Submitted:
14 August 2024
Posted:
14 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Gathering and Editing
2.2. Trait Groups
- 2.
- Carcass traits: Backfat thickness, rib eye area, rump fat thickness, hot carcass weight, subcutaneous fat thickness, intramuscular fat content, longissimus muscle area, marbling, tenderness, shear force tenderness, meat color.
- ∙
- Subgroup: Meat quality
- 3.
- Growth-related traits: Residual body weight gain, average daily gain, accumulated productivity, birth weight, weaning weight, yearling weight, adult cow weight, weight gain from birth to weaning, weight gain from weaning to yearling, yearling height, residual feed intake, dry matter intake, feed efficiency, feed conversion ratio.
- ∙
- Subgroup: Efficiency
- 4.
- Morphological traits: Body conformation, muscularity, precocity, feet and leg deformation, feet and leg conformation.
- ∙
- Subgroup: Visual scores
- ∙
- Included traits: Conformation, precocity, muscling.
2.3. Overrepresentation and Prioritization Analyses
2.4. Functional Analysis
2.5. Venn Diagrams and Gene Network Integration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gene annotation and Prioritization Analysis
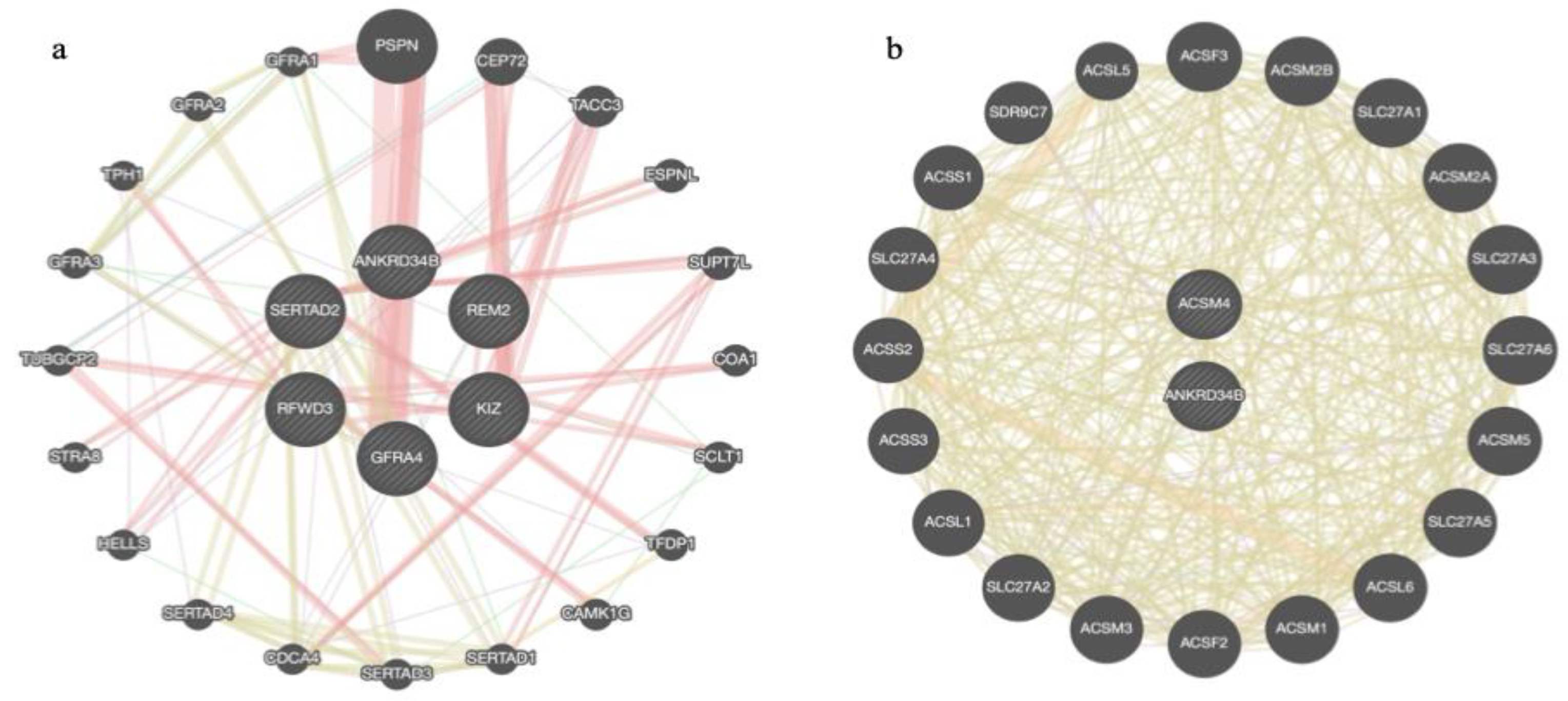
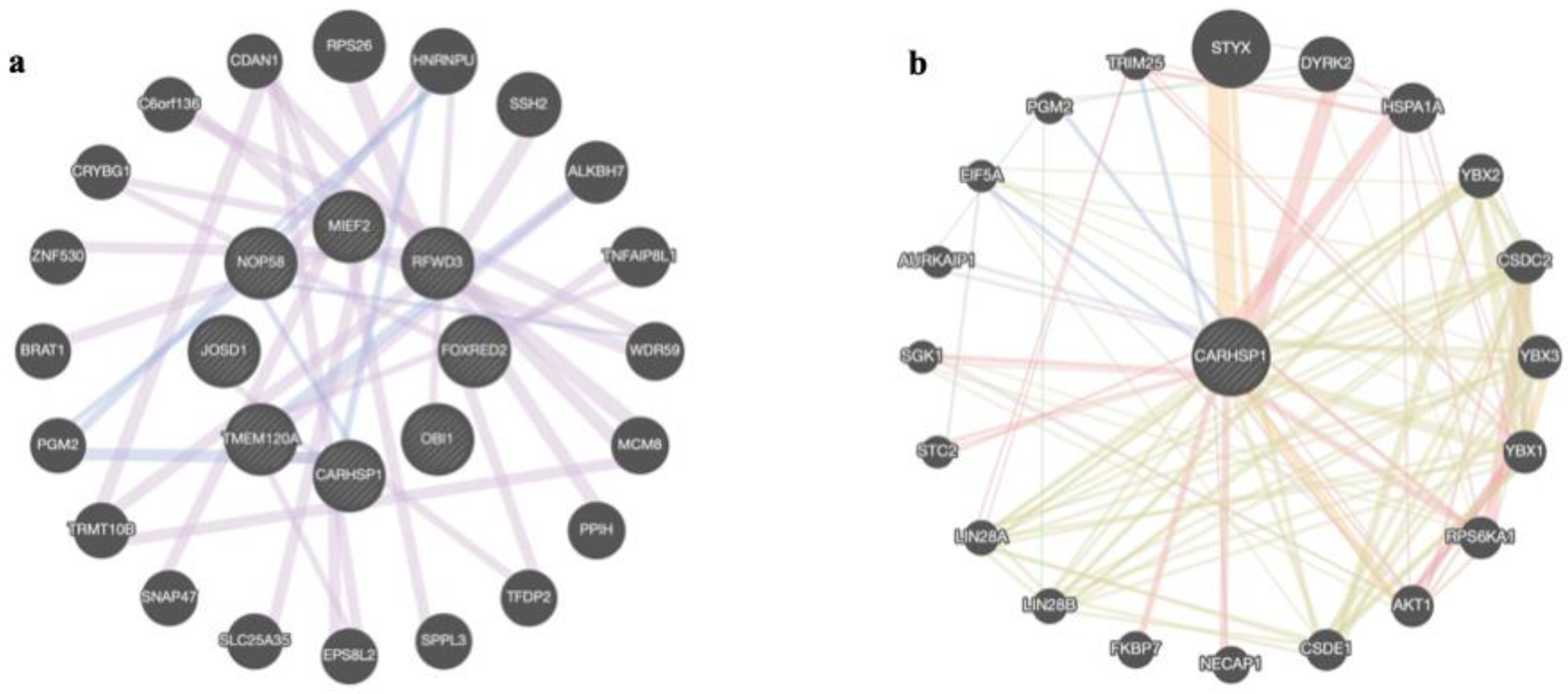
3.2. Enrichment and Gene Integration Analysis of the Functional Candidate Genes Identified within Groups
3.2.1. Reproduction and Sexual Precocity Traits
3.2.2. Carcass and Meat Quality Traits
3.2.3. Growth-Related and Efficiency Traits
3.2.4. Morphological and Visual Score Traits
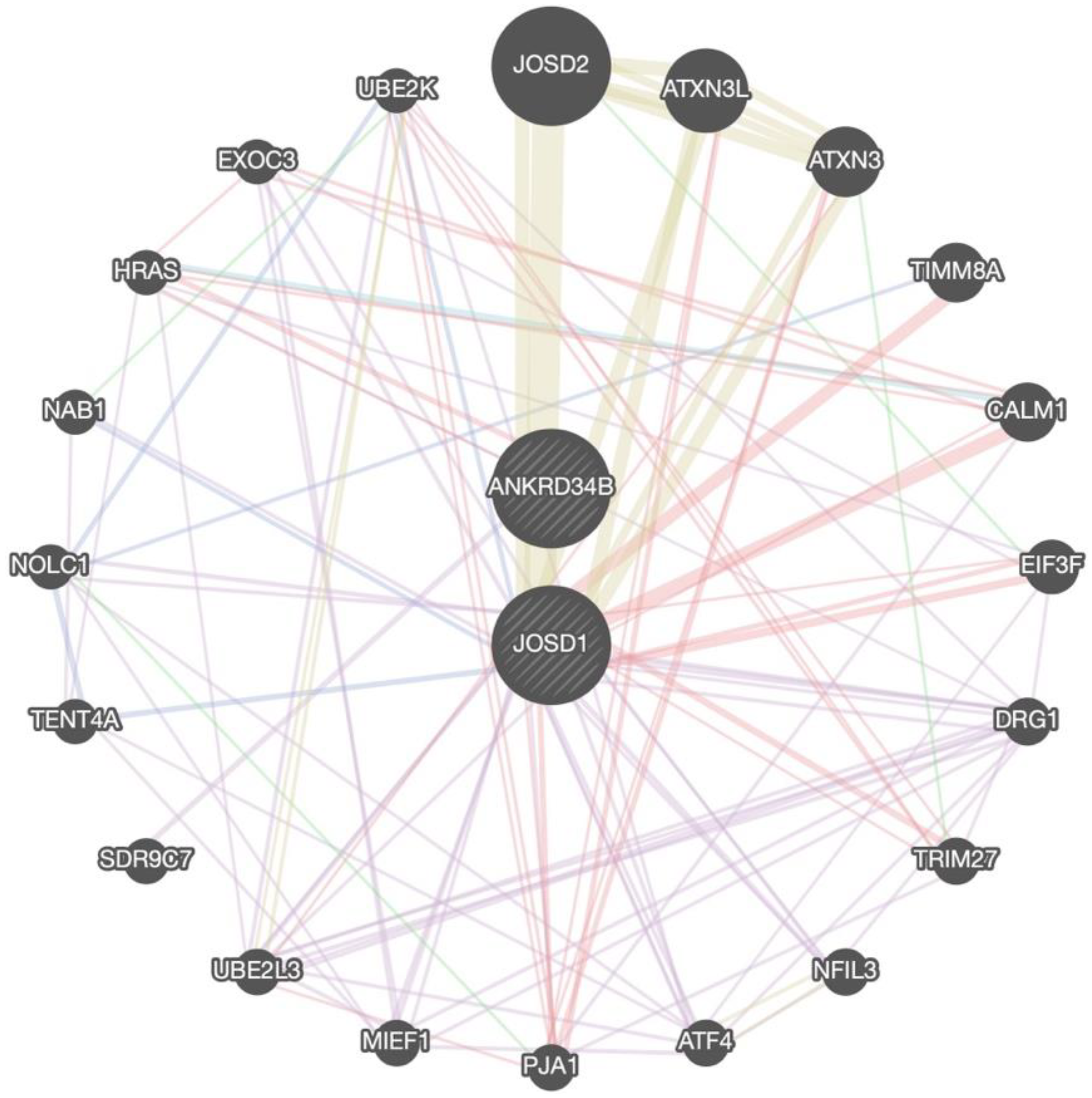
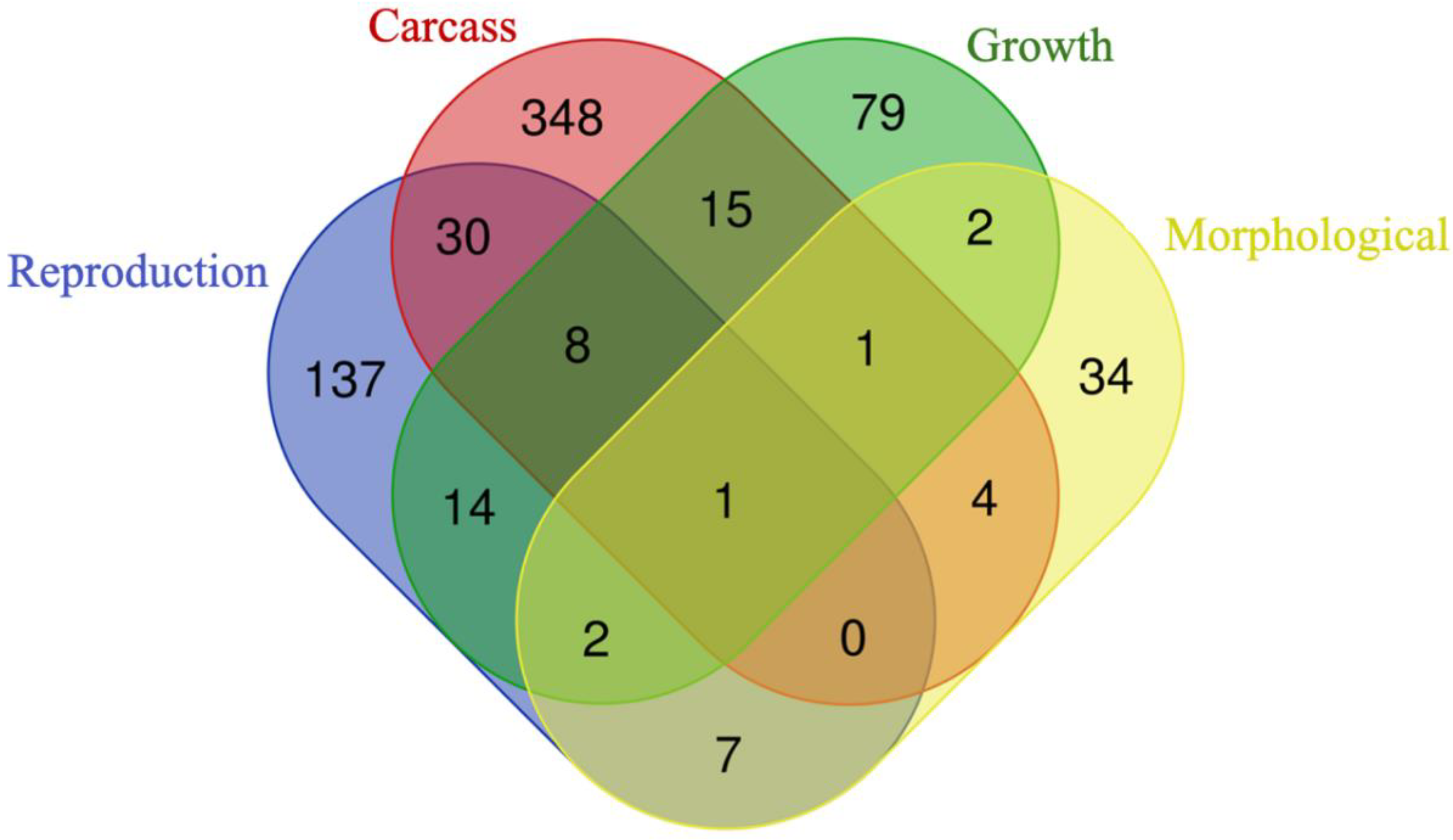
3.3. Genes Shared among Groups
3.3.1. Overrepresented Genes
3.3.2. Prioritized Genes
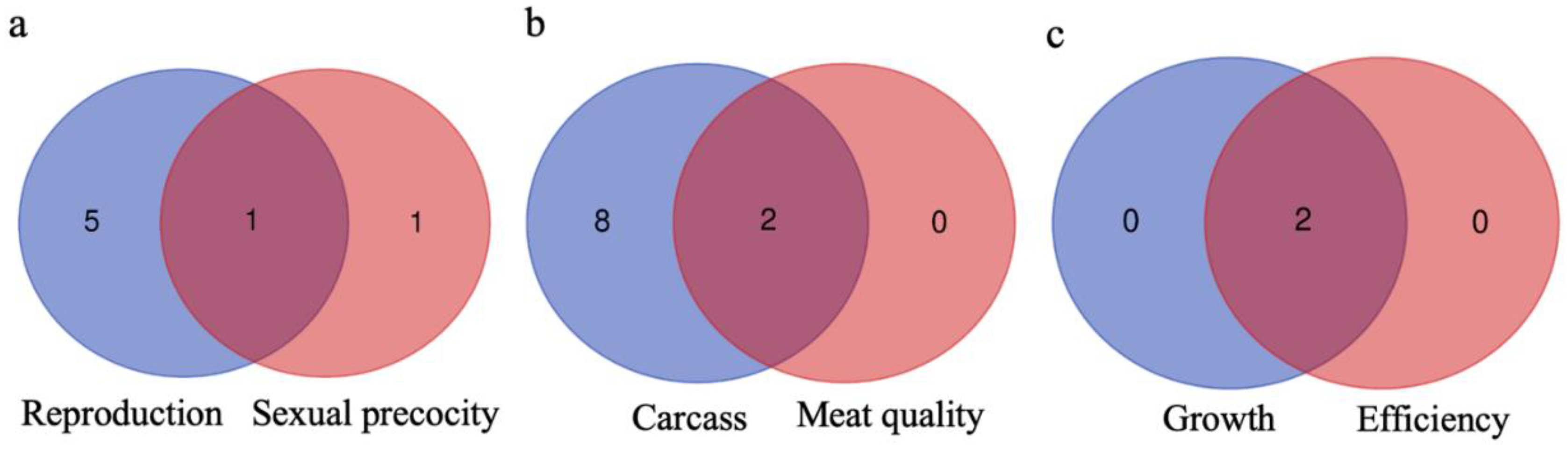
3.4. Genes Shared between Groups and Subgroups
4. Limitations of this Study and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Utsunomiya, Y. T.; Do Carmo, A. S.; Carvalheiro, R.; Neves, H. H.; Matos, M. C.; Zavarez, L. B.; Pérez O’Brien, A. M.; Sölkner, J.; McEwan, J. C.; Cole, J. B.; Van Tassell, C. P.; Schenkel, F. S.; Da Silva, M. V.; Porto Neto, L. R.; Sonstegard, T. S.; & Garcia, J. F.; & Garcia, J. F. Genome-wide association study for birth weight in Nellore cattle points to previously described orthologous genes affecting human and bovine height. BMC Genetics 2013, 14(1), 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, D.; Sevane, N.; Nicolazzi, E. L.; MacHugh, D. E.; Park, S. D. E.; Colli, L.; Martinez, R.; Bruford, M. W.; & Orozco-terWengel, P.; & Orozco-terWengel, P. Domestication of cattle: Two or three events? Evolutionary applications 2018, 12(1), 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, L. G. de. Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production. Instituto Prociência (2006).
- Porto-Neto, L. R. , Reverter, A., Prayaga, K. C., Chan, E. K., Johnston, D. J., Hawken, R. J., Fordyce, G., Garcia, J. F., Sonstegard, T. S., Bolormaa, S., Goddard, M. E., Burrow, H. M., Henshall, J. M., Lehnert, S. A., & Barendse, W. The genetic architecture of climatic adaptation of tropical cattle. PloS one, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiro, R. , Boison, S. A., Neves, H. H., Sargolzaei, M., Schenkel, F. S., Utsunomiya, Y. T., O'Brien, A. M., Sölkner, J., McEwan, J. C., Van Tassell, C. P., Sonstegard, T. S., & Garcia, J. F. Accuracy of genotype imputation in Nellore cattle. Genetics, selection, evolution: GSE. [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L. , Fernandes Júnior, G., & Carvalheiro, R. (2018). BEEF CATTLE GENOMIC SELECTION IN TROPICAL ENVIRONMENTS.
- Fernandes Júnior, G. A. , Peripolli, E., Schmidt, P. I., Campos, G. S., Mota, L. F. M., Mercadante, M. E. Z., Baldi, F., Carvalheiro, R., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Current applications and perspectives of genomic selection in Bos indicus (Nellore) cattle. Livestock Science, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, A. , & Farlow, A. The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: A review. Plant Methods. [CrossRef]
- Mokry, F. B. , Buzanskas, M. E., De Alvarenga Mudadu, M., Do Amaral Grossi, D., Higa, R. H., Ventura, R. V., De Lima, A. O., Sargolzaei, M., Conceição Meirelles, S. L., Schenkel, F. S., Da Silva, M. V. G. B., Méo Niciura, S. C., De Alencar, M. M., Munari, D. P., & De Almeida Regitano, L. C. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype block structure in a composite beef cattle breed. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.-P. , Tribout, T., Kadri, N. K., Chitneedi, P. K., Maak, S., Hozé, C., Boussaha, M., Croiseau, P., Philippe, R., Spengeler, M., Kühn, C., Wang, Y., Li, C., Plastow, G., Pausch, H., & Boichard, D. Sequence-based GWAS meta-analyses for beef production traits. Genetics Selection Evolution. [CrossRef]
- Irano, N. , De Camargo, G. M. F., Costa, R. B., Terakado, A. P. N., Magalhães, A. F. B., Silva, R. M. D. O., Dias, M. M., Bignardi, A. B., Baldi, F., Carvalheiro, R., De Oliveira, H. N., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-Wide Association Study for Indicator Traits of Sexual Precocity in Nellore Cattle. PLOS ONE 2016. ,. [CrossRef]
- Silva, D. O. , Fernandes Júnior, G. A., Fonseca, L. F. S., Mota, L. F. M., Bresolin, T., Carvalheiro, R., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide association study for stayability at different calvings in Nellore beef cattle. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F. E. , Espigolan, R., Berton, M. P., Neto, J. B. S., Silva, R. P., Grigoletto, L., Silva, R. M. O., Ferraz, J. B. S., Eler, J. P., Aguilar, I., Lôbo, R. B., & Baldi, F. Genome-wide association study and predictive ability for growth traits in Nellore cattle. Livestock Science 2020, 231, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H. B. D. , Carvalho, M. E., Espigolan, R., Poleti, M. D., Ambrizi, D. R., Berton, M. P., Ferraz, J. B. S., De Mattos Oliveira, E. C., & Eler, J. P. Genome-Wide Association (GWAS) Applied to Carcass and Meat Traits of Nellore Cattle. Metabolites. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Júnior, G. A. , Santos, D. J. A., Cesar, A. S. M., Boison, S. A., Ventura, R. V., Perez, B. C., Garcia, J. F., Ferraz, J. B. S., & Garrick, D. J. Fine mapping of genomic regions associated with female fertility in Nellore beef cattle based on sequence variants from segregating sires. Journal of animal science and biotechnology 2019, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börnigen, D. , Tranchevent, L. C., Bonachela-Capdevila, F., Devriendt, K., De Moor, B., De Causmaecker, P., & Moreau, Y. An unbiased evaluation of gene prioritization tools. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadifar, S. , & Ahmadi, A. A novel candidate disease gene prioritization method using deep graph convolutional networks and semi-supervised learning. BMC Bioinformatics, 23(1) 2022. ,. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P. A. D. S. , Dos Santos, F. C., Lam, S., Suárez-Vega, A., Miglior, F., Schenkel, F. S., Diniz, L. D. A. F., Id-Lahoucine, S., Carvalho, M. R. S., & Cánovas, A. Genetic mechanisms underlying spermatic and testicular traits within and among cattle breeds: Systematic review and prioritization of GWAS results1. Journal of Animal Science. [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S. G. , de Jong, E., Schenkel, F. S., Fonseca, P. A. S., Chud, T. C. S., Powell, D., Wachoski-Dark, G., Ronksley, P. E., Miglior, F., Orsel, K., & Barkema, H. W. Underlying genetic architecture of resistance to mastitis in dairy cattle: A systematic review and gene prioritization analysis of genome-wide association studies. Journal of dairy science. [CrossRef]
- Silva, T. D. L. , Gondro, C., Fonseca, P. A. D. S., Da Silva, D. A., Vargas, G., Neves, H. H. D. R., Filho, I. C., Teixeira, C. D. S., Albuquerque, L. G. D., & Carvalheiro, R. Testicular hypoplasia in Nellore Cattle: Genetic analysis and functional analysis of genome-wide association study results. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Silva, T. D. L. , Gondro, C., Fonseca, P. A. D. S., Silva, D. A. D., Vargas, G., Neves, H. H. D. R., Carvalho Filho, I., Teixeira, C. D. S., Albuquerque, L. G. D., & Carvalheiro, R. Feet and legs malformation in Nellore cattle: Genetic analysis and prioritization of GWAS results. Frontiers in Genetics, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J. , McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, n71. [CrossRef]
- Sarkis-Onofre, R. , Catalá-López, F., Aromataris, E., & Lockwood, C. How to properly use the PRISMA Statement. Systematic Reviews 2021, 10(1), 117, s13643-021-01671-z. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L. , Park, C. A., & Reecy, J. M. Bringing the Animal QTLdb and CorrDB into the future: Meeting new challenges and providing updated services. Nucleic Acids Research. [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E. W. , Bolton, E. E., Brister, J. R., Canese, K., Chan, J., Comeau, D. C., Connor, R., Funk, K., Kelly, C., Kim, S., Madej, T., Marchler-Bauer, A., Lanczycki, C., Lathrop, S., Lu, Z., Thibaud-Nissen, F., Murphy, T., Phan, L., Skripchenko, Y., … Sherry, S. T. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Research. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P. A. S. , Suárez-Vega, A., Marras, G., & Cánovas, Á. GALLO: An R package for genomic annotation and integration of multiple data sources in livestock for positional candidate loci. GigaScience 2020, 9(12), giaa149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2016. https://www.R-project.
- Nicolazzi, E. L. , Caprera, A., Nazzicari, N., Cozzi, P., Strozzi, F., Lawley, C., Pirani, A., Soans, C., Brew, F., Jorjani, H., Evans, G., Simpson, B., Tosser-Klopp, G., Brauning, R., Williams, J. L., & Stella, A. SNPchiMp v.3: Integrating and standardizing single nucleotide polymorphism data for livestock species. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Martin, F. J. , Amode, M. R., Aneja, A., Austine-Orimoloye, O., Azov, A. G., Barnes, I., Becker, A., Bennett, R., Berry, A., Bhai, J., Bhurji, S. K., Bignell, A., Boddu, S., Branco Lins, P. R., Brooks, L., Ramaraju, S. B., Charkhchi, M., Cockburn, A., Da Rin Fiorretto, L., … Flicek, P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Research. [CrossRef]
- Shamimuzzaman, M. , Le Tourneau, J. J., Unni, D. R., Diesh, C. M., Triant, D. A., Walsh, A. T., Tayal, A., Conant, G. C., Hagen, D. E., & Elsik, C. G. Bovine Genome Database: new annotation tools for a new reference genome. Nucleic acids research. [CrossRef]
- Raney, B. J. , Barber, G. P., Benet-Pagès, A., Casper, J., Clawson, H., Cline, M. S., Diekhans, M., Fischer, C., Navarro Gonzalez, J., Hickey, G., Hinrichs, A. S., Kuhn, R. M., Lee, B. T., Lee, C. M., Le Mercier, P., Miga, K. H., Nassar, L. R., Nejad, P., Paten, B., … Haeussler, M. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Research, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S. J. , Schopen, M., Savage, A. G., Schulman, J. L., & Arluk, N. The MeSH translation maintenance system: structure, interface design, and implementation. Studies in health technology and informatics.
- Adams, W. T. , & Skopek, T. R. Statistical test for the comparison of samples from mutational spectra. Journal of molecular biology 1987, 194(3), 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morota, G. , Peñagaricano, F., Petersen, J. L., Ciobanu, D. C., Tsuyuzaki, K., & Nikaido, I. An application of MeSH enrichment analysis in livestock. Animal Genetics 2015, 46(6), 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuyuzaki, K. , Morota, G., Ishii, M., Nakazato, T., Miyazaki, S., & Nikaido, I. MeSH ORA framework: R/Bioconductor packages to support MeSH over-representation analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Using meshes for MeSH term enrichment and semantic analyses. Bioinformatics 2018, 34(21), 3766–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. , Bardes, E. E., Aronow, B. J., & Jegga, A. G. ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Research 2009, 37(Web Server), W305–W311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney, E. , Garcia-Garcia, J., & Oliva, B. GUILDify: A web server for phenotypic characterization of genes through biological data integration and network-based prioritization algorithms. Bioinformatics 2014, 30(12), 1789–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Plans, J. , Piñero, J., Sanz, F., Furlong, L. I., Fernandez-Fuentes, N., Oliva, B., & Guney, E.. GUILDify v2.0: A Tool to Identify Molecular Networks Underlying Human Diseases, Their Comorbidities and Their Druggable Targets. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominakis, A. , Hager-Theodorides, A. L., Zoidis, E., Saridaki, A., Antonakos, G., & Tsiamis, G. Combined GWAS and ‘guilt by association’-based prioritization analysis identifies functional candidate genes for body size in sheep. Genetics Selection Evolution. [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. , Wang, L.-G., Han, Y., & He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology. [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D. , Donaldson, S. L., Comes, O., Zuberi, K., Badrawi, R., Chao, P., & Morris, Q. (2010). The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Research, 38(suppl_2), W214-W220. [CrossRef]
- Soares, R. A. N. , Vargas, G., Muniz, M. M. M., Soares, M. A. M., Cánovas, A., Schenkel, F., & Squires, E. J. Differential gene expression in dairy cows under negative energy balance and ketosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of dairy science. [CrossRef]
- Oshimori, N. , Li, X., Ohsugi, M., & Yamamoto, T. Cep72 regulates the localization of key centrosomal proteins and proper bipolar spindle formation. The EMBO Journal 2009, 28(14), 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Tubulin-Gamma Complex-associated Protein 2 (TUBGCP2) 2022. www.alliancegenome. 27 July 1859.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Espin Like (ESPNL) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2793.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Solute Carrier Family 27 Member 1 (SLC27A1) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2793.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Acyl-CoA synthetase medium chain family member 2A (ACSM2A) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 3201.
- Oshimori, N. , Ohsugi, M., & Yamamoto, T. The Plk1 target Kizuna stabilizes mitotic centrosomes to ensure spindle bipolarity. Nature cell biology 2006, 8(10), 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. , Liu, J., Wu, Y., Zhao, X., Hao, Y., Wang, X., Xue, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, R., & Zhang, X. Long Noncoding RNA SERTAD2-3 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Proliferation and Migration by Competitively Binding miR-29c. Genetic testing and molecular biomarkers. [CrossRef]
- Darwish, H. Genomic and functional studies of SERTAD3, an oncogenic protein of the SERTAD family of transcription factors. Master's thesis, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2006. eScholarship@McGill. https://escholarship.mcgill. 4168. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X. , Yucer, N., Liu, S., Li, M., Yi, P., Mu, J. J., Yang, T., Chu, J., Jung, S. Y., O'Malley, B. W., Gu, W., Qin, J., & Wang, Y. RFWD3-Mdm2 ubiquitin ligase complex positively regulates p53 stability in response to DNA damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107(10), 4579–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamsam-Casalotti, S. , Onoda, M., Papadopoulos, V., & Dym, M. Developmental expression of GTP-binding proteins in rat testes. Journal of reproduction and fertility. [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Acyl-CoA synthetase medium chain family member 4 (ACSM4) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 3201.
- Manna, P. R. , Stetson, C. L., Slominski, A. T., & Pruitt, K. Role of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in health and disease. Endocrine 2016, 51(1), 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errico, A. , Vinco, S., Ambrosini, G., Dalla Pozza, E., Marroncelli, N., Zampieri, N., & Dando, I. Mitochondrial Dynamics as Potential Modulators of Hormonal Therapy Effectiveness in Males. Biology 2023, 12(4), 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. AlkB homolog 7 (ALKBH7) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2130.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Codanin 1 (CDAN1) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 1713.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 3093.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 1A (HSPA1A) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 5232.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. synaptosome associated protein 47 (SNAP47) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 3066.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. ORC ubiquitin ligase 1(OBI1) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2030.
- Nassar, J. Studying the function(s) of OBI1, a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase, involved in DNA replication [Doctoral thesis]. HAL open archive, 0340. [Google Scholar]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Transmembrane protein 120A (TMEM120A) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2169.
- Batrakou, D. G. , De Las Heras, J. I., Czapiewski, R., Mouras, R., & Schirmer, E. C. TMEM120A and B: Nuclear Envelope Transmembrane Proteins Important for Adipocyte Differentiation. PLOS ONE, 0127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Dual specificity phosphatase 29 (DUSP29) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2348.
- Cooper, L. M. , West, R. C., Hayes, C. S., & Waddell, D. S. Dual-specificity phosphatase 29 is induced during neurogenic skeletal muscle atrophy and attenuates glucocorticoid receptor activity in muscle cell culture. American journal of physiology. Cell physiology. [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Josephin domain containing 1 (JOSD1) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2895.
- Seki, T. , Gong, L., Williams, A. J., Sakai, N., Todi, S. V., & Paulson, H. L. JosD1, a membrane-targeted deubiquitinating enzyme, is activated by ubiquitination and regulates membrane dynamics, cell motility, and endocytosis. The Journal of biological chemistry, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeneCards. LOXL1 Antisense RNA 1 (LOXL1-AS1). https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl? 27 July.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. calcium regulated heat stable protein 1 (CARHSP1) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 1715.
- Kociucka, B. , Stachecka, J., Szydlowski, M., & Szczerbal, I. Rapid Communication: The correlation between histone modifications and expression of key genes involved in accumulation of adipose tissue in the pig. Journal of animal science, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane 8A (TIMM8A) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 1181.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Terminal nucleotidyltransferase 4A (TENT4A) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 1670.
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Ankyrin repeat domain 34B (ANKRD34B) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 3373.
- Tartaglia G., G. The Grand Challenge of Characterizing Ribonucleoprotein Networks. Frontiers in molecular biosciences 2016, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Patterns and evolutionary consequences of pleiotropy. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. [CrossRef]
- Alliance of Genome Resources. Ring finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) 2022. https://www.alliancegenome. 27 July 2553.
- Ménézo, Y. , Dale, B., & Cohen, M. DNA damage and repair in human oocytes and embryos: a review. Zygote (Cambridge, England). [CrossRef]
- Inano, S. , Sato, K., Katsuki, Y., Kobayashi, W., Tanaka, H., Nakajima, K., Nakada, S., Miyoshi, H., Knies, K., Takaori-Kondo, A., Schindler, D., Ishiai, M., Kurumizaka, H., & Takata, M. RFWD3-Mediated Ubiquitination Promotes Timely Removal of Both RPA and RAD51 from DNA Damage Sites to Facilitate Homologous Recombination. Molecular cell. [CrossRef]
- Bovine Genome Sequencing and Analysis Consortium, Elsik, C. G., Tellam, R. L., Worley, K. C., Gibbs, R. A., Muzny, D. M., Weinstock, G. M., Adelson, D. L., Eichler, E. E., Elnitski, L., Guigó, R., Hamernik, D. L., Kappes, S. M., Lewin, H. A., Lynn, D. J., Nicholas, F. W., Reymond, A., Rijnkels, M., Skow, L. C., Zdobnov, E. M., … Zhao, F. Q. The genome sequence of taurine cattle: a window to ruminant biology and evolution. Science (New York, N.Y.), 5926. [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, J. B. Comparing cows with humans. Genome Biology, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermisdorff, I. D. C. , Diaz, I. D. P. S., De Camargo, G. M. F., De Albuquerque, L. G., & Costa, R. B. Effect of genomic X-chromosome regions on Nelore bull fertility. Journal of Applied Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, Y. T. , Carmo, A. S., Neves, H. H. R., Carvalheiro, R., Matos, M. C., Zavarez, L. B., Ito, P. K. R. K., Pérez O’Brien, A. M., Sölkner, J., Porto-Neto, L. R., Schenkel, F. S., McEwan, J., Cole, J. B., Da Silva, M. V. G. B., Van Tassell, C. P., Sonstegard, T. S., & Garcia, J. F. Genome-Wide Mapping of Loci Explaining Variance in Scrotal Circumference in Nellore Cattle. PLoS ONE, 8856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafuzza, N. B. , Costa E Silva, E. V. D., Silva, R. M. D. O., Costa Filho, L. C. C. D., Barbosa, F. B., Macedo, G. G., Lobo, R. B., & Baldi, F. Genome-wide association study for age at puberty in young Nelore bulls. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F. E. , Espigolan, R., Berton, M. P., Neto, J. B. S., Silva, R. P., Grigoletto, L., Silva, R. M. O., Ferraz, J. B. S., Eler, J. P., Aguilar, I., Lôbo, R. B., & Baldi, F. Genome-wide association study and predictive ability for growth traits in Nellore cattle. Livestock Science 2020, 231, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M. H. , Utsunomiya, Y. T., Neves, H. H., Gomes, R. C., Garcia, J. F., Fukumasu, H., Silva, S. L., Oliveira Junior, G. A., Alexandre, P. A., Leme, P. R., Brassaloti, R. A., Coutinho, L. L., Lopes, T. G., Meirelles, F. V., Eler, J. P., & Ferraz, J. B. Genome-wide association analysis of feed intake and residual feed intake in Nellore cattle. BMC Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Brunes, L. C. , Baldi, F., Lopes, F. B., Lôbo, R. B., Espigolan, R., Costa, M. F. O., Stafuzza, N. B., & Magnabosco, C. U. Weighted single-step genome-wide association study and pathway analyses for feed efficiency traits in Nellore cattle. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A. F. B. , De Camargo, G. M. F., Fernandes, G. A., Gordo, D. G. M., Tonussi, R. L., Costa, R. B., Espigolan, R., Silva, R. M. D. O., Bresolin, T., De Andrade, W. B. F., Takada, L., Feitosa, F. L. B., Baldi, F., Carvalheiro, R., Chardulo, L. A. L., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-Wide Association Study of Meat Quality Traits in Nellore Cattle. PLOS ONE, 0157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R. B. , Camargo, G. M., Diaz, I. D., Irano, N., Dias, M. M., Carvalheiro, R., Boligon, A. A., Baldi, F., Oliveira, H. N., Tonhati, H., & Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide association study of reproductive traits in Nellore heifers using Bayesian inference. Genetics Selection Evolution. [CrossRef]
- Melo, T. P. D. , De Camargo, G. M. F., De Albuquerque, L. G., & Carvalheiro, R. Genome-wide association study provides strong evidence of genes affecting the reproductive performance of Nellore beef cows. PLOS ONE, 0178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, R. R. , Guimarães, S. E. F., Fortes, M. R. S., Hayes, B., Silva, F. F., Verardo, L. L., Kelly, M. J., De Campos, C. F., Guimarães, J. D., Wenceslau, R. R., Penitente-Filho, J. M., Garcia, J. F., & Moore, S. Genome-wide association study and annotating candidate gene networks affecting age at first calving in Nellore cattle. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Martins, R. , Brito, L. F., Machado, P. C., Pinto, L. F. B., Silva, M. R., Schenkel, F. S., & Pedrosa, V. B. Genome-wide association study and pathway analysis for carcass fatness in Nellore cattle measured by ultrasound. Animal Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Regatieri, I. C. , Boligon, A. A., Costa, R. B., De Souza, F. R. P., Baldi, F., Takada, L., Venturini, G. C., De Camargo, G. M. F., Fernandes, G. A., Tonhati, H., De Oliveira, H. N., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms and sexual precocity in Nellore heifers. Animal Reproduction Science. [CrossRef]
- Machado, P. C. , Brito, L. F., Martins, R., Pinto, L. F. B., Silva, M. R., & Pedrosa, V. B. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Reveals Novel Loci Related with Visual Score Traits in Nellore Cattle Raised in Pasture–Based Systems. Animals, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, D.B. A, Fernandes Júnior, A.G., Silva, B.S.D., Costa, B.R., Takada, L., Gustavo Mansan Gordo, G.M.D., Bresolin, T., Carvalheiro, R., Baldi, F., & Galvão de Albuquerque, L. (2017). Genomic analysis of stayability in Nellore cattle. PloS one, 0179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T. L. , Gondro, C., Fonseca, P. A. S., da Silva, D. A., Vargas, G., Neves, H. H. R., Filho, I. C., Teixeira, C. S., Albuquerque, L. G., & Carvalheiro, R. Testicular hypoplasia in Nellore Cattle: Genetic analysis and functional analysis of genome-wide association study results. Journal of animal breeding and genetics = Zeitschrift fur Tierzuchtung und Zuchtungsbiologie. [CrossRef]
- Neves, H. H. R. , Vargas, G., Brito, L. F., Schenkel, F. S., Albuquerque, L. G., & Carvalheiro, R. Genetic and genomic analyses of testicular hypoplasia in Nellore cattle. PloS one, 0211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbardella, A. P. , Watanabe, R. N., Da Costa, R. M., Bernardes, P. A., Braga, L. G., Baldi Rey, F. S., Lôbo, R. B., & Munari, D. P. Genome-Wide Association Study Provides Insights into Important Genes for Reproductive Traits in Nelore Cattle. Animals, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Garzón, N. A. , Magalhães, A. F. B., Mota, L. F. M., Fonseca, L. F. S., Chardulo, L. A. L., & Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide association study identified genomic regions and putative candidate genes affecting meat color traits in Nellore cattle. Meat Science, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M. H. A. , Utsunomiya, Y. T., Neves, H. H. R., Gomes, R. C., Garcia, J. F., Fukumasu, H., Silva, S. L., Leme, P. R., Coutinho, L. L., Eler, J. P., & Ferraz, J. B. S. Genome-wide association study for feedlot average daily gain in Nellore cattle (Bos indicus). Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Santana, M. H. A. , Ventura, R. V., Utsunomiya, Y. T., Neves, H. H. R., Alexandre, P. A., Oliveira Junior, G. A., Gomes, R. C., Bonin, M. N., Coutinho, L. L., Garcia, J. F., Silva, S. L., Fukumasu, H., Leme, P. R., & Ferraz, J. B. S. A genomewide association mapping study using ultrasound-scanned information identifies potential genomic regions and candidate genes affecting carcass traits in Nellore cattle. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Marín-Garzón, N. A. , Magalhães, A. F. B., Schmidt, P. I., Serna, M., Fonseca, L. F. S., Salatta, B. M., Frezarim, G. B., Fernandes-Júnior, G. A., Bresolin, T., Carvalheiro, R., & Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide scan reveals genomic regions and candidate genes underlying direct and maternal effects of preweaning calf mortality in Nellore cattle. Genomics, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espigolan, R. , Baldi, F., Boligon, A. A., Souza, F. R. P., Fernandes Júnior, G. A., Gordo, D. G. M., Venturini, G. C., De Camargo, G. M. F., Feitosa, F. L. B., Garcia, D. A., Tonhati, H., Chardulo, L. A. L., Oliveira, H. N., & Albuquerque, L. G. Associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms and carcass traits in Nellore cattle using high-density panels. Genetics and Molecular Research, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L. F. M. , Santos, S. W. B., Júnior, G. A. F., Bresolin, T., Mercadante, M. E. Z., Silva, J. A. V., Cyrillo, J. N. S. G., Monteiro, F. M., Carvalheiro, R., & Albuquerque, L. G. Meta-analysis across Nellore cattle populations identifies common metabolic mechanisms that regulate feed efficiency-related traits. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Martins, R. , Machado, P. C., Pinto, L. F. B., Silva, M. R., Schenkel, F. S., Brito, L. F., & Pedrosa, V. B. Genome-wide association study and pathway analysis for fat deposition traits in nellore cattle raised in pasture–based systems. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Santana, M. H. A. , Gomes, R. C., Utsunomiya, Y. T., Neves, H. H. R., Novais, F. J., Bonin, M. N., Fukumasu, H., Garcia, J. F., Alexandre, P. A., Oliveira Junior, G. A., Coutinho, L. L., & Ferraz, J. B. S. Short Communication Genome-wide association with residual body weight gain in Bos indicus cattle. Genetics and Molecular Research, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikawa, L. M. , Mota, L. F. M., Schmidt, P. I., Frezarim, G. B., Fonseca, L. F. S., Magalhães, A. F. B., Silva, D. A., Carvalheiro, R., Chardulo, L. A. L., & Albuquerque, L. G. D. Genome-wide scans identify biological and metabolic pathways regulating carcass and meat quality traits in beef cattle. Meat Science, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L. F. M. , Lopes, F. B., Fernandes Júnior, G. A., Rosa, G. J. M., Magalhães, A. F. B., Carvalheiro, R., & Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide scan highlights the role of candidate genes on phenotypic plasticity for age at first calving in Nellore heifers. Scientific Reports, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, B. F. , Mercadante, M. E., Cyrillo, J. N., Branco, R. H., Bonilha, S. F., de Albuquerque, L. G., Silva, R. M., & Baldi, F. Genomic Regions Associated with Feed Efficiency Indicator Traits in an Experimental Nellore Cattle Population. PloS one, 0164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Vignato, B. , Cesar, A. S. M., Afonso, J., Moreira, G. C. M., Poleti, M. D., Petrini, J., Garcia, I. S., Clemente, L. G., Mourão, G. B., Regitano, L. C. D. A., & Coutinho, L. L. Integrative Analysis Between Genome-Wide Association Study and Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Reveals Bovine Muscle Gene Expression Regulatory Polymorphisms Associated with Intramuscular Fat and Backfat Thickness. Frontiers in Genetics, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubon, M. A. C. , Pedrosa, V. B., Feitosa, F. L. B., Costa, R. B., De Camargo, G. M. F., Silva, M. R., & Pinto, L. F. B. Identification of novel candidate genes for age at first calving in Nellore cows using a SNP chip specifically developed for Bos taurus indicus cattle. Theriogenology. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A. V. , Matos, M. C., Seno, L. O., Romero, A. R. S., Garcia, J. F., & Grisolia, A. B. Genome wide association study on early puberty in Bos indicus. Genetics and Molecular Research. [CrossRef]
- Júnior, G. A. O. , Perez, B. C., Cole, J. B., Santana, M. H. A., Silveira, J., Mazzoni, G., Ventura, R. V., Júnior, M. L. S., Kadarmideen, H. N., Garrick, D. J., & Ferraz, J. B. S. Genomic study and Medical Subject Headings enrichment analysis of early pregnancy rate and antral follicle numbers in Nelore heifers. Journal of animal science, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H. B. D. , Carvalho, M. E., Espigolan, R., Poleti, M. D., Ambrizi, D. R., Berton, M. P., Ferraz, J. B. S., De Mattos Oliveira, E. C., & Eler, J. P. Genome-Wide Association (GWAS) Applied to Carcass and Meat Traits of Nellore Cattle. Metabolites. [CrossRef]
- Grigoletto, L. , Santana, M. H. A., Bressan, F. F., Eler, J. P., Nogueira, M. F. G., Kadarmideen, H. N., Baruselli, P. S., Ferraz, J. B. S., & Brito, L. F. Genetic Parameters and Genome-Wide Association Studies for Anti-Müllerian Hormone Levels and Antral Follicle Populations Measured After Estrus Synchronization in Nellore Cattle. Animals, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L. M. , Rosa, G. J. M., Lopes, F. B., Regitano, L. C. A., Rosa, A. J. M., & Magnabosco, C. U. Genomewide association mapping and pathway analysis of meat tenderness in Polled Nellore cattle1. Journal of Animal Science 2017, 95(5), 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D. O. , Fernandes Júnior, G. A., Fonseca, L. F. S., Mota, L. F. M., Bresolin, T., Carvalheiro, R., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide association study for stayability at different calvings in Nellore beef cattle. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Alves, A. A. C. , Da Costa, R. M., Fonseca, L. F. S., Carvalheiro, R., Ventura, R. V., Rosa, G. J. D. M., & Albuquerque, L. G. A Random Forest-Based Genome-Wide Scan Reveals Fertility-Related Candidate Genes and Potential Inter-Chromosomal Epistatic Regions Associated with Age at First Calving in Nellore Cattle. Frontiers in Genetics, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, G. , Neves, H. H. R., Camargo, G. M. F., Cardoso, V., Munari, D. P., & Carvalheiro, R. Genome-wide association study and functional analysis of feet and leg conformation traits in Nellore cattle. Journal of Animal Science, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P. I. , Mota, L. F. M., Fonseca, L. F. S., Dos Santos Silva, D. B., Frezarim, G. B., Arikawa, L. M., De Abreu Santos, D. J., Magalhães, A. F. B., Cole, J. B., Carvalheiro, R., De Oliveira, H. N., Null, D. J., VanRaden, P., Ma, L., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Identification of candidate lethal haplotypes and genomic association with post-natal mortality and reproductive traits in Nellore cattle. Scientific Reports, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M. S. , Pedrosa, V. B., Rocha Da Cruz, V. A., Silva, M. R., & Batista Pinto, L. F. Genome-wide association and functional annotation analysis for the calving interval in Nellore cattle. Theriogenology. [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, Y. T. , Do Carmo, A. S., Carvalheiro, R., Neves, H. H., Matos, M. C., Zavarez, L. B., Pérez O’Brien, A. M., Sölkner, J., McEwan, J. C., Cole, J. B., Van Tassell, C. P., Schenkel, F. S., Da Silva, M. V., Porto Neto, L. R., Sonstegard, T. S., & Garcia, J. F. Genome-wide association study for birth weight in Nellore cattle points to previously described orthologous genes affecting human and bovine height. BMC Genetics. [CrossRef]
- Carreño, L. O. D. , Da Conceição Pessoa, M., Espigolan, R., Takada, L., Bresolin, T., Cavani, L., Baldi, F., Carvalheiro, R., De Albuquerque, L. G., & Da Fonseca, R. Genome Association Study for Visual Scores in Nellore Cattle Measured at Weaning. BMC Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Terakado, A. P. N. , Costa, R. B., De Camargo, G. M. F., Irano, N., Bresolin, T., Takada, L., Carvalho, C. V. D., Oliveira, H. N., Carvalheiro, R., Baldi, F., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome-wide association study for growth traits in Nelore cattle. Animal, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R. P. , Espigolan, R., Berton, M. P., Stafuzza, N. B., Santos, F. S., Negreiros, M. P., Schuchmann, R. K., Rodriguez, J. D., Lôbo, R. B., Banchero, G., Pereira, A. S. C., Bergmann, J. A. G., & Baldi, F. Genetic parameters and genomic regions associated with calving ease in primiparous Nellore heifers. Livestock Science, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R. P. D. Genomic selection and genome-wide association study with carcass composition indicator traits in Nellore cattle. Doutorado em Qualidade e Produtividade Animal, Universidade de São Paulo, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Júnior, G. A. F. , Costa, R. B., De Camargo, G. M. F., Carvalheiro, R., Rosa, G. J. M., Baldi, F., Garcia, D. A., Gordo, D. G. M., Espigolan, R., Takada, L., Magalhães, A. F. B., Bresolin, T., Feitosa, F. L. B., Chardulo, L. A. L., De Oliveira, H. N., & De Albuquerque, L. G. Genome scan for postmortem carcass traits in Nellore cattle1. Journal of Animal Science, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M. H. A. , Freua, M. C., Do, D. N., Ventura, R. V., Kadarmideen, H. N., & Ferraz, J. B. S. Systems genetics and genome-wide association approaches for analysis of feed intake, feed efficiency, and performance in beef cattle. Genetics and Molecular Research. [CrossRef]
- Medeiros de Oliveira Silva, R. , Bonvino Stafuzza, N., de Oliveira Fragomeni, B., Miguel Ferreira de Camargo, G., Matos Ceacero, T., Noely Dos Santos Gonçalves Cyrillo, J., Baldi, F., Augusti Boligon, A., Zerlotti Mercadante, M. E., Lino Lourenco, D., Misztal, I., & Galvão de Albuquerque, L. Genome-Wide Association Study for Carcass Traits in an Experimental Nelore Cattle Population. PloS one, 0169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M. E. , Baldi, F. S., Alexandre, P. A., Santana, M. H. A., Ventura, R. V., Bueno, R. S., Bonin, M. N., Rezende, F. M., Coutinho, L. L., Eler, J. P., & Ferraz, J. B. S. Research Article Genomic regions and genes associated with carcass quality in Nelore cattle. Genetics and Molecular Research. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P. S. , Cesar, A. S., do Nascimento, M. L., Chaves, A. S., Tizioto, P. C., Tullio, R. R., Lanna, D. P., Rosa, A. N., Sonstegard, T. S., Mourao, G. B., Reecy, J. M., Garrick, D. J., Mudadu, M. A., Coutinho, L. L., & Regitano, L. C. Identification of genomic regions associated with feed efficiency in Nelore cattle. BMC genetics. [CrossRef]

| 1Trait groups | Studies | Genomic regions | Candidate genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reproduction | 23 | 605 | 8 569 |
| Sexual precocity | 19 | 387 | 5 412 |
| Carcass | 14 | 607 | 11 195 |
| Meat quality | 8 | 294 | 6 646 |
| Growth | 12 | 360 | 5 239 |
| Efficiency | 7 | 217 | 3 319 |
| Morphological | 5 | 189 | 3 483 |
| Visual scores | 3 | 132 | 2 114 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




