Submitted:
02 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
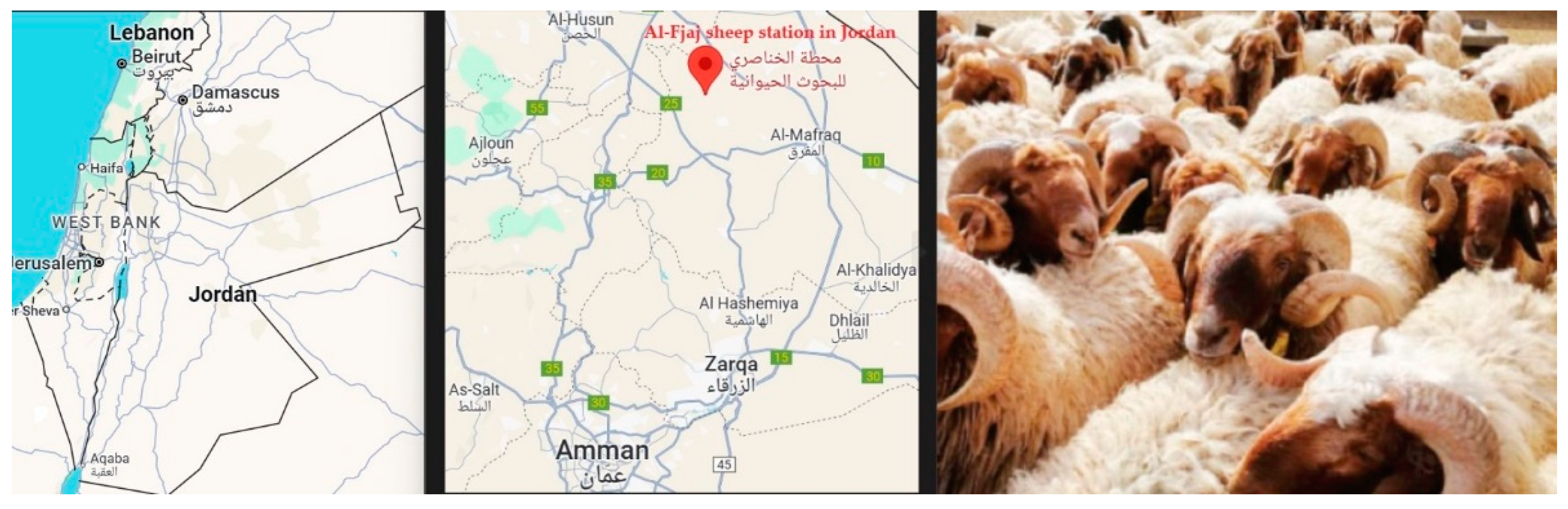
2.1. the location
2.2. The sheep care
2.3. Data analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Barakeh, F.; Khashroum, A.O.; Tarawneh, R.A.; Al-Lataifeh, F.A.; Al-Yacoub, A.N.; Dayoub, M.; Al-Najjar, K. Sustainable Sheep and Goat Farming in Arid Regions of Jordan. Ruminants 2024, 4, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, R.; Al-Azzawi, W.; Al-Najjar, K.; Masri, Y.; Salhab, S.; Abdo, Z.; El-Herek, I.; Omed, H.; Saatci, M. Factors influencing the milk production of Awassi sheep in a flock with the selected lines at the Agricultural Scientific Research Centre. Kafkas Univ. Vet Fak Derg. 2010, 16, 425-430. Available online: https://vetdergikafkas.org/ uploads/pdf/pdf_KVFD_667.pdf.
- Al-Momani, A.; Ata, M.; Al-Najjar, K. Evaluation of Weight and Growth Rates of Awassi Sheep Lambs. Asian Journal of Research in Animal and Veterinary Sciences 2020, 5, 26-32. Available online: https://www.journalajravs.com/ index.php/ AJRAVS/article/view/114/227.
- Al-Najjar, K., A.Q. Al-Momani, A.N. Al-Yacoub, A. Elnahas, Reda Elsaid. Estimation of Genetic Parameters and Non-Genetic Factors for Milk Yield and Litter Size at Birth of Awassi Sheep in Drylands, 2022, Vol. 17, No. 2, P: 19-2. Available online: https://ejsgs.journals.ekb.eg/article_266898.html.
- Al-Najjar, K.; Al-Momani, A.; Al-Yacoub, A.; Elsaid, R. Evaluation of Some Productive Characteristics of Jordanian Awassi. International Journal of Livestock Research, /: 11, 1-6. https; 11.
- Alkass, J.E.; Hermiz, H.N.; Baper, M.I. Some aspects of reproductive efficiency in Awassi ewes: A review. Iraqi Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2021, 52, 20-27. 20-27. https. Available online: https://jcoagri.uobaghdad.edu.iq/index.php/intro/article/view/1232.
- Gootwine, E.; Zenu, A.; Bor, A.; Yossafi, S.; Rosov, A.; Pollott, G.E. Genetic and economic analysis of introgression of the B allele of the FecB (Booroola) gene into the Awassi and Assaf dairy breeds. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2001, 71, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, S.; Gürsoy, O.; Shaat, I. Awassi sheep as a genetic resource and efforts for their genetic improvement—A review. Small Ruminant Research 2008, 79, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karablieh, E.K.; Jabarin, A.S. Different rangeland management systems to reduce livestock feeding costs in arid and semi-arid areas in Jordan. Quarterly Journal of International Agriculture 2010, 49, 91-109. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/155543/?v=pdf.
- SAS, Institute Inc.: SAS/STAT User’s Guide: Version 9.1, 2003, SAS Institute Inc., and Cary, NC, USA. https://www.sas.com/en_us/software/stat.html.
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics, 1955, 11, 1-42. Available online: http://176.9.41.242/doc/statistics/1955-duncan.pdf.
- Becker, W.A. A Fortran Program for testing and analyzing multiple comparisons. Journal of Educational Statistics 1992, 17, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjosubroto, P. Breeding value of sires based on offspring weaning weight as a recommendation for selecting kebumen ongole grade cattle. Journal of Animal Science 1994, 72, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar]
- Gbangboche, A.; Adamou-Ndiaye, M.; Youssao, A.; Farnir, F.; Detilleux, J.; Abiola, F.; Leroy, P. Non-genetic factors affecting the reproduction performance, lamb growth, and productivity indices of Djallonke sheep. Small Ruminant Research 2006, 64, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahala, S.; Saini, S.; Kumar, A.; Prince, L.; Gowane, G. Effect of non-genetic factors on growth traits of Avikalin sheep. Small Ruminant Research 2019, 174, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, B.A.; Salifu, S.; Asumah, C.; Yeboah, E.D.; Boa-Amponsem, K. Effects of genetic and non-genetic factors on body weight, pre-weaning growth, birth type and pre-weaning survivability of lambs in a sheep nucleus station. Department of Animal Production and Health 2022, 34. Available online: https://www.lrrd.cipav.org.co/lrrd34/4/3430bern.html.
- Luis, J.; Victoria, M.; Feyjoo, P.; Cáceres, E.; Hernández, F.; Vicente, J.; Astiz, S. Influence of Maternal Factors (Weight, Body Condition, Parity, and Pregnancy Rank) on Plasma Metabolites of Dairy Ewes and Their Lambs. Animals 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaña-Monforte, J.G.; Huchin-Cab, M.; Ake-López, R.J.; et al. A field study of reproductive performance and productivity of Pelibuey ewes in Southeastern Mexico. Trop Anim Health Prod 2013, 45, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Allah, M. Effects of parity and nutrition plane during late pregnancy on metabolic responses, colostrum production and lamb output of Rahmani ewes. Egyptian Journal of Animal Production 2013, 50, 132-142. Available online: https://ejap. journals.ekb.eg/article_93673_fefee43ee4a0271dfca101a8809e7527.pdf.
- Walkom, S.F.; Brown, D.J. Genetic evaluation of adult ewe bodyweight and condition: relationship with lamb growth, reproduction, carcass and wool production. Animal Production Science 2016, 57, 20-32. Available online: https://www. publish. csiro.au/AN/AN15091.
- Caro-Petrović, V.; Petrović, M.P.; Ružić-Muslić, D.; Maksimović, N.; Sycheva, I.N.; Cekić, B.; Ćosić, I. Interrelation between body weights of sire, dam and their lambs at early stage of growth. Biotechnology in Animal Husbandry 2020, 36, 205-214. Available online: https://doiserbia.nb.rs/Article.aspx?id=1450-91562002205C.
- Kader Esen, V. ; Elmacı; C. The Estimation of Live Weight from Body Measurements in Different Meat-Type Lambs. Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2021, 27, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Dávila, F.; Bernal-Barragán, H.; Padilla-Rivas, G.; et al. Environmental factors and ram influence litter size, birth, and weaning weight in Saint Croix hair sheep under semi-arid conditions in Mexico. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2015, 47, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, M.M.; El-wakeel, E.L.A.; Ahmed, M.H.; Zahran, S.M.; EL-Rewany, A.M. Effect of breed of ram on reproductive performance of Barki ewes and their lambs. Alexandria Science Exchange Journal 2013, 34, 222-227. Available online: https://journals.ekb.eg/article_3041_607f55a38b44d551da923d70fad00e79.pdf.
- Aktaş, A.H.; Dursun, Ş.; Doğan, Ş.; Kiyma, Z.; Demirci, U.; Halıcı; İ. Effects of ewe live weight and age on reproductive performance, lamb growth, and survival in Central Anatolian Merino sheep. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2015, 58, 451–459. Available online: https://aab.copernicus.org/articles/58/451/2015/aab-58-451-2015. pdf.
- Petrovic, M.P.; Muslic, D.R.; Petrovic, V.C.; Maksimovic, N. Influence of environmental factors on birth weight variability of indigenous Serbian breeds of sheep. African journal of Biotechnology 2011, 10, 4673-4676. Available online: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/view/94136.
- Kramarenko, A.S.; Markowska, A.V.; Salamatina, O.O.; Kravchenko, O.O.; Kramarenko, S.S. Genetic and environmental factors influenced the birth and weaning weight of lambs. Ukrainian Journal of Ecology 2021, 11, 195-201. Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/genetic-and-environmental-factors-influenced-the-birth-and-weaning-weight-of-lambs.
- El-Wakil, S.I.; Elsayed, M. Genetic, phenotypic and environmental trends towards improving body weight in Barki sheep. Egyptian Journal of Sheep and Goats Sciences 2013, 8, 1-10. Available online: https://journals.ekb.eg/article_26769_ d92ae6e0a45a44fecc73b3aa1ce12cfc.pdf.
- Gizaw, S.; Lemma, S.; Komen, H.; Van Arendonk, J.A. Estimates of genetic parameters and genetic trends for live weight and fleece traits in Menz sheep. Small Ruminant Research 2007, 70, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizaw, S.; Getachew, T.; Tibbo, M.; Haile, A.; Dessie, T. Congruence between selection on breeding values and farmers’ selection criteria in sheep breeding under conventional nucleus breeding schemes. Animal 2015, 5, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizaw, S.; Komen, H.; Van Arendonk, J.A. Participatory definition of breeding objectives and selection indexes for sheep breeding in traditional systems. Livestock Science 2010, 128, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Molano, E.; Kapsona, V.V.; Oikonomou, S.; et al. Breeding strategies for animal resilience to weather variation in meat sheep. BMC Genet 2020, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granleese, T.; Clark, S.A.; Swan, A.A.; et al. Increased genetic gains in sheep, beef and dairy breeding programs from using female reproductive technologies combined with optimal contribution selection and genomic breeding values. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2015, 47, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahek, I.; Ekert kabalin, A.; Menčik, S.; Maurić maljković, M.; Piplica, A.; Kabalin, H.; Šavorić, J.; Sušić, V. The effect of non-genetic factors on the birth weight of Romanov sheep. Vet. arhiv 2021, 91, 615-624. Available online: https://vetarhiv.vef. unizg.hr/ papers/2021-91-6-5.pdf.
- AL-Qasimi, R.H.; Shatha, M.A.; Allawi, L.D.K. Effect of Breed and Some Non-Genetic Factors on Milk Production and Some Proportions of Its Chemical Components in Two Breeds of Local Sheep. Al-Qadisiyah Journal for Agriculture Sciences (QJAS) 2020, 10, 227-231. Available online: http://qu.edu.iq/ jouagr/index.php/QJAS/index.
- Lupi, T.M.; Nogales, S.; León, J.M.; Barba, C.; Delgado, J.V. Analysis of the Non-Genetic Factors Affecting the Growth of Segureño Sheep. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirban, L.K.; Joshi, R.K.; Narula, H.K.; Singh, H.; Bhakar, S. Genetic and non-genetic factors affecting body weights in Marwari sheep. Indian Journal of Small Ruminants 2015, 21, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Pannu, U.; Narula, H.K.; Chopra, A.; Murdia, C.K. Influence of genetic and non-genetic factors on pre-weaning growth in Marwari sheep. Indian Journal of Small Ruminants 2013, 19, 142-145. Available online: https://www. indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijsr&volume=19&issue=2&article=z003.
- Vatankhah, M.; Salehi, S. Genetic and non-genetic factors affecting Lori-Bakhtiari ewe body weight and its relationship with productivity. Small Ruminant Research 2010, 94, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, N.; Makuza, S.M. The Effect of Non-genetic Factors on Birth Weight and Weaning Weight in Three Sheep Breeds of Zimbabwe. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences 2005, 18, 151-157. [CrossRef]
| Traits | Birth Weight |
Weaning Weight | Weight at 6 Months | Annual Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | |||||
| Overall mean | 3.83±0.17 | 16.34±0.93 | 30.15±1.84 | 64.75±2.66 | |
| Birth Type | Single | 4.75±0.03a | 18.30±0.20a | 34.86±0.41a | 60.79±0.59a |
| twins | 4.08±0.04b | 16.57±0.24b | 32.86±0.48b | 58.46±0.69b | |
| Lamb Sex | Male | 4.51±0.04a | 17.85±0.22a | 34.06±0.44a | 60.09±0.62a |
| Female | 4.31±0.04b | 17.03±0.21b | 33.67±0.43a | 59.16±0.63b | |
| Parity | 1st | 4.20±0.05b | 18.19±0.26b | 35.55±0.52b | 56.63±0.75c |
| 2nd | 4.32±0.04ab | 17.21±0.22b | 34.52±0.44c | 57.17±0.64c | |
| 3rd | 4.49±0.04a | 17.92±0.22b | 35.34±0.43b | 59.00±0.62c | |
| 4th | 4.62±0.05a | 16.98±0.29b | 33.49±0.58bc | 58.27±0.84c | |
| 5th | 4.49±0.07ab | 16.88±0.39b | 32.01±0.78bc | 58.28±1.12c | |
| 6th | 4.47±0.09ab | 16.94±0.49b | 29.11±0.97bc | 58.25±1.41c | |
| 7th | 4.51±0.13ab | 16.76±0.69b | 36.56±1.36a | 62.93±1.97b | |
| 8th | 4.20±0.12b | 18.63±0.66a | 37.30±1.31a | 66.45±1.89a | |
| Traits | Weaning Weight | Weight at 6 Months | Annual Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight | 0.17** | 0.07** | 0.02ns |
| Weaning weight | 0.36** | 0.33** | |
| Weight at 6 months | 0.66** |
| Variance component | The weights | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth | Weaning | 6 months | Annual | |
| Vs | 0.02326 | 0.694 | 18.9368 | 38.8642 |
| Vw | 0.53 | 14.55 | 40.96 | 85.48 |
| h2 ± SE | 0.17±0.08 | 0.18±0.07 | 0.32±0.04 | 0.31±.05 |
| Breeding Values | BVBW | BVWW | BVW6M | BVYW | TBV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BV(S) | 0.02±0.01 | -0.11±0.01 | -0.26±0.17 | -0.53±0.15 | -0.97±0.51 |
| BVBW | 0.96** | 0.97** | 0.96** | 0.64** | |
| BVWW | 0.92** | 0.98** | 0.62** | ||
| BVW6M | 0.93** | 0.63** |
| BV(S) | BVBW | BVWW | BVW6M | BVYW | TBV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights | ||||||
| MBW | 0.96** | 0.97** | ||||
| MWW | 0.97** | 0.98** | ||||
| MW6M | 0.99** | 0.99** | ||||
| MYW | 0.95** | 0.97** | ||||
| Rams Rank | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | and so on | 109th | 110th | 111th | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traits | ||||||||
| MBW | 5.22 | 5.34 | 5.14 | … | 3.83 | 3.91 | 2.00 | |
| BVBW | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.49 | … | -0.48 | -0.56 | -0.64 | |
| MWW | 20.99 | 20.83 | 20.39 | … | 15.50 | 15.39 | 15.52 | |
| BVWW | 2.29 | 2.21 | 1.99 | … | -2.06 | -2.30 | -2.34 | |
| MW6M | 43.19 | 42.89 | 42.93 | … | 27.70 | 15.50 | 26.24 | |
| BVW6M | 6.32 | 6.15 | 5.83 | … | -7.15 | -8.00 | -8.52 | |
| MYW | 71.68 | 71.60 | 71.90 | … | 43.78 | 43.89 | 40.54 | |
| BVYW | 10.97 | 10.78 | 10.52 | … | -11.33 | -11.70 | -13.48 | |
| TBV | 20.11 | 19.63 | 18.83 | … | -21.02 | -22.56 | -24.98 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





