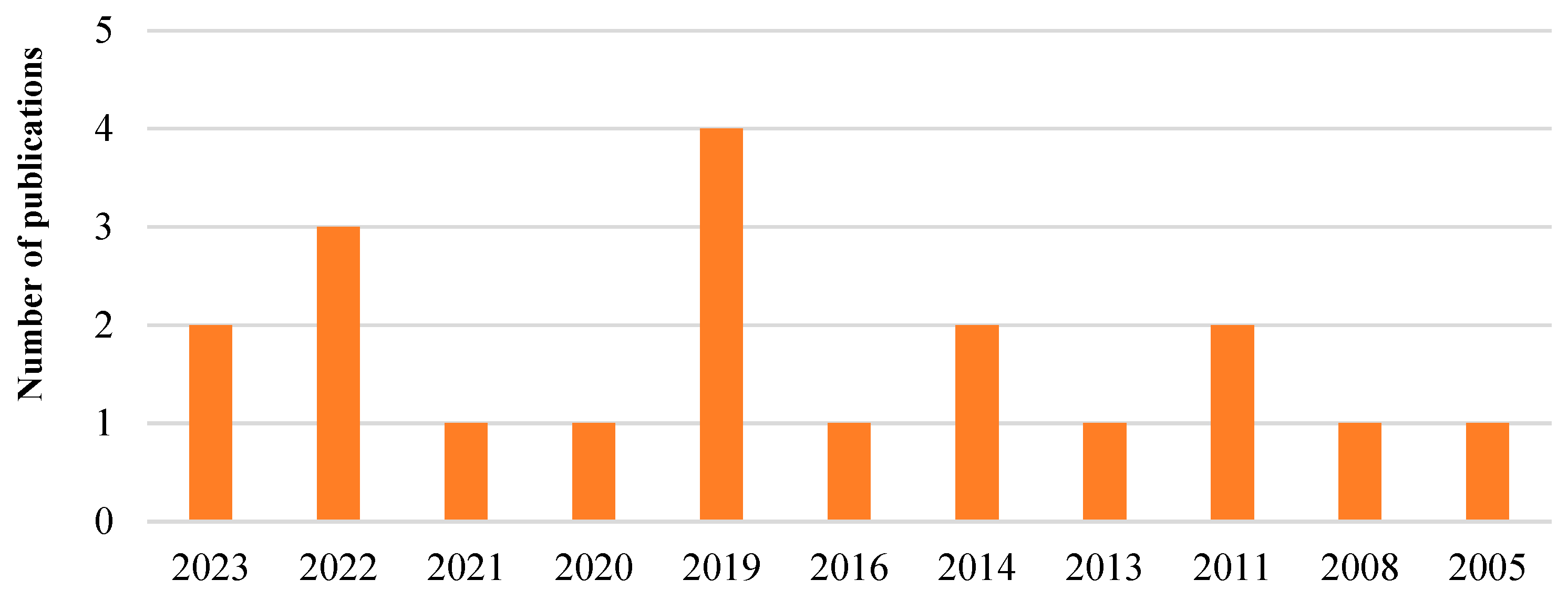1. Introduction
Global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, especially in the energy and transportation sectors, have been steadily increasing. Since 1990, global emissions have grown by 41%, with the energy sector responsible for 73% of these emissions. Among them, the transportation sector alone contributes 15% of total emissions, primarily due to fossil fuel consumption in internal combustion engines [
1,
2,
3].
In this context, Brazil predominantly relies on a fleet powered by internal combustion engines, underscoring the importance of seeking alternatives and adopting technologies to promote sustainability in the transportation sector aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of Agenda 2030 and the commitments of the Paris Agreement for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Moreover, Brazil has committed to reducing CO2 emissions by 37% by 2025, with a target of 43% reduction by 2030 [
1,
2,
3].
In light of these challenges, the development and implementation of advanced techniques using non-invasive sensors are crucial for the widespread adoption of prediction and fault identification systems in internal combustion engines. These technologies aim not only to maximize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs but also play a crucial role in reducing GHG emissions. Effective data management and efficiency improvements enable enhanced operational and maintenance efficiency, prolonging equipment lifespan and mitigating pollutant emissions through optimized real-time operations. This approach not only aligns with global climate mitigation commitments but also drives the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Against this backdrop, this article presents a systematic review aimed at providing a comprehensive mapping of the state-of-the-art in non-invasive techniques and the quest for open-access datasets for prediction and fault diagnosis in internal combustion engines. Motivated by mapping the state-of-the-art in non-invasive techniques in internal combustion engines using the Proknow-C and Methodi Ordinatio methods to efficiently systematize and categorize relevant scientific literature, the study enables rigorous and structured literature selection based on relevance and credibility of databases, resulting in a structured bibliographic portfolio that provides a solid foundation for analysis of these techniques [
4,
5,
6,
7].
Furthermore, the analyses contained in the systematic review contribute not only to identifying gaps and opportunities for future developments but also to driving advancements towards the creation of digital twins for internal combustion engines, promoting energy digitalization. The paper’s contributions are summarized as follows:
Systematic Review Applying Proknow-C and Methodi Ordinatio Methods: An innovative approach to fault research in internal combustion engines demonstrating the effectiveness of combining these methods to efficiently systematize and categorize relevant scientific literature, resulting in a structured bibliographic portfolio that offers a solid foundation for significant insights and future research and development in the field.
Mapping of Non-Invasive Techniques: The study identifies and analyzes non-invasive methods for detecting faults in internal combustion engines, emphasizing their importance in minimizing interference in monitored systems and ensuring engine integrity.
Mapping and Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Digital Signal Processors (DSP): Analysis of AI algorithms used for fault diagnosis, demonstrating the flexibility and effectiveness of combining various acquisition systems (such as sound, vibration, temperature, and current) with advanced AI and DSP techniques for comprehensive and efficient fault diagnostics.
Finally, the article is structured into four sections addressing different aspects discussed.
Section 1 provides a brief introduction to the importance of non-invasive techniques for prediction and fault diagnosis in internal combustion engines and their contribution to energy sustainability.
Section 2 details a systematic review using the Proknow-C and Methodi Ordinatio methods, enabling rigorous and structured literature selection, mapping the state-of-the-art in studies, experiments, and availability of open datasets for the applicability of these techniques.
Section 3 discusses the key findings and advancements resulting from the systematic review, emphasizing the significant contributions of non-invasive techniques to fault diagnosis and detection in internal combustion engines. Finally,
Section 4 offers concluding remarks and suggestions for future research, exploring potential developments based on artificial intelligence and the creation of digital twins for internal combustion engines in different scenarios, identifying gaps and opportunities for future research.
2. Systematic Review
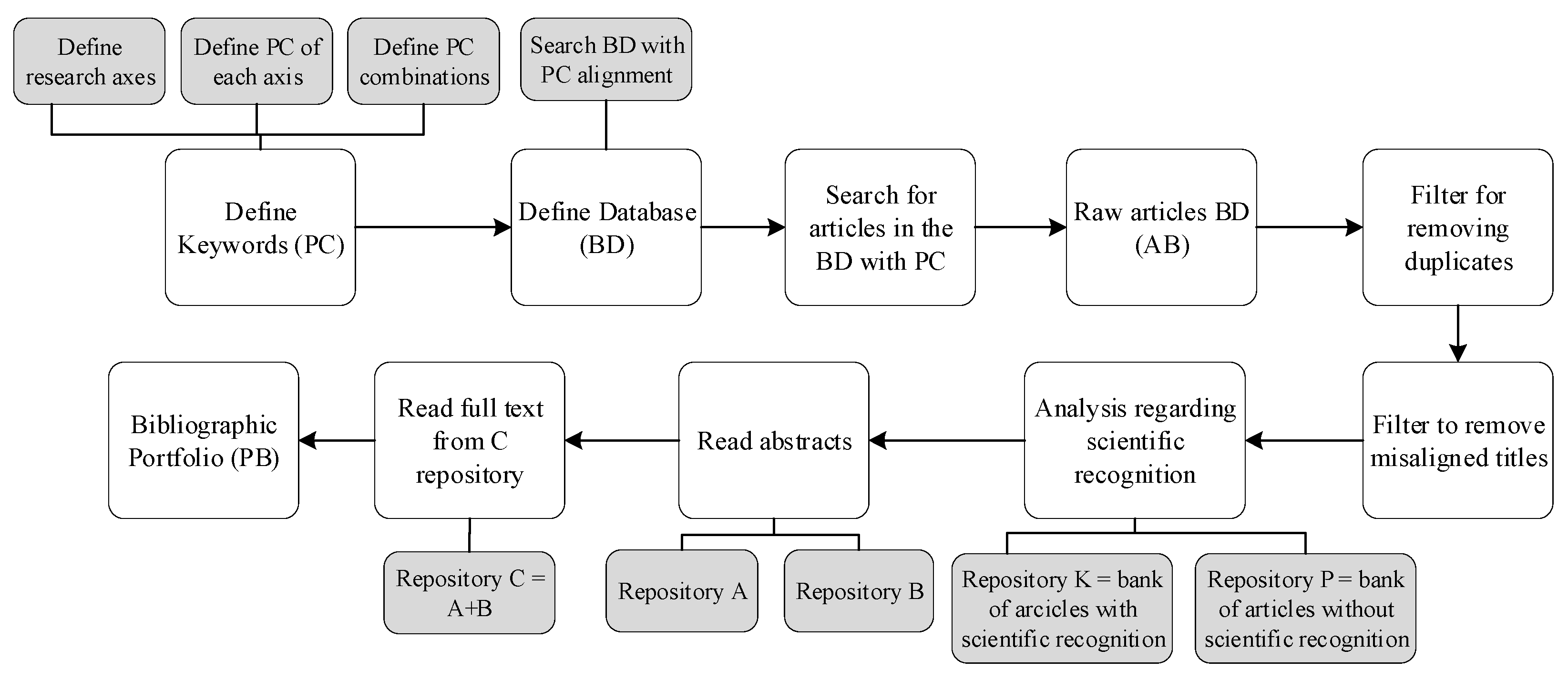
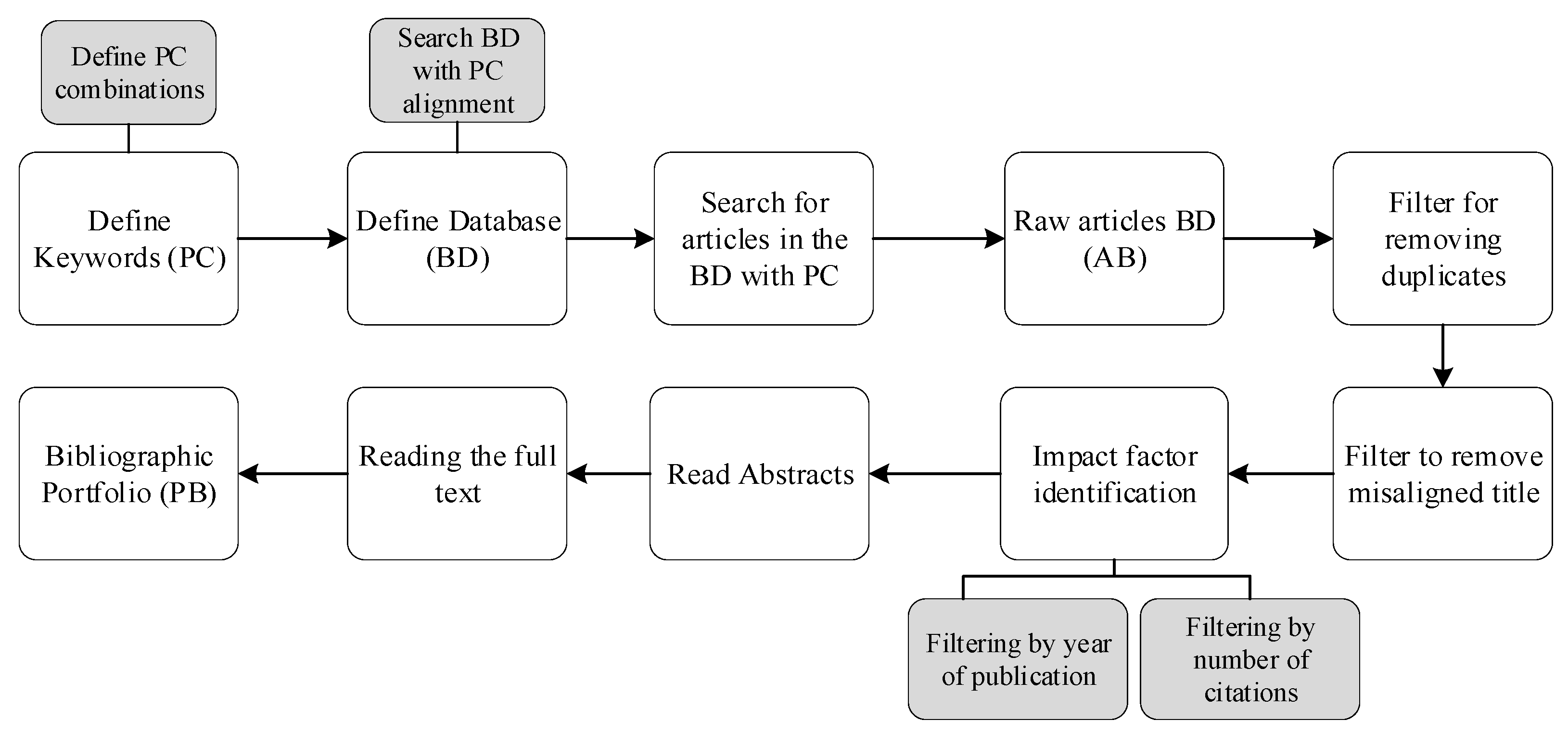
This section describes the process used to search, analyze, and select the set of relevant scientific research on the topic, which are used as the theoretical basis, called the Bibliographic Portfolio (BP). The literature review was conducted on the research topic “Telemetry platform for coastal waterway transport,” applying the Proknow-C [
6] and Ordinatio [
7] methods to obtain a well-structured BP without gaps in the searches, allowing for a more rigorous selection of relevant literature, thereby increasing the quality and credibility of the results. Both methods allow for the systematic bibliographic research and structured and efficient identification of a BP with the most relevant scientific articles on the research topic. The
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 show the process of each approach, respectively [
6,
7].
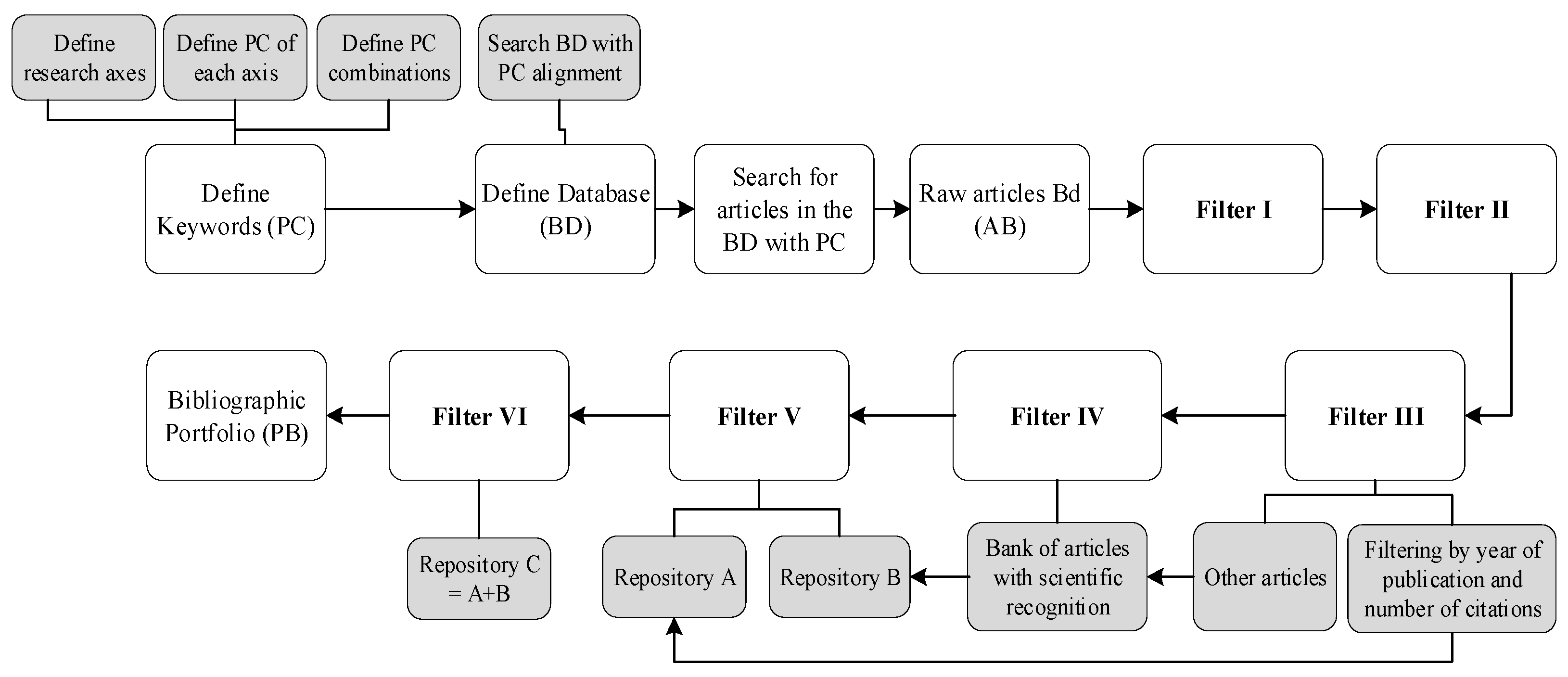
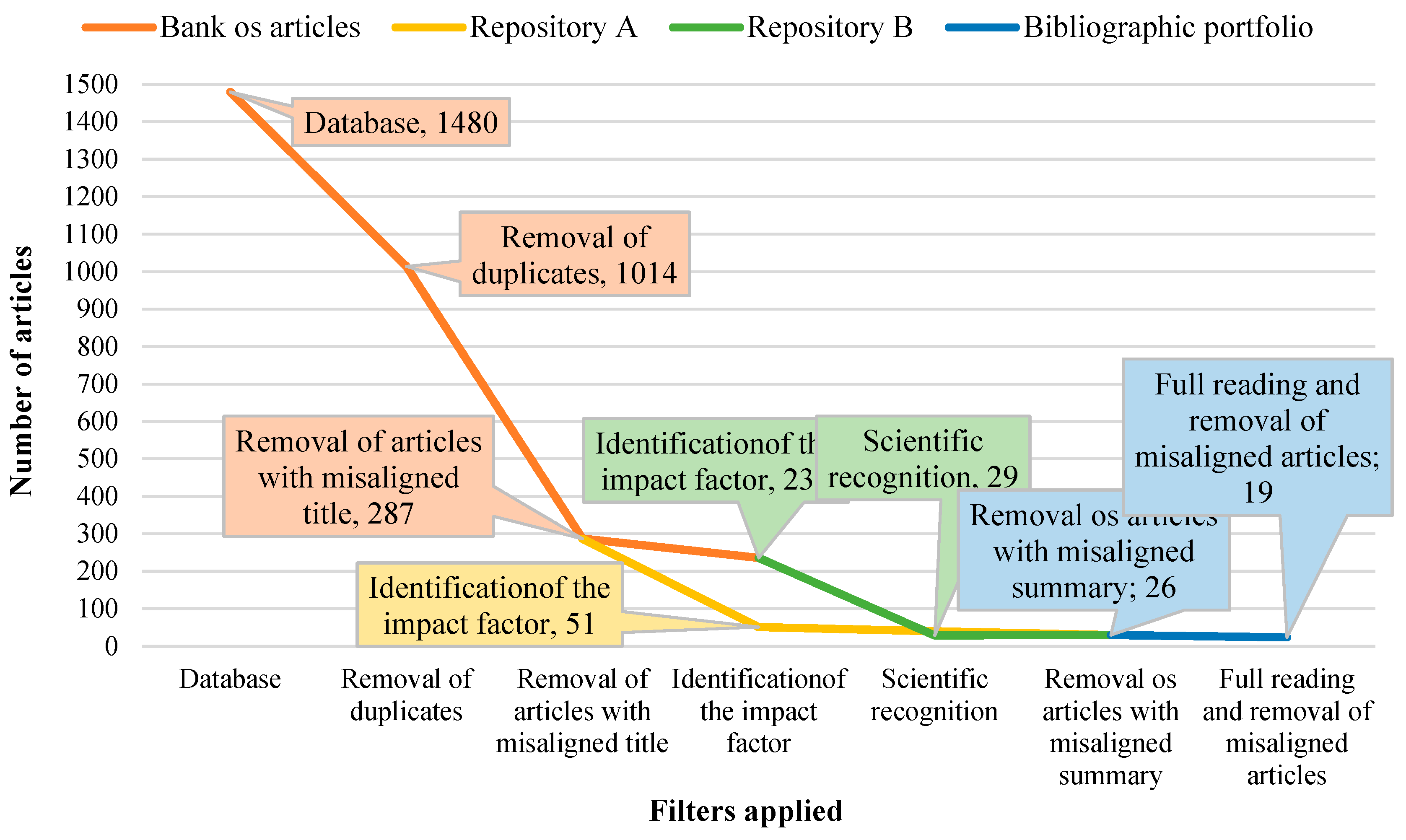
Figure 3 shows the process carried out to classify the order of filtering the databases from the raw articles to obtain the BP:
(i) Removal of duplicates; (ii) Removal of articles with titles misaligned with the project; (iii) Identification of impact factor, originating repository A;
(iv) Scientific recognition, originating repository B;
(v) Removal of articles with abstracts misaligned with the project, originating repository C;
(vi) Full reading and removal of articles misaligned with the theme, originating the BP.
Through the proposed method, the keywords (KW) were defined from the research axes described below. Knowing that the state of the art should include techniques for fault detection to address points 1, 2, and 4 (Application of a new technique to identify faults in combustion engines with high sensitivity to initial conditions and low computational effort; Development of an algorithm for identifying ignition and combustion faults in combustion engines; Diagnosis of ignition, combustion, and engine faults), considering non-invasive methods, the three research axes were defined: a) Non-invasive methods; b) Fault detection; c) Internal combustion engines.
After defining the KWs for each axis, combinations were elaborated based on the logical expressions “Axis 1 and Axis 3,” “Axis 2 and Axis 3,” and “Axis 1 and Axis 2 and Axis 3,” searched on 25/05/2024. Only articles in English published in qualified journals and up to 20 years old were considered. Theses, dissertations, and conference papers were disregarded to ensure a high level of quality, validity, and reliability.
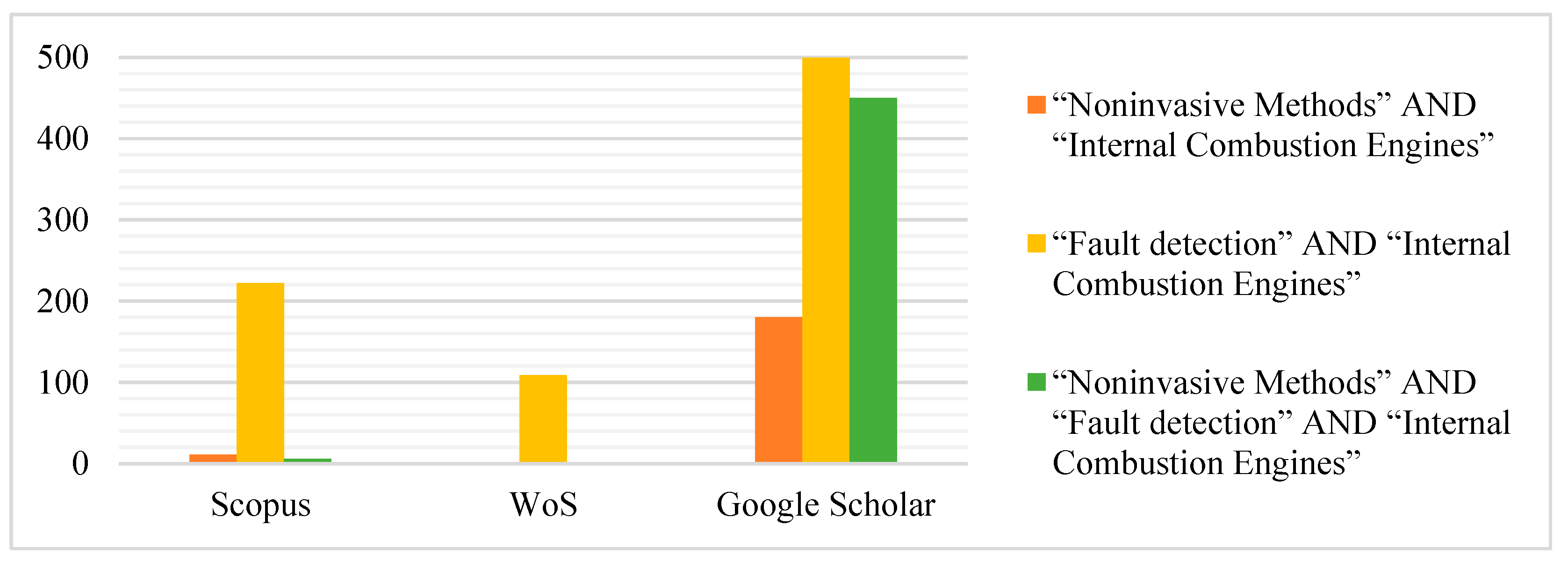
Next, a search was conducted in three academic article databases using the Publish or Perish
® software: SCOPUS, Web of Science (WoS), and Google Scholar. The search results are described in
Table 1 and
Figure 4.
The search results were exported to Mendeley® software, a reference manager, containing a raw article base of 1480. Applying the first and second filters of the methodology used, 287 articles with titles aligned with the project theme and without duplicates were obtained. Analyzing the remaining articles for impact factor, filtering by date and most cited, 51 articles were added to repository A. For the remaining articles, the analysis was based on scientific recognition, resulting in 29 articles, added to repository B. After reading the abstracts of the articles in repositories A and B, 30 articles proved relevant and were added to repository C.
To conduct the full reading of the articles in repository C, articles not freely available were excluded, along with articles analyzed and found irrelevant to the theme. Thus, the BP is composed of 19 articles.
Table 2 presents the BP, ordered by the number of citations and
Figure 5 graphically shows the entire process.
3. Results and Discussions
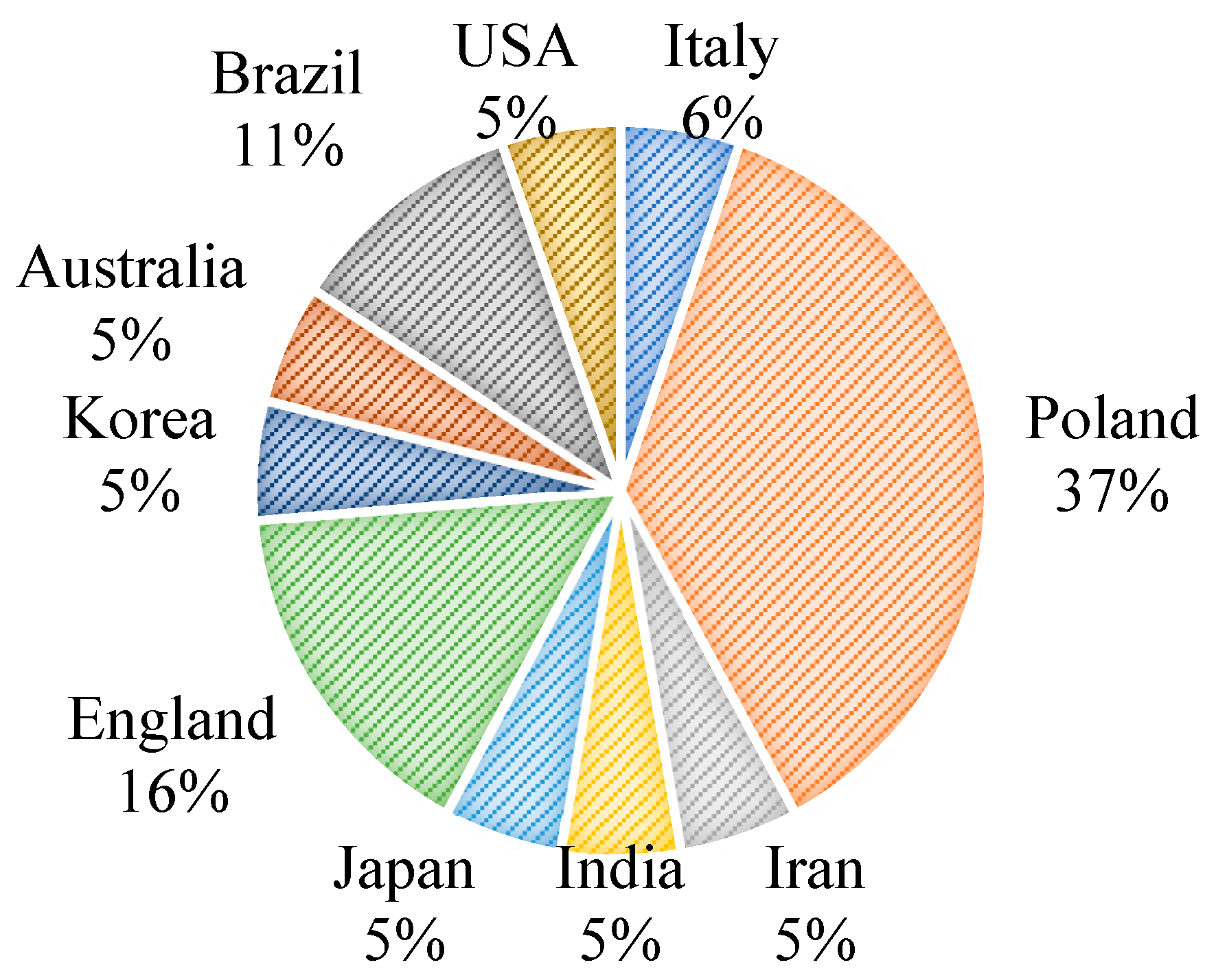
Analyzing the articles in the bibliographic portfolio (PB), it is observed that the majority of important articles (11 articles) are from the last 5 years, with 2019 having the highest number of relevant publications (4 articles) for this research. Additionally, Poland is the country with the most publications, as shown in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7, respectively.
In [
8,
9,
24], the means of signal acquisition are sound and vibration, used to identify mechanical damage in internal combustion engines (ICEs), differing in the methods adopted for signal processing.
In the first study [
8], vibration measurements were carried out by PCB piezotronics accelerometers placed at four points on the engine head surface, and the received signals were processed using Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). Acoustic signals were captured using a spectrum analyzer, random incidence microphone, condenser preamplifier, and a calibrator, processed by Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The collected signals can be used to detect phenomena in the combustion chamber, indicating ignition failures.
The study [
9] utilizes Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and Probabilistic Neural Networks (PNN); tests were performed using a multichannel recording device where vibratory signals were recorded at a frequency of 50kHz, measured by vibration acceleration transducers. The recorded signals were pre-processed using DWT, allowing the extraction of the correct signal from random noise and enabling the development of a real-time operating system. Various DWT types were tested, and the Meyer Wavelet proved most advantageous. The PNN consists of three layers (input, hidden, and output), with experiments dividing the data into 50% training and 50% testing groups. Depending on the data pattern, the network can have 2 to 11 inputs, with 100 neurons in the hidden layer, resulting in 4 outputs. Consequently, neural classifiers were developed that function perfectly or nearly perfectly, distinguishing mechanical damage in engines.
The third study [
24] presents a more current procedure focused on marine ICEs, proposing a system for reliability identification from sound and vibration signals collected in each cylinder of the engine using Machine Learning. The innovation in this method is the increased case count and the implementation of the Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. The technique’s efficiency was tested for complete and incomplete learning datasets, resulting in 100% reliability identification in both cases.
Vibration is used as a signal acquisition method in [
10,
11,
13,
19,
21,
26], diagnosing valve clearance size, valve failure, various failure types, ignition failure, and both ignition and mechanical failures in ICEs, respectively. The methodology proposed by [
10] is based on signal analysis using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). Vibrations were measured using two piezoelectric accelerometers mounted on the engine head casing. For the ANN, the classifier database was created by training the network from engine vibration signals with predefined valve clearances. With the classifier diagnosing correctly, the technique can be applied to both the training engine and other engines of the same type. A data acquisition system is presented in [
13], comprising a single-axis ceramic shear accelerometer, sound and vibration input module, and an Ethernet module. Data is processed in MATLAB using FFT and the SVM algorithm, showing a diagnostic accuracy of 97%. The method in [
19] proposes an automated system based on ANN, specifically MLP and PNN, to diagnose a series of various types of ICE failures. The system automation was divided into three parts: detection, localization, and severity identification. The network was entirely trained from simulated models and tested in real experimental cases. The signal processing approach for diagnosis was based on envelope analysis of vibration signals captured by accelerometers on the engine block surface, demonstrating that networks trained through simulation can efficiently detect combustion and mechanical failures, and identify failure location and severity. The procedure in [
21] bases vibration signal capture on a smartphone placed on the engine, processed by two different methods to test viability and computational effort: Wavelet Multiresolution Analysis (WMA) and chaos-based signal analysis using maximum density (SAC-DM) for ignition failure identification. Both techniques achieved a 100% failure diagnosis rate, with SAC-DM requiring less computational effort. The technique developed in [
26] distinguishes itself by learning only from healthy sample data based on ICE vibration signals processed using FFT and DWT, classified using One Class Support Vector Machine (OCSVM). Classification algorithms were tested on twelve real engines, showing that all ignition and mechanical failures could be detected with minimal false positives and an error rate of 0.15%. In [
11], vibration capture is also used, presenting a state-of-the-art study where the FFT and Morlet Wavelet methods stand out.
In studies [
12,
16,
20,
25], acoustic signals are used to diagnose ICE conditions, differing in the processing methods developed. The first primarily uses a decision tree, tested with a sound pressure level meter. Thirteen acoustic wave spectrum measurements were performed for different induced engine failure cases, with the decision tree used for damage diagnosis from spectral sound emission characteristics. The second detects fuel injection system failures specifically in a marine ICE, with sound recorded in two locations: the injector pump outlet and the injector inlet, using a broadband accelerometer and a sound card. The amplitudes of vibratory pulses in a normally operating ICE change when a failure occurs, enabling the proposed system to detect malfunction. The third study uses ANN, DWT, and fractal dimension, integrating low-cost signal acquisition hardware (Arduino Due and electret condenser microphone CMA-4544PF-W) and processing software running on smartphones (Android). Fractal dimension application expedited analysis with low computational demand, distinct from DWT processing, with ANN applied for classification, achieving a 99.58% performance rate. The last proposes an acoustic characterization system using sound captured by a smartphone, processed by a deep learning method with a cascaded architecture, defined as conditional networks extracting sound for fault characterization. A multitask Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) predicts and characterizes the engine to detect ignition failures, achieving 87% diagnostic accuracy.
In [
14,
17,
18], exhaust gas temperature is measured to detect ignition failures in the first and last studies, and combustion instability in the second.
The method in [
14] uses a lambda sensor (O2) to capture temperature due to its low cost and computational effort, employing False Alarm Rate (FAR) and Success Detection Rate (SDR) techniques to avoid detection errors, as exhaust temperature fluctuates even under normal conditions. The sensor reading drops during ignition failure and rises upon normal combustion resumption, establishing diagnostic rules based on failure duration and sampling interval, resulting in an SDR of 0.75 and a fixed FAR, achieving 75% effectiveness.
An ultrasonic thermometry system is developed in [
17], based on the thermal dependency of sound speed, with temperature measured by detecting the ultrasonic wave (USW) time-of-flight between the transmitter and receiver. This system offers high-speed response and an uncertainty rate below 0.73%, outperforming thermocouples.
In [
18], temperature is measured using a laser-induced grating spectroscopy (LIGS) system, based on oscillation frequency measurement of the detected signal, less susceptible to noise effects. LIGS’s drawback is weaker signals at higher temperatures due to lower density and faster decay from rapid diffusion.
Seeking to reduce emission rates from an ICE, [
15] develops a method to capture the oil film formed in the cylinder using ultrasonic imaging. A straight-beam ultrasonic contact transducer was used for wave propagation through the cylinder wall, collecting reflections as piston rings passed the detection area. The reflection coefficient varies with layer stiffness and corresponding acoustic properties of materials and lubricants, successfully diagnosing oil film thickness (OFT).
Vibration and pressure signals in the combustion chamber were analyzed in [
22] to diagnose damage development in some marine ICE components, with data collection during natural vessel operation conditions during port maneuvers. Signals were processed by FFT, DWT, Time-Frequency domain analysis, and machine learning, used for ANN classification. The technique achieved an 80% result for fault identification and classification.
In [
23], the fuel injector plays a crucial role in an ICE and is particularly susceptible to damage, directly affecting engine efficiency. Electrical properties of the injector coil can be collected from voltage and current curve analysis, determining injector health. Waveform analysis of the current by Derivative Sign Change (DSC) provides information on injector operation quality. Parameter changes are reflected in the initial waveform and DSC value and phase, verifying system status and detecting faults. Given the above, it is possible to visualize the methodology scheme used in each study for ICE fault diagnosis: first, the acquisition system is characterized, followed by the processing system, and classification system for articles using Artificial Intelligence (AI).
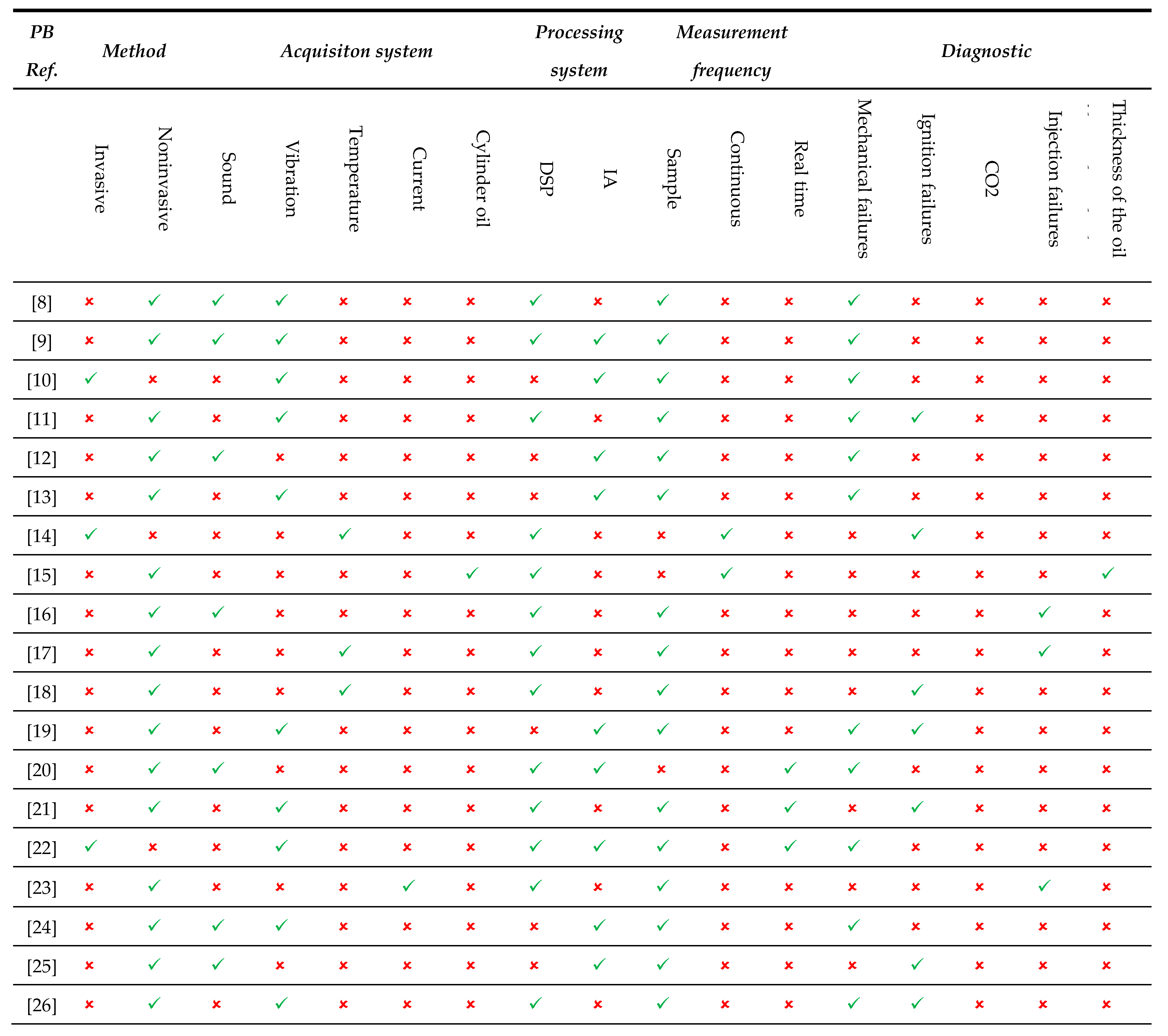
Table 3 summarizes the research found in PB, which initially show that non-invasive methods are the most used for fault detection, although there are still 15% (3 articles) that use invasive methods. The PB articles, where 73% (14 articles) use periodic sampling, 5% (1 article) use real-time measurement, 11% (2 articles) combine both forms, and 11% (2 articles) use continuous measurement. Among the articles found, 47% diagnose mechanical faults, 21% diagnose ignition faults, 16% diagnose both faults and ignition, another 16% diagnose injection faults, and 5% diagnose oil film thickness.
This underscores the importance of using non-invasive methods for detecting faults in internal combustion engines. The table further shows that sound and vibration are the most commonly used acquisition systems for fault detection. Some articles even employ both acquisition systems together for fault detection, and there are also articles that utilize temperature, current, and cylinder oil systems.
It’s important to note that articles using temperature, current, and cylinder oil acquisition systems employ Digital Signal Processor (DSP) processing systems, while others use AI-based processing systems, or a combination of both. This approach leverages real-time efficiency and precision of DSPs alongside the adaptive capability and advanced analysis of AI, resulting in a more robust and efficient system for identifying faults in internal combustion engines.
Table 3 highlights that no article addresses CO2 diagnostics or monitors acquisition systems such as temperature, current, sound, vibration, fuel consumption, and overall quality control, nor does it monitor vessel data like location, displacement, route, and speed. Therefore, these would be unique aspects of the proposed development.
Table 4 presents a survey of PB articles utilizing AI, describing classification systems and indicating the datasets used for training. It’s notable that out of 9 sampled articles, 7 employ various neural network architectures, offering a robust and flexible approach to diagnostic and predictive maintenance. Another parameter discussed is the sampling rate, ranging widely from 200 samples to 16,384 samples, highlighting the need for substantial and well-balanced datasets to accurately train, test, and validate AI models across a broad range of operational conditions and fault types.
Regarding the datasets presented in
Table 4, many are proprietary, making them unavailable to the public. This difficulty in replicating results and independently validating models underscores another unique aspect of the proposed project: the development of a robust and comprehensive database that ensures appropriate partitioning for training, testing, and validation. This approach aims to achieve precise and replicable results, enabling the scientific community to validate and compare findings across different approaches.
In conclusion,
Table 3 and
Table 4 demonstrate a growing trend towards the use of non-invasive methods for fault detection, crucial for minimizing engine downtime and reducing maintenance costs. The combination of DSP and AI, validated by the articles in the tables, along with real-time and continuous monitoring, is essential for engine diagnostics and maintenance, addressing a gap identified in the literature. Another gap highlighted by both tables is the study of diverse parameters such as vibration, temperature, sound, current, fuel consumption, among others, enabling a comprehensive and accurate analysis of internal combustion engine conditions and thus providing a robust and effective approach to fault diagnosis. Addressing the lack of publicly available data is also crucial for facilitating result validation and replication, as shown in the tables.
4. Conclusions
This study conducted a systematic review of non-invasive techniques for fault identification in internal combustion engines, using the Proknow-C and Methodi Ordinatio methods to categorize and systematize scientific literature. We provided a pioneering review of non-invasive techniques for fault detection, resulting in a comprehensive bibliographic portfolio.
In summary, the systematic review enabled a comprehensive mapping of non-invasive techniques for fault identification in internal combustion engines, highlighting: (i) the use of a wide range of AI algorithms, demonstrating the flexibility and effectiveness of these methods for fault diagnostics; (ii) the prevalence of non-invasive methods, emphasizing the importance of techniques that minimize interference in monitored systems; (iii) the combination of diverse acquisition systems with advanced data processing techniques, essential for comprehensive and accurate diagnostics; (iv) the need for continuous real-time monitoring, indicating the demand for systems capable of providing data instantly for monitoring and fault detection; and (v) the lack of public datasets limits the replication of results and cross-validation across different studies.
Detailed analysis of the results revealed significant advances in the application of artificial intelligence and digital signal processing for precise and efficient fault diagnostics. Thus, research on non-invasive techniques for fault diagnosis in internal combustion engines is crucial for the development of more efficient, reliable, and sustainable engines. Artificial intelligence emerges as a powerful tool to enhance fault diagnosis and prediction, contributing to optimizing the operation of internal combustion engines, enabling real-time predictive management, and potential for energy efficiency optimization and emissions reduction. The gaps identified in this systematic review highlight the following recommendations for future research:
Multimodal data fusion: Explore advanced methods to combine and analyze data from different sources (e.g., multiple sensor data, maintenance records, operational data) to enhance the accuracy of fault detection. This includes multimodal data fusion techniques, integrating structured and unstructured data to provide a comprehensive view of the engine’s condition.
AI for fault prognosis and maintenance planning: Develop predictive models using advanced artificial intelligence algorithms such as deep neural networks, support vector machines, and reinforcement learning algorithms to forecast faults. This includes developing systems that not only identify faults but also recommend specific preventive actions to optimize engine life and efficiency.
Multiple diagnostics systems: Develop integrated systems capable of monitoring and diagnosing multiple aspects of engine performance, including mechanical failures, ignition problems, and CO2 emissions. These systems should operate in real-time, providing immediate information to operators and management systems, enabling rapid and efficient corrective actions.
Public datasets: Encourage the creation and sharing of high-quality datasets that include standardized and well-documented test data. This facilitates democratizing research and enables validation and comparison of different fault diagnostic approaches, promoting consistent and replicable advances in the field.
Finally, it underscores the ongoing importance of technological innovations in fault diagnosis in internal combustion engines to promote energy digitalization and energy sustainability.