Chiang, P.F.R.; Ho, H.H. Probiotics and their metabolites reduce oxidative stress in middle-aged mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79(4), 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ton, A.M.M.; Campagnaro, B.P.; Alves, G.A.; Aires, R.; Côco, L.Z.; Arpini, C.M.; Oliveira, T.G.E.; Campos-Toimil, M.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Oxidative stress and dementia in Alzheimer’s patients: effects of synbiotic supplementation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





