Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction:
Neutrophils
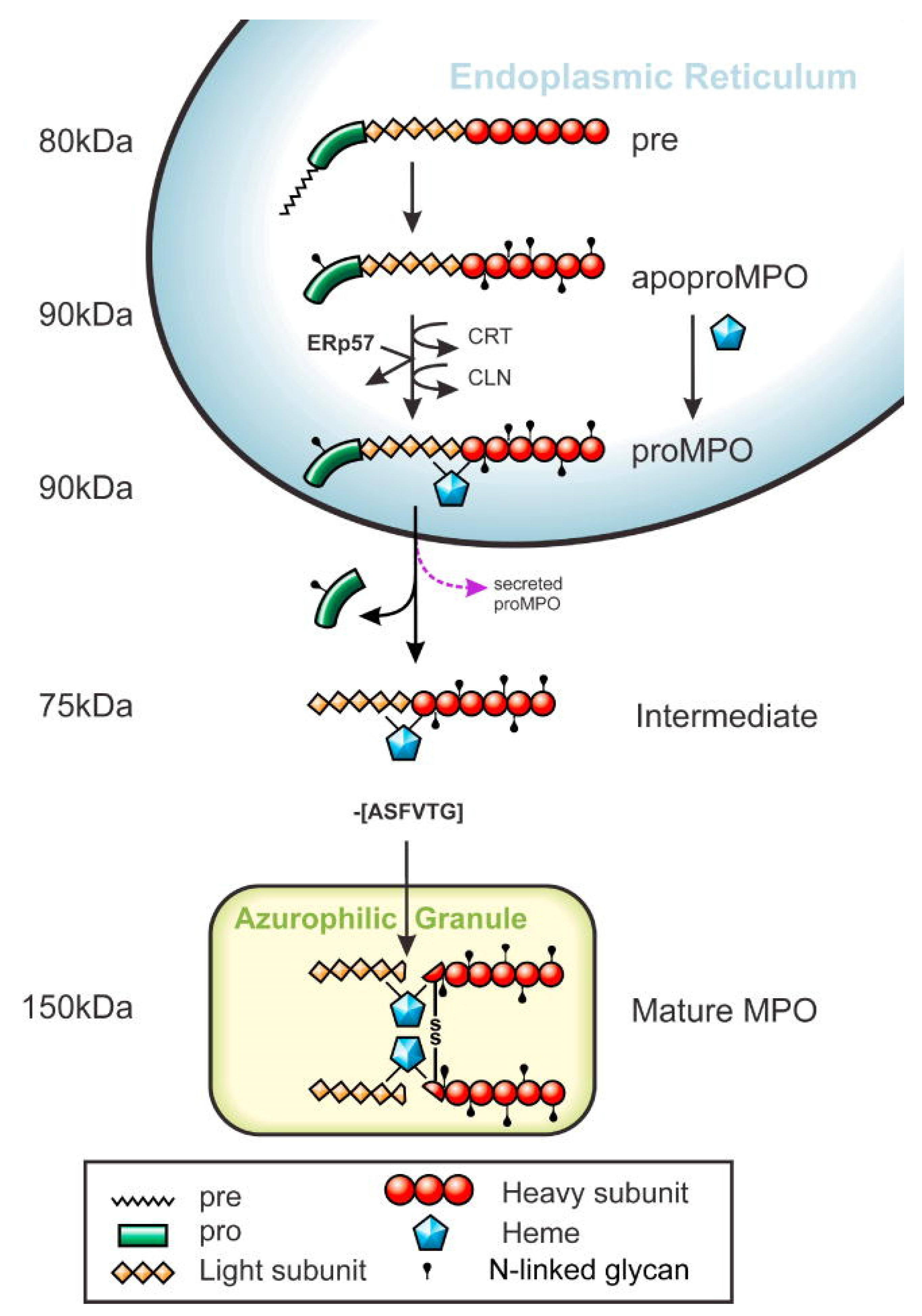
Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
MPO and Immune System
MPO in Diseases
MPO and Cancer
MPO and Cardiovascular Diseases
MPO and Nervous System
MPO Inhibition
Concluding remarks
Funding
Declaration of competing interest
References
- Németh, T.; Sperandio, M.; Mócsai, A. Neutrophils as emerging therapeutic targets. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2020, 19, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroca-Crevillén, A.; Adrover, J.M.; Hidalgo, A. Circadian features of neutrophil biology. Frontiers in Immunology. 2020, 11, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Role of myeloperoxidase and oxidant formation in the extracellular environment in inflammation-induced tissue damage. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2021, 172, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fousert, E.; Toes, R.; Desai, J. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) take the central stage in driving autoimmune responses. Cells. 2020, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndrepepa, G. Myeloperoxidase–A bridge linking inflammation and oxidative stress with cardiovascular disease. Clinica chimica acta. 2019, 493, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.P.; Segal, A.W. The NADPH oxidase and microbial killing by neutrophils, with a particular emphasis on the proposed antimicrobial role of myeloperoxidase within the phagocytic vacuole. Myeloid Cells in Health and Disease: A Synthesis. 2017, 599–613. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Veen, B.S.; de Winther, M.P.; Heeringa, P. Myeloperoxidase: molecular mechanisms of action and their relevance to human health and disease. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 2009, 11, 2899–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, D.C.; Gomez Mejiba, S.E. Pulmonary Neutrophilic Inflammation and Noncommunicable Diseases: Pathophysiology, Redox Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutics. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2020, 33, 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef, W.M. Biosynthesis of human myeloperoxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018, 642, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnhold, J. The Dual Role of Myeloperoxidase in Immune Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. Journal of investigative dermatology. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-M.; Wang, M.-H.; Soung, H.-S.; Tseng, H.-C.; Fang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-W.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of l-theanine in a rat model of chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve-induced neuropathic pain. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association. 2022, 121, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, R.; Al Talebi, Z.A.; Al-Kawaz, H.S.; Alta'ee, A.H.; Alsalman, A.R.S.; Hadwan, A.M.; et al. Novel fluorometric protocol for assessing myeloperoxidase activity. Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 2023, 171, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Cosmes, P.; Raftopoulou, S.; Mihalic, Z.N.; Marsche, G.; Kargl, J. Myeloperoxidase: Growing importance in cancer pathogenesis and potential drug target. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2022, 236, 108052. [Google Scholar]
- Rizo-Téllez, S.A.; Sekheri, M.; Filep, J.G. Myeloperoxidase: regulation of neutrophil function and target for therapy. Antioxidants. 2022, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratani, Y. Myeloperoxidase: Its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 2018, 640, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kebir, D.; József, L.; Pan, W.; Filep, J.n.G. Myeloperoxidase delays neutrophil apoptosis through CD11b/CD18 integrins and prolongs inflammation. Circulation research. 2008, 103, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, V.M.; Rovira-Llopis, S.; Banuls, C.; Diaz-Morales, N.; Martinez de Maranon, A.; Rios-Navarro, C.; et al. Insulin resistance in PCOS patients enhances oxidative stress and leukocyte adhesion: role of myeloperoxidase. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0151960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang W-w Wu, L.; Lu, W.; Chen, W.; Yan, W.; Qi, C.; et al. Lipopolysaccharides increase the risk of colorectal cancer recurrence and metastasis due to the induction of neutrophil extracellular traps after curative resection. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2021, 147, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeindler, J.; Angehrn, F.; Droeser, R.; Däster, S.; Piscuoglio, S.; Ng, C.K.; et al. Infiltration by myeloperoxidase-positive neutrophils is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Breast cancer research and treatment. 2019, 177, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y.; Sano, M.; Kajiwara, I.; Ichimaru, Y.; Itaya, T.; Kuramochi, T.; et al. Midazolam exhibits antitumour and anti-inflammatory effects in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. British journal of anaesthesia. 2022, 128, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Myeloperoxidase as an active disease biomarker: recent biochemical and pathological perspectives. Medical sciences. 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangie, C.; Daher, J. Role of myeloperoxidase in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Biomedical reports. 2022, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandra, C.J.; Ja, K.M.M.; Chua, J.; Cong, S.; Shim, W.; Hausenloy, D.J. Myeloperoxidase as a multifaceted target for cardiovascular protection. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 2020, 32, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Janus, S.E.; Hajjari, J.; Chami, T.; Karnib, M.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Rashid, I. Myeloperoxidase is independently associated with incident heart failure in patients with coronary artery disease and kidney disease. Current Problems in Cardiology. 2022, 47, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, L.C.; Murray, H.C.; Hill, M.; van Leeuwen, E.; Highet, B.; Magon, N.J.; et al. Neutrophil-vascular interactions drive myeloperoxidase accumulation in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 2022, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wu, Y.; Pulli, B.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Iwamoto, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Myeloperoxidase molecular MRI reveals synergistic combination therapy in murine experimental autoimmune neuroinflammation. Radiology. 2019, 293, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, R.A.; Holzer, M.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Malle, E.; Masliah, E.; Marsche, G.; et al. Human myeloperoxidase (hMPO) is expressed in neurons in the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease and in the hMPO-α-synuclein-A53T mouse model, correlating with increased nitration and aggregation of α-synuclein and exacerbation of motor impairment. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2019, 141, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.; Yue, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhou, C.; Guo, M.; Sun, C.; et al. Increased MPO in colorectal cancer is associated with high peripheral neutrophil counts and a poor prognosis: A TCGA with propensity score-matched analysis. Frontiers in Oncology. 2022, 12, 940706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymaszewski, A.L.; Tate, E.; Yimbesalu, J.P.; Gelman, A.E.; Jarzembowski, J.A.; Zhang, H.; et al. The role of neutrophil myeloperoxidase in models of lung tumor development. Cancers. 2014, 6, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsis, M.; Drosou, P.; Tatsis, V.; Markopoulos, G.S. Neutrophil extracellular traps and pancreatic cancer development: a vicious cycle. Cancers. 2022, 14, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangeten, C.; Zouaoui Boudjeltia, K.; Delporte, C.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Korpak, K. Unexpected role of MPO-oxidized LDLs in atherosclerosis: In between inflammation and its resolution. Antioxidants. 2022, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Aiyasiding, X.; Li, W.-J.; Liao, H.-H.; Tang, Q.-Z. Neutrophil degranulation and myocardial infarction. Cell Communication and Signaling. 2022, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inghardt, T.; Antonsson, T.; Ericsson, C.; Hovdal, D.; Johannesson, P.; Johansson, C.; et al. Discovery of AZD4831, a mechanism-based irreversible inhibitor of myeloperoxidase, as a potential treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2022, 65, 11485–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, L.C.; Murray, H.C.; Hill, M.; van Leeuwen, E.; Highet, B.; Magon, N.J.; et al. Neutrophil-vascular interactions drive myeloperoxidase accumulation in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta neuropathologica communications. 2022, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, N.; Yevgi, R.; Kızıldağ, N.; Kızıltunç, A. Low Serum Myeloperoxidase Levels in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. New Trends in Medicine Sciences. 2021, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gellhaar, S.; Sunnemark, D.; Eriksson, H.; Olson, L.; Galter, D. Myeloperoxidase-immunoreactive cells are significantly increased in brain areas affected by neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell and tissue research. 2017, 369, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandolara, T.B.; Panis, C. Neutrophil traps, anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies and cancer: Are they linked? Immunology Letters. 2020, 221, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betten Å, Dahlgren C, Mellqvist U-H, Hermodsson S, Hellstrand K. Oxygen radical-induced natural killer cell dysfunction: role of myeloperoxidase and regulation by serotonin. Journal of Leucocyte Biology. 2004, 75, 1111–1115.
- Aloe, C.; Wang, H.; Vlahos, R.; Irving, L.; Steinfort, D.; Bozinovski, S. Emerging and multifaceted role of neutrophils in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2806–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhamme, L.; Boudjeltia, K.Z.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Delporte, C. The other myeloperoxidase: Emerging functions. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 2018, 649, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Lian, S.; et al. A neutrophil extracellular traps-related classification predicts prognosis and response to immunotherapy in colon cancer. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 19297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Bian, J.; Yi, H.; et al. Identifying neutrophil-associated subtypes in ulcerative colitis and confirming neutrophils promote colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1095098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulos, V.; Leach, D.A.; Zinonos, I.; Ponomarev, V.; Licari, G.; Liapis, V.; et al. Inflammatory peroxidases promote breast cancer progression in mice via regulation of the tumour microenvironment. International journal of oncology. 2017, 50, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás-Pérez, S.; Oto, J.; Aghababyan, C.; Herranz, R.; Cuadros-Lozano, A.; González-Cantó, E.; et al. Increased levels of NETosis biomarkers in high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients' biofluids: Potential role in disease diagnosis and management. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saed, G.M.; Nawaz, A.; Alvero, A.A.; Harper, A.K.; Morris, R.T. Monomeric myeloperoxidase is a specific biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer. Biomarkers. 2023, 28, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sincan, S.; Sincan, G.; Aşkın, S.; Kızıltunç, A. Evaluation of Serum Paraoxonase, Myeloperoxidase, and HDL-Cholesterol Levels in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Inflammation. 2023, 46, 2470–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Andrés Juan, C.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Superoxide Anion Chemistry-Its Role at the Core of the Innate Immunity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. HOCl-dependent singlet oxygen and hydroxyl radical generation modulate and induce apoptosis of malignant cells. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3589–3602. [Google Scholar]
- Nadel, J.; Jabbour, A.; Stocker, R. Arterial myeloperoxidase in the detection and treatment of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: a new dawn for an old light. Cardiovasc Res. 2023, 119, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Lu, Y.-B.; Huang, X.-L.; Lao, Y.-F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Myeloperoxidase: a new target for the treatment of stroke? Neural Regeneration Research. 2022, 17, 1711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, S.; Kugiyama, K.; Aikawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ogawa, H.; Libby, P. Hypochlorous acid, a macrophage product, induces endothelial apoptosis and tissue factor expression: involvement of myeloperoxidase-mediated oxidant in plaque erosion and thrombogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004, 24, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopowicz, Z.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Katz, D.R.; Chain, B.M. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase: soldier and statesman. Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis. 2012, 60, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadhan, S.; Ramesh, V.; Jawahar, R.; Pai, M.M.; Simon, A.S. OxLDL/HDL ratio and its correlation to myeloperoxidase activity in ACS patients. International Journal of Health Sciences. (II):10438-46. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Doctor, B.; Verma, M.K.; Vamne, A. Myeloperoxidase and troponin T are linked with myocardial infarction among young Indians. Bioinformation. 2022, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulendijks, E.R.; Al-Shama, R.F.M.; Kawasaki, M.; Fabrizi, B.; Neefs, J.; Wesselink, R.; et al. Atrial epicardial adipose tissue abundantly secretes myeloperoxidase and activates atrial fibroblasts in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Transl Med. 2023, 21, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Zhou, T.; Bao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Plasma myeloperoxidase: association with atrial fibrillation progression and recurrence after catheter ablation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023, 10, 1150324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; Sun, L.; Guo, D.; et al. Association between myeloperoxidase and the risks of ischemic stroke, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023, 33, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettersheim, F.S.; Schlüter, J.D.; Kreuzberg, W.; Mehrkens, D.; Grimm, S.; Nemade, H.; et al. Myeloperoxidase is a critical mediator of anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol. 2023, 118, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.D.; Anthopolos, R.; Ruggles, K.V.; Cornwell, M.; Reynolds, H.R.; Bangalore, S.; et al. Biomarkers and cardiovascular events in patients with stable coronary disease in the ISCHEMIA Trials. Am Heart J. 2023, 266, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Aiyasiding, X.; Li, W.J.; Liao, H.H.; Tang, Q.Z. Neutrophil degranulation and myocardial infarction. Cell Commun Signal. 2022, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Hazen, S.L. Myeloperoxidase and cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005, 25, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollenhauer, M.; Friedrichs, K.; Lange, M.; Gesenberg, J.; Remane, L.; Kerkenpaß, C.; et al. Myeloperoxidase mediates postischemic arrhythmogenic ventricular remodeling. Circulation research. 2017, 121, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smorodinova, N.; Blaha, M.; Melenovský, V.; Rozsivalova, K.; Přidal, J.; Ďurišová, M.; et al. Analysis of immune cell populations in atrial myocardium of patients with atrial fibrillation or sinus rhythm. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0172691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikijurajai, T.; Tang, W.H.W. Myeloperoxidase: a potential therapeutic target for coronary artery disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020, 24, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraya, H.; Farajnia, S.; Khani, S.; Rameshrad, M.; Khorrami, A.; Banani, A.; et al. Short-term treatment with metformin suppresses toll like receptors (TLRs) activity in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rat: are AMPK and TLRs connected? International immunopharmacology. 2012, 14, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Javidmehr, A.; Askari, B.; Janssen, P.M.; Soraya, H. Memantine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, attenuates cardiac remodeling, lipid peroxidation and neutrophil recruitment in heart failure: A cardioprotective agent? Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2018, 108, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Javidmehr, A.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Kian, M.; Hamedeyazdan, S.; Soraya, H. Hydroalcoholic extract of Arum orientale ameliorates myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol in rats. J Res Pharm. 2021, 25, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, K.; Soraya, H.; Fathiazad, F.; Khorrami, A.; Hamedeyazdan, S.; Maleki-Dizaji, N.; et al. Cardioprotective effect of methanolic extract of Marrubium vulgare L. on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction in rats. 2013.
- Jannesar, K.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Malekinejad, H.; Soraya, H. Cardioprotective effects of memantine in myocardial ischemia: Ex vivo and in vivo studies. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2020, 882, 173277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, D.L.; Lefkowitz, S.S. Microglia and myeloperoxidase: a deadly partnership in neurodegenerative disease. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2008, 45, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravalika, K.; Sarmah, D.; Kaur, H.; Wanve, M.; Saraf, J.; Kalia, K.; et al. Myeloperoxidase and neurological disorder: a crosstalk. ACS chemical neuroscience. 2018, 9, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Katyal, A. Myeloperoxidase: bridging the gap in neurodegeneration. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2016, 68, 611–620. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.R.; Deen, Q.F.E.; Stevenson, A.; Telford-Cooke, L.L.; Parker, C.; Martin-Ruiz, C.; et al. Plasma Myeloperoxidase as a Potential Biomarker of Patient Response to Anti-Dementia Treatment in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 89, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.T.; Sharma, R.; Lim, J.L.; Haider, L.; Frischer, J.M.; Drexhage, J.; et al. NADPH oxidase expression in active multiple sclerosis lesions in relation to oxidative tissue damage and mitochondrial injury. Brain. 2012, 135, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzepa, A.; Pritchard, K.A.; Dittel, B.N. Myeloperoxidase: A new player in autoimmunity. Cellular immunology. 2017, 317, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, J. The dual role of myeloperoxidase in immune response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020, 21, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska-Pniewska, B.; Styczynska, M.; Podlecka, A.; Samocka, R.; Peplonska, B.; Barcikowska, M.; et al. Association of apolipoprotein E and myeloperoxidase genotypes to clinical course of familial and sporadic multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2004, 10, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, R.L.; Benner, E.J.; Kadiu, I.; Thomas, M.; Boska, M.D.; Hasan, K.; et al. Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Clinical neuroscience research. 2006, 6, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpraman N, Yoon S, Kim CY, Moon JS, Yi SS. NOX4 as a critical effector mediating neuroinflammatory cytokines, myeloperoxidase and osteopontin, specifically in astrocytes in the hippocampus in Parkinson's disease. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102698.
- Talarowska, M.; Szemraj, J.; Gałecki, P. Myeloperoxidase gene expression and cognitive functions in depression. Adv Med Sci. 2015, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, M.; Zarghani, S.S.; Milani, M.M.; Soraya, H. Pre-treatment with metformin in comparison with post-treatment reduces cerebral ischemia reperfusion induced injuries in rats. Bulletin of Emergency & Trauma. 2018, 6, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanein, E.H.M.; Saleh, F.M.; Ali, F.E.M.; Rashwan, E.K.; Atwa, A.M.; Abd El-Ghafar, O.A.M. Neuroprotective effect of canagliflozin against cisplatin-induced cerebral cortex injury is mediated by regulation of HO-1/PPAR-γ, SIRT1/FOXO-3, JNK/AP-1, TLR4/iNOS, and Ang II/Ang 1-7 signals. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023, 45, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrhaghighi, G.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Babataheri, S.; Garjani, A.; Soraya, H. Effects of pre-treatment with metoprolol and diltiazem on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injuries. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2023, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, C.; Seiiedy, M.; Soraya, H.; Fazli, F.; Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M. Pretreatment with bisoprolol and vitamin E alone or in combination provides neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 2021, 394, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babataheri, S.; Malekinejad, H.; Mosarrezaii, A.; Soraya, H. Pre-treatment or post-treatment with hydroxychloroquine demonstrates neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology. 2023, 37, 589–598. [Google Scholar]
- Acik, V.; Kulahcı, O.; Arslan, A.; İstemen, İ.; Olguner, S.K.; Arslan, B.; et al. The Impact of Myeloperoxidase in the Rupturing of Cerebral Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2021, 147, e105–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Wei, Y.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Chen, J.W. Reducing myeloperoxidase activity decreases inflammation and increases cellular protection in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joaquim, L.S.; Danielski, L.G.; Bonfante, S.; Biehl, E.; Mathias, K.; Denicol, T.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation increases brain oxidative stress after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Neurosci. 2023, 133, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wei, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Moskowitz, M.A.; et al. Myeloperoxidase Inhibition Increases Neurogenesis after Ischemic Stroke. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016, 359, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, I.; Tagzirt, M.; Gautier, S.; Dupont, A.; Mendyk, A.M.; Susen, S.; et al. Analysis of the association of MPO and MMP-9 with stroke severity and outcome: Cohort study. Neurology. 2020, 95, e97–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, M.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Zou, X.H.; Mao, L.L. The value of serum Lp-PLA2 combined with MPO in the diagnosis of cerebral infarction caused by large artery atherosclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2023, 232, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galijasevic, S. The development of myeloperoxidase inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2019, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Sui, Y.; Tian, R.; Peng, Y.-Y. Inhibitive effects of quercetin on myeloperoxidase-dependent hypochlorous acid formation and vascular endothelial injury. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2018, 66, 4933–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witting, P.K. Hypochlorous acid generated in the heart following acute ischaemic injury promotes myocardial damage: a new target for therapeutic development.
- Chaikijurajai, T.; Tang, W.W. Myeloperoxidase: a potential therapeutic target for coronary artery disease. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2020, 24, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarevic-Pasti, T.; Leskovac, A.; Vasic, V. Myeloperoxidase inhibitors as potential drugs. Current drug metabolism. 2015, 16, 168–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Keat, K. Myeloperoxidase and associated lung disease: Review of the latest developments. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases. 2021, 24, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kang, I.S.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine selectively regulates neutrophil degranulation through the inhibition of myeloperoxidase and upregulation of lactoferrin. Amino acids. 2020, 52, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Du, Q.; Shen, J. Targeting myeloperoxidase (MPO) mediated oxidative stress and inflammation for reducing brain ischemia injury: Potential application of natural compounds. Frontiers in physiology. 2020, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Talib, J.; Stanley, C.P.; Rashid, I.; Michaëlsson, E.; Lindstedt, E.-L.; et al. Inhibition of MPO (myeloperoxidase) attenuates endothelial dysfunction in mouse models of vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2019, 39, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Pulli, B.; Courties, G.; Tricot, B.; Sebas, M.; Iwamoto, Y.; et al. Myeloperoxidase inhibition improves ventricular function and remodeling after experimental myocardial infarction. JACC: Basic to Translational Science. 2016, 1, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosic-Mujkanovic, N.; Valadez-Cosmes, P.; Maitz, K.; Lueger, A.; Mihalic, Z.N.; Runtsch, M.C.; et al. Myeloperoxidase Alters Lung Cancer Cell Function to Benefit Their Survival. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaëlsson, E.; Lund, L.H.; Hage, C.; Shah, S.J.; Voors, A.A.; Saraste, A.; et al. Myeloperoxidase Inhibition Reverses Biomarker Profiles Associated With Clinical Outcomes in HFpEF. JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.W.; Gammon, S.T.; Yang, P.; Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Inhibition of myeloperoxidase enhances immune checkpoint therapy for melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Milton, A.; Arnold, R.D.; Huang, H.; Smith, F.; Panizzi, J.R.; et al. Methods for measuring myeloperoxidase activity toward assessing inhibitor efficacy in living systems. Journal of Leucocyte Biology. 2016, 99, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diseases | Results | Pathological/Protective Role |
|---|---|---|
| Colon Cancer | High levels of MPO was observed in CRC tumors that can be considered as worse survival factor in patients [29]. | Pathological Role |
| Breast Cancer | Penetration of MPO-positive cells is a new factor for improving survival of patients with breast cancer [20] | Protective Role |
| Lung Cancer | Inhibition of MPO leads to reducing size and number of lung tumors and can be used as a protection agent of lung cancer [30] | Pathological Role |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Increasing levels of NETs (such as MPO) are significantly related to tumor progression and malignancy of Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [31] | Pathological role |
| Arthrosclerosis | MPO contributes to arteriosclerosis by disrupting the function of endothelial cells, oxidation of LDL, and a high level of MPO is observed in all lesions of this disease [32]. | Pathological Role |
| Myocardial Infarction | Reduced level of MPO and neutrophils is significantly contributed to decreased amount of myocardial infarction injury [33] | Pathological Role |
| Heart Failure | Irreversible inhibition of MPO leads to reduced rate of heart failure injuries and also improving quality of life in patients with heart failure [34] | Pathological Role |
| Alzheimer Disease | The increase in the adhesion of neutrophils and the amount of MPO caused by neutrophils causes vascular oxidative stress and can be one of the therapeutic goals of Alzheimer's disease [35]. | Pathological Role |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Patients with multiple sclerosis have shown low serum levels of MPO, and low levels of MPO play an important role in the pathogenesis of this disease [36]. | Protective Role |
| Parkinson Disease | High levels of MPO is observed in some brain areas related to this disease (such as putamen, caudate nucleus, and substantianigra) [37] | Pathological Role |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




