Submitted:
12 November 2024
Posted:
13 November 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
From a previously performed proteomics screen, GPP130, or Golgi phosphoprotein of 130 kDa, was identified as a potential substrate of the proprotein convertase 7 (PC7; PCSK7). GPP130 is a type-II transmembrane protein with a luminal domain containing endosomal and Golgi-retrieval determinants, enabling a unique trafficking route. Most of the previous work on GPP130 relates to its binding and retrograde trafficking of the Shiga toxin. Recently, GPP130 was reported to be implicated in cell cycle progression and cell proliferation in head and neck cancer cells. This led us to analyze the cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics, revealing that the GPP130/GOLIM4 gene is amplified in up to 35% of patients with lung cancer. This observation led us to use the A549 lung cancer cell line to investigate the growth-regulating roles of endogenous and overexpressed GPP130 and to analyze the impact of its cleavage/shedding by PC7 and/or Furin on cellular growth. Our cell-based assays suggest that GPP130 increases cell proliferation and that the latter activity is enhanced following its cleavage by PC7 and/or Furin into a membrane-bound N-terminal product and secreted C-terminal fragments. This work sheds light on the proliferative activity of GPP130 and its modulation upon its shedding by PC7 and Furin in lung cancer progression.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Cell Culture, Transfections, and Cell Treatments
2.3. Cell Treatments
2.4. Immunoflorecesnce
2.5. Western Blot Analysis and Antibodies Used
2.6. Cell Proliferation Analysis
3. Results
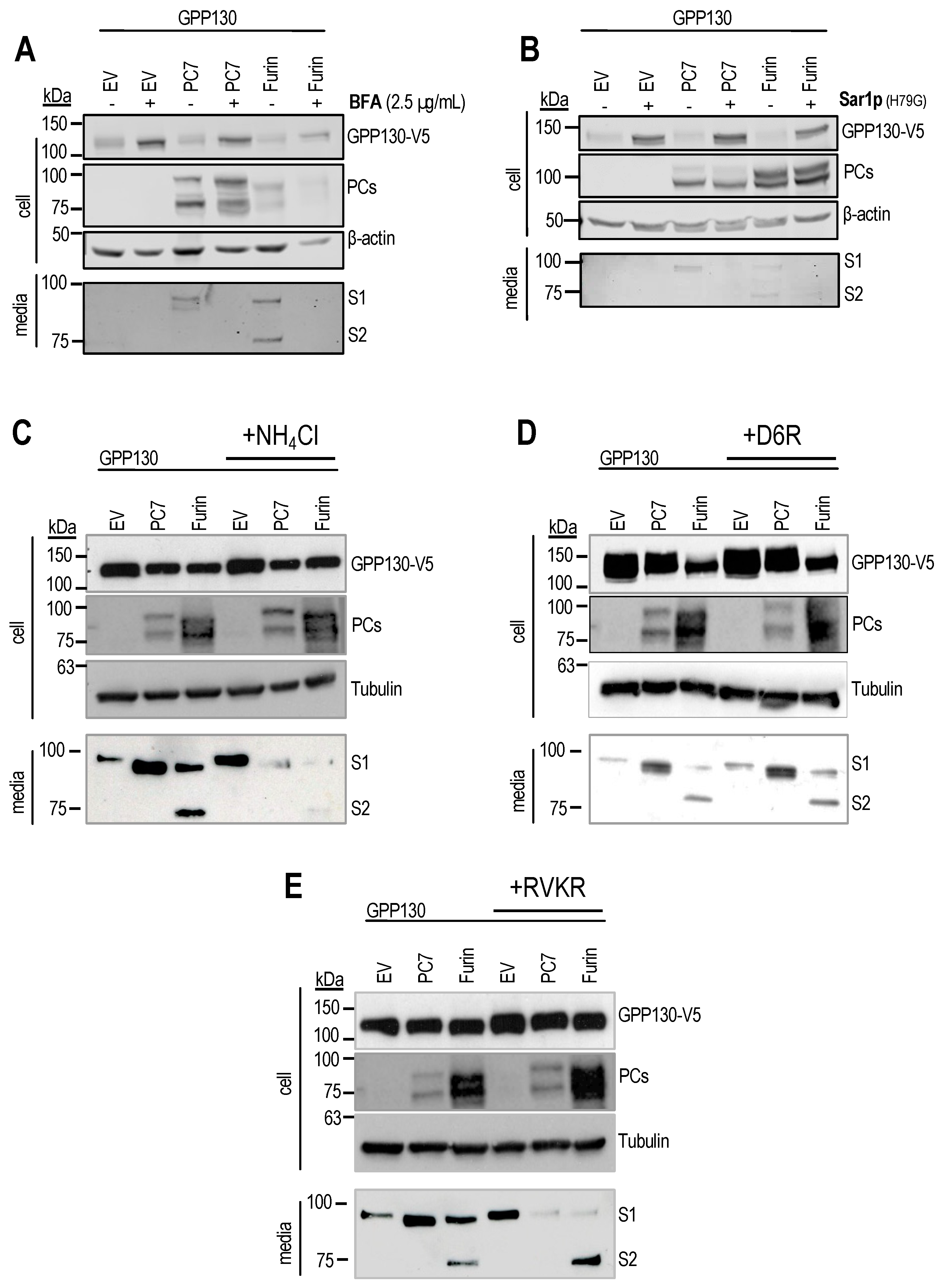
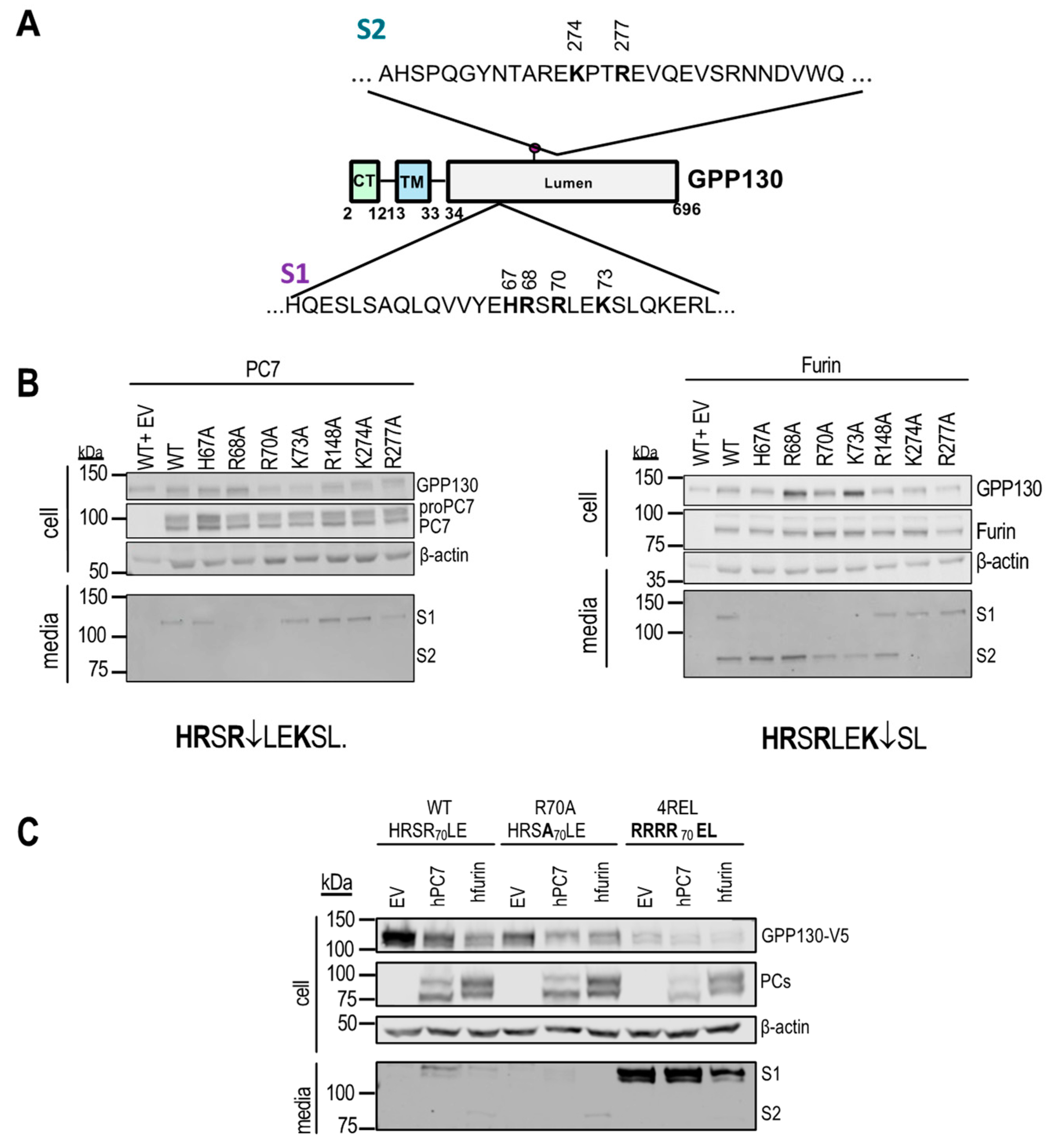
3.1. GPP130 Is Cleaved and Shed by PC7 and Furin
3.2. Identification of GPP130 Sites Shed by PC7 and Furin
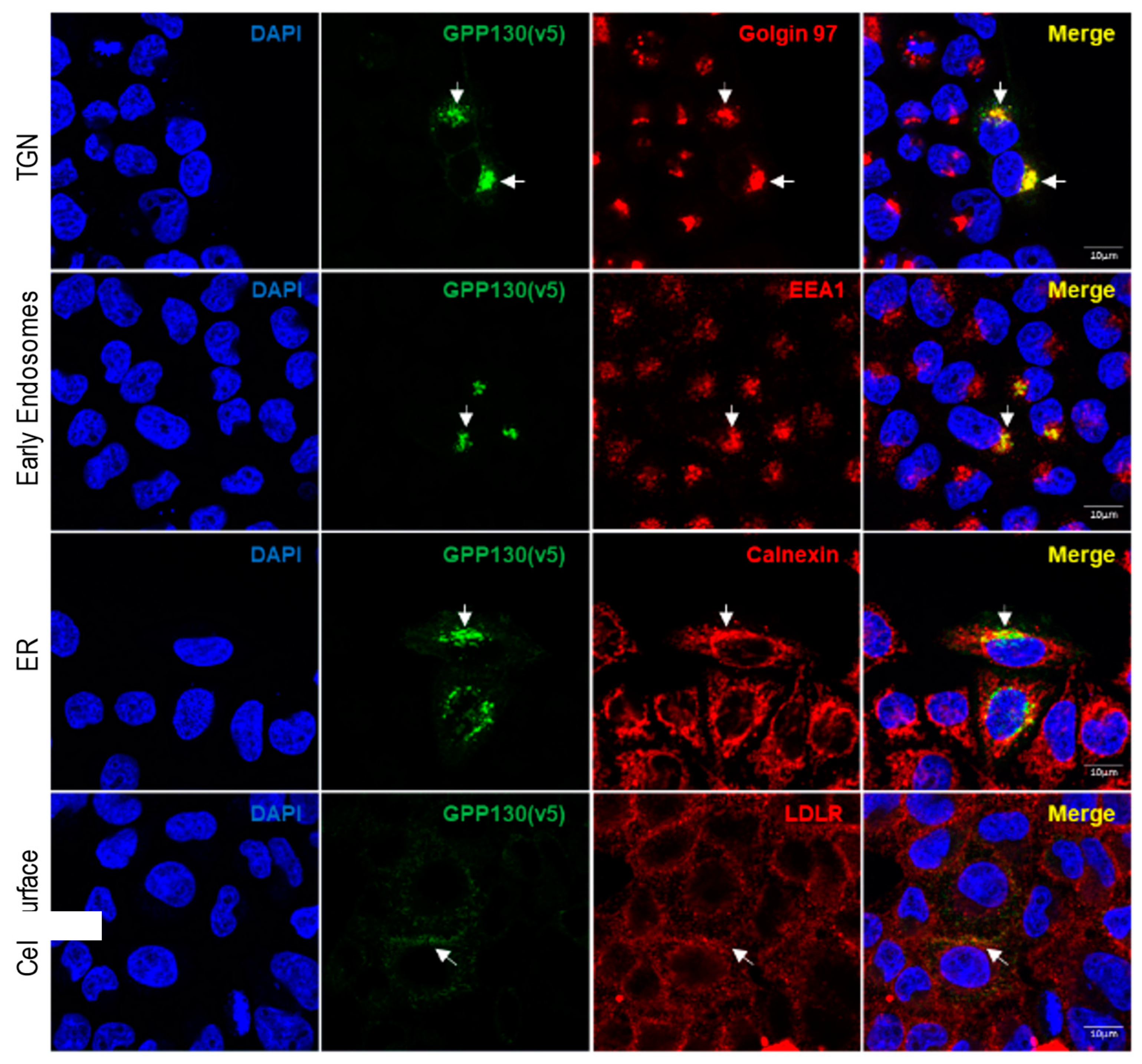
3.3. GPP130 Is Cleaved in Post-ER Acidic Compartments
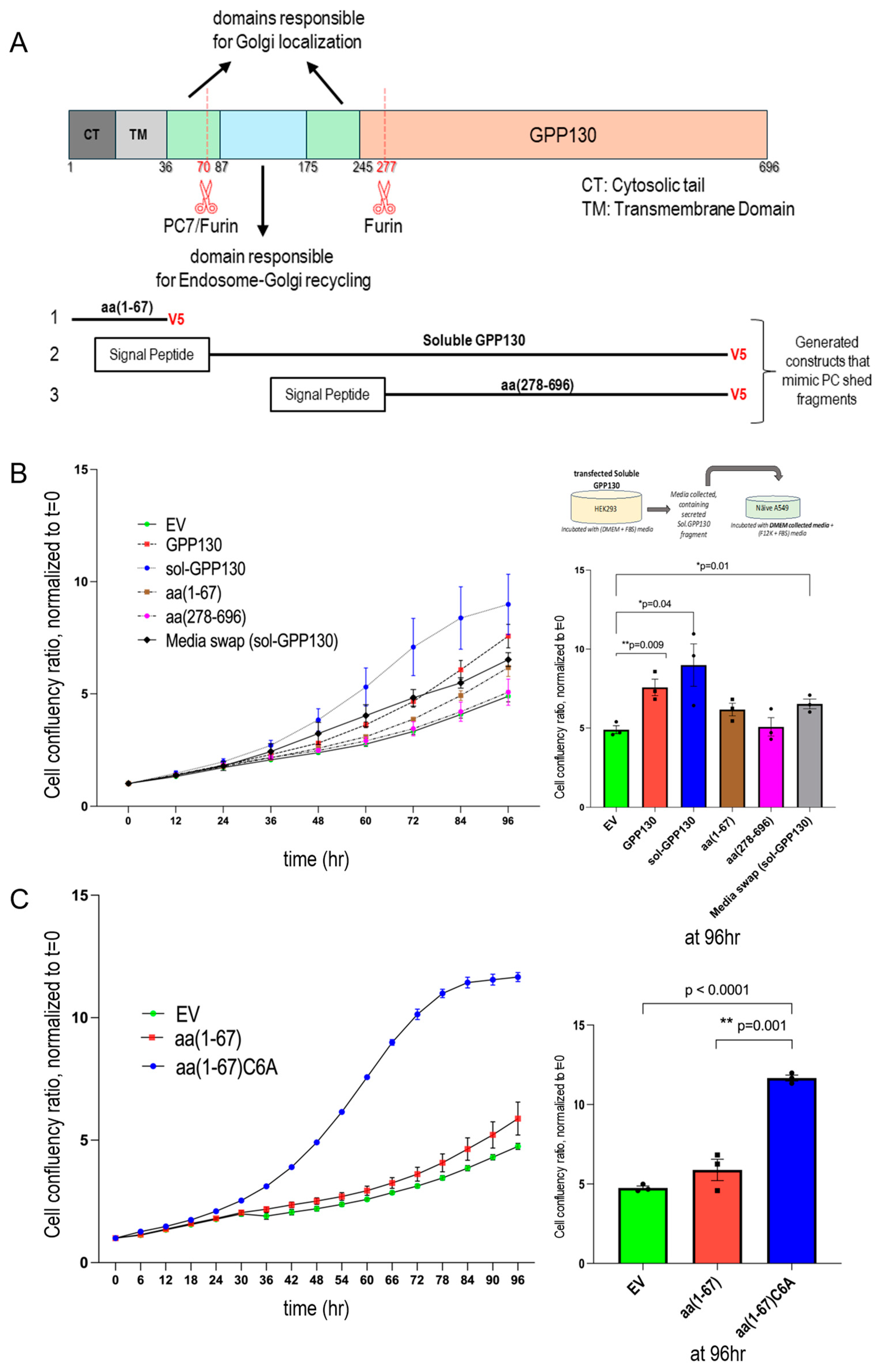
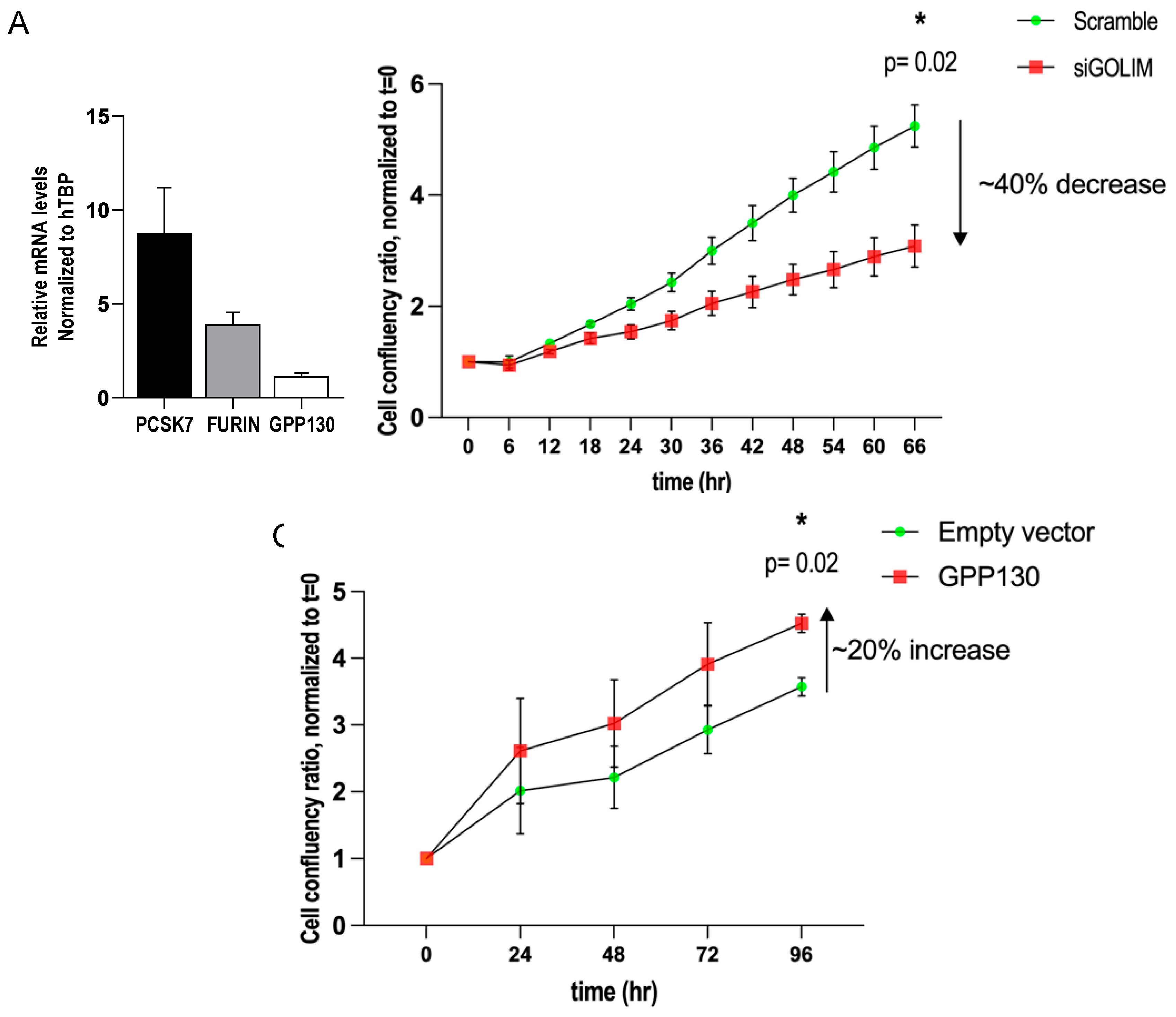
3.4. GPP130 Influences Cell Proliferation in Lung Cancer Cells
3.5. Identification of Critical Domains and Palmitoylation of GPP130 Implicated in Enhanced Proliferation
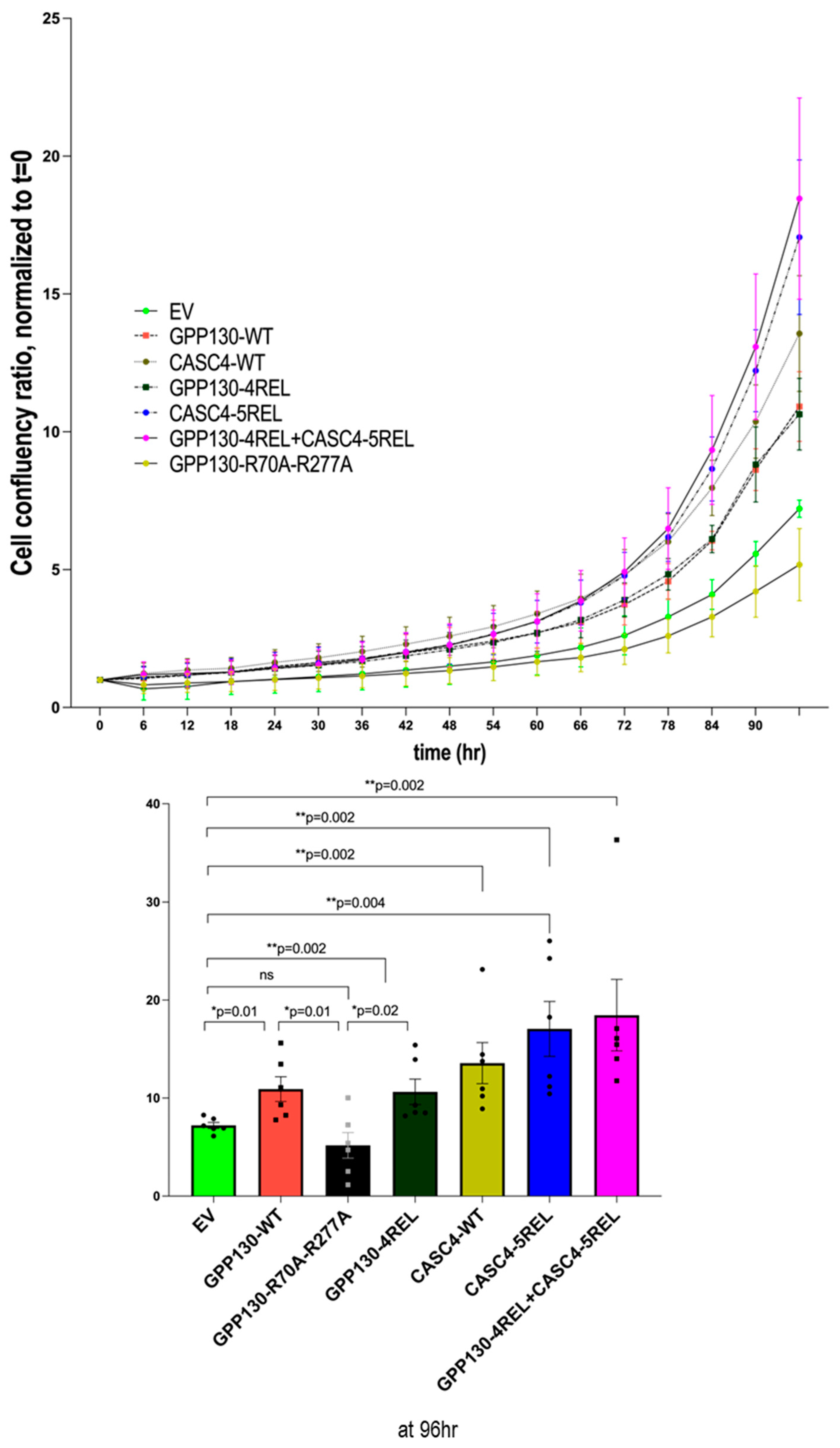
3.6. Comparative Growth of A549 Cells Overexpressing GPP130 or CASC4 Constructs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. The biology and therapeutic targeting of the proprotein convertases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012, 11, 367-383. [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Descarpentrie, J.; Badiola, I.; Siegfried, G.; Evrard, S.; Pernot, S.; Khatib, A.M. Reprogramming immune cells activity by furin-like enzymes as emerging strategy for enhanced immunotherapy in cancer. Br J Cancer 2023, 128, 1189-1195. [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Khatib, A.M.; Creemers, J.W.M. The proprotein convertase furin in cancer: more than an oncogene. Oncogene 2022. [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Abu-Thuraia, A.; Elkholi, I.E.; Chen, R.; Seebun, D.; Mayne, J.; Côté, J.F.; Figeys, D.; Seidah, N.G. Shedding of cancer susceptibility candidate 4 by the convertases PC7/furin unravels a novel secretory protein implicated in cancer progression. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 665. [CrossRef]
- Couture, F.; Sabbagh, R.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Desjardins, R.; Guay, S.P.; Bouchard, L.; Day, R. PACE4 Undergoes an Oncogenic Alternative Splicing Switch in Cancer. Cancer Res 2017. [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, C.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Metze, D.; Kemper, B.; Stegemann, A.; Picardo, M.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.P.; Böhm, M. Paired Basic Amino Acid-cleaving Enzyme 4 (PCSK6): An Emerging New Target Molecule in Human Melanoma. Acta Derm Venereol 2020, 100, adv00157. [CrossRef]
- Navals, P.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Mekdad, N.; Couture, F.; Desjardins, R.; Day, R.; Dory, Y.L. Enhancing the Drug-Like Profile of a Potent Peptide PACE4 Inhibitor by the Formation of a Host-Guest Inclusion Complex with β-Cyclodextrin. Mol Pharm 2023, 20, 4559-4573. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Essalmani, R.; Day, R.; Khatib, A.M.; Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 deficiency reduces melanoma metastasis in liver. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 1122-1131.
- Gangloff, A.; Calon, F.; Seidah, N.G. Can iPCSK9-induced hypocholesterolemia starve cancer cells? J Clin Lipidol 2017, 11, 600-601. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, X.; Dong, Y.; Wood, G.; Seidah, N.G.; Werstuck, G.; Major, P.; Bonert, M.; Kapoor, A.; Tang, D. PCSK9 facilitates melanoma pathogenesis via a network regulating tumor immunity. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2023, 42, 2. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Fan, M.; Tu, B.; Tang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Bai, J.; Huo, S.; et al. The Lin28b/Wnt5a axis drives pancreas cancer through crosstalk between cancer associated fibroblasts and tumor epithelium. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6885. [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A.; Pirillo, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Norata, G.D. Novel strategies to target proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9: beyond monoclonal antibodies. Cardiovasc Res 2019, 115, 510-518. [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Tokgözoğlu, L. Chasing LDL cholesterol to the bottom - PCSK9 in perspective. Nat Cardiovasc Res 2022, 1, 554-561. [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Garçon, D. Expanding Biology of PCSK9: Roles in Atherosclerosis and Beyond. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2022, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Hamelin, J.; Mamarbachi, M.; Dong, W.; Tardos, H.; Mbikay, M.; Chretien, M.; Day, R. cDNA structure, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of rat PC7, a novel mammalian proprotein convertase closest to yeast kexin-like proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 3388-3393. [CrossRef]
- Sachan, V.; Le Dévéhat, M.; Roubtsova, A.; Essalmani, R.; Laurendeau, J.F.; Garçon, D.; Susan-Resiga, D.; Duval, S.; Mikaeeli, S.; Hamelin, J.; et al. PCSK7: A novel regulator of apolipoprotein B and a potential target against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2024, 150, 155736. [CrossRef]
- Linstedt, A.D.; Mehta, A.; Suhan, J.; Reggio, H.; Hauri, H.P. Sequence and overexpression of GPP130/GIMPc: evidence for saturable pH-sensitive targeting of a type II early Golgi membrane protein. Mol Biol Cell 1997, 8, 1073-1087. [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, R.; Linstedt, A.D. A cycling cis-Golgi protein mediates endosome-to-Golgi traffic. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2004, 15, 4798-4806.
- Bachert, C.; Fimmel, C.; Linstedt, A.D. Endosomal trafficking and proprotein convertase cleavage of cis Golgi protein GP73 produces marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Traffic. 2007, 8, 1415-1423.
- Puri, S.; Bachert, C.; Fimmel, C.J.; Linstedt, A.D. Cycling of early Golgi proteins via the cell surface and endosomes upon lumenal pH disruption. Traffic. 2002, 3, 641-653.
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Redler, B.; Linstedt, A.D. Shiga toxin-binding site for host cell receptor GPP130 reveals unexpected divergence in toxin-trafficking mechanisms. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2013, 24, 2311-2318.
- Mallard, F.; Johannes, L. Shiga toxin B-subunit as a tool to study retrograde transport. Methods Mol Med 2003, 73, 209-220. [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bachert, C.; Smith, D.R.; Linstedt, A.D. Manganese-induced trafficking and turnover of the cis-Golgi glycoprotein GPP130. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2010, 21, 1282-1292.
- Tewari, R.; Jarvela, T.; Linstedt, A.D. Manganese induces oligomerization to promote down-regulation of the intracellular trafficking receptor used by Shiga toxin. Mol Biol Cell 2014, 25, 3049-3058. [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, G.Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Yu, J.; Duose, D.Y.; Xi, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Chromosomal 3q amplicon encodes essential regulators of secretory vesicles that drive secretory addiction in cancer. J Clin Invest 2024, 134. [CrossRef]
- Monteith, G.R.; Prevarskaya, N.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J. The calcium-cancer signalling nexus. Nat Rev Cancer 2017, 17, 367-380. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cui, X.; Gao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, W. Golgi integral membrane protein 4 manipulates cellular proliferation, apoptosis, and cell cycle in human head and neck cancer. Biosci Rep 2018, 38. [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Shi, E.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, R. MiR-105-3p acts as an oncogene to promote the proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells by targeting GOLIM4. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 275. [CrossRef]
- Kan, B.; Yan, G.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, H. CircRNA RNF10 inhibits tumorigenicity by targeting miR-942-5p/GOLIM4 axis in breast cancer. Environ Mol Mutagen 2022, 63, 362-372. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.H.; Konje, J.C.; Ayakannu, T. Identification of Potentially Novel Molecular Targets of Endometrial Cancer Using a Non-Biased Proteomic Approach. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Ginefra, P.; Filippi, B.G.H.; Donovan, P.; Bessonnard, S.; Constam, D.B. Compartment-Specific Biosensors Reveal a Complementary Subcellular Distribution of Bioactive Furin and PC7. Cell Rep 2018, 22, 2176-2189. [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, J.; Canuel, M.; Essalmani, R.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G. Implication of the proprotein convertases in iron homeostasis: proprotein convertase 7 sheds human transferrin receptor 1 and furin activates hepcidin. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2514-2524. [CrossRef]
- Durand, L.; Duval, S.; Evagelidis, A.; Guillemot, J.; Dianati, V.; Sikorska, E.; Schu, P.; Day, R.; Seidah, N.G. The motif ExExxxL in the cytosolic tail of the secretory human proprotein convertase PC7 regulates its trafficking and cleavage activity. J Biol Chem 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Yuan, L.; Tipper, C.; Amherdt, M.; Orci, L.; Klausner, R.D. Brefeldin A’s effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell 1991, 67, 601-616. [CrossRef]
- Aridor, M.; Bannykh, S.I.; Rowe, T.; Balch, W.E. Sequential coupling between COPII and COPI vesicle coats in endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Cell Biol 1995, 131, 875-893. [CrossRef]
- Susan-Resiga, D.; Essalmani, R.; Hamelin, J.; Asselin, M.C.; Benjannet, S.; Chamberland, A.; Day, R.; Szumska, D.; Constam, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Furin is the major processing enzyme of the cardiac-specific growth factor bone morphogenetic protein 10. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 22785-22794. [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bachert, C.; Smith, D.R.; Linstedt, A.D. Manganese-induced trafficking and turnover of the cis-Golgi glycoprotein GPP130. Mol Biol Cell 2010, 21, 1282-1292. [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Benjannet, S.; Hamelin, J.; Canuel, M.; Seidah, N.G. The Proprotein Convertase PC7: unique zymogen activation and trafficking pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2011, 286, 2728-2738.
- Thomas, G. Furin at the cutting edge: from protein traffic to embryogenesis and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002, 3, 753-766. [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Fierke, C.A. Understanding Protein Palmitoylation: Biological Significance and Enzymology. Sci China Chem 2011, 54, 1888-1897. [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.T.; Conibear, E. ABHD17 proteins are novel protein depalmitoylases that regulate N-Ras palmitate turnover and subcellular localization. Elife 2015, 4, e11306. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S.; Song, W.; Qiao, J.; Ruan, H. Types of nuclear localization signals and mechanisms of protein import into the nucleus. Cell Commun Signal 2021, 19, 60. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.W. The γ-secretase complex: from structure to function. Front Cell Neurosci 2014, 8, 427. [CrossRef]
- Hann, H.W.; Wang, M.; Hafner, J.; Long, R.E.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, M.; Park, S.; Comunale, M.A.; Block, T.M.; Mehta, A. Analysis of GP73 in patients with HCC as a function of anti-cancer treatment. Cancer Biomark 2010, 7, 269-273. [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Romano, P.R.; Nikolaeva, O.; Steel, L.; Mehta, A.; Fimmel, C.J.; Comunale, M.A.; D’Amelio, A.; Lok, A.S.; Block, T.M. GP73, a resident Golgi glycoprotein, is a novel serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2005, 43, 1007-1012. [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Testa, C.L.; Klein-Szanto, A.J. Regulation of HIF-1 alpha by the proprotein convertases furin and PC7 in human squamous carcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog. 2015, 54, 698-706.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




