Submitted:
17 November 2024
Posted:
19 November 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamics of Apparent Horizon
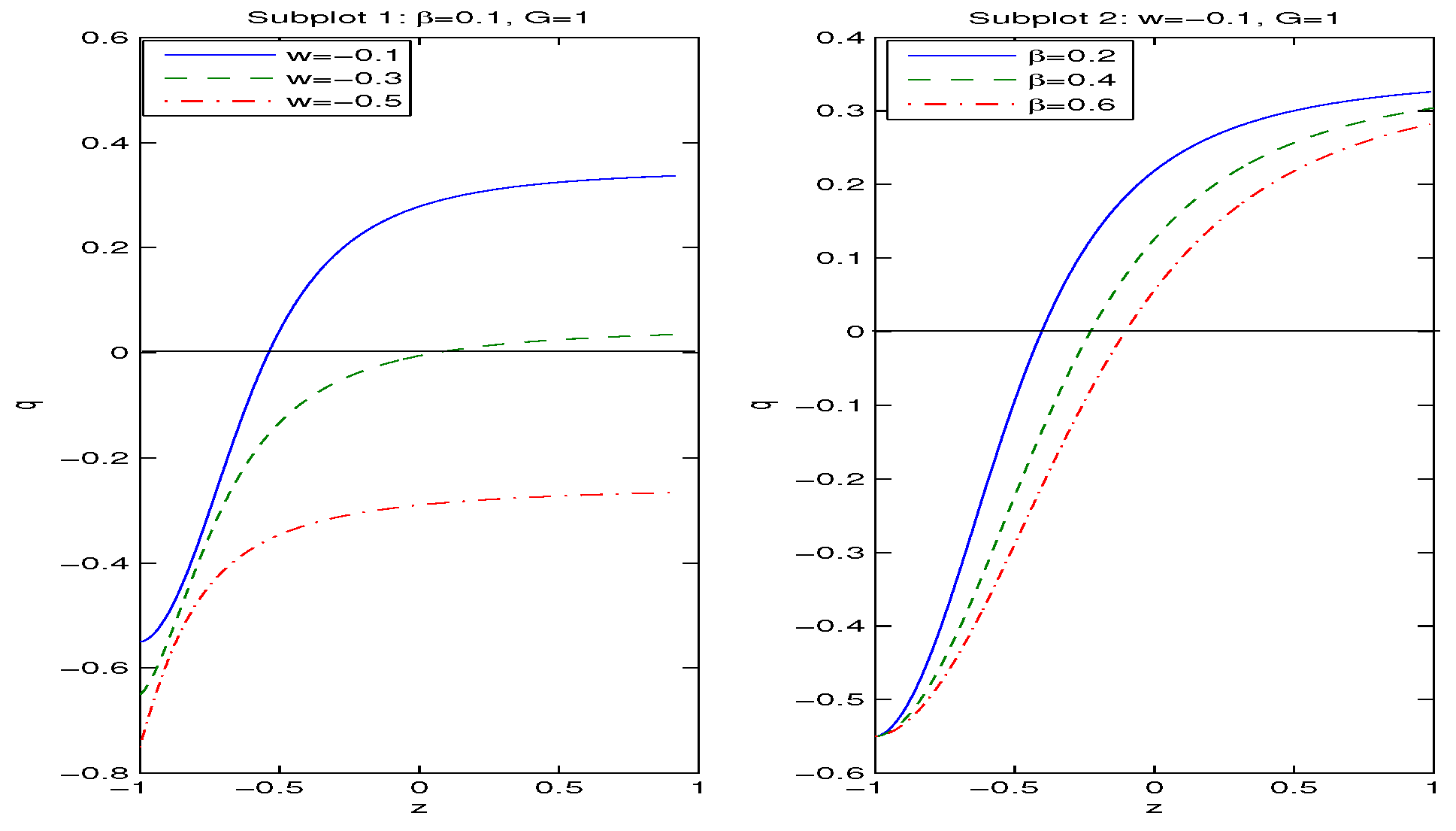
3. Modified FLRW Equations
4. Summary
References
- J. D. Bekenstein, Black Holes and Entropy, Phys. Rev. D 7 (1973), 2333-2346.
- S. W. Hawking, Particle creation by black holes, Commun. Math. Phys. 43 (1975), 199-220; Erratum: ibid. 46 (1976), 206.
- T. Jacobson, Thermodynamics of Spacetime: The Einstein Equation of State, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995), 1260.
- T. Padmanabhan, Gravity and the Thermodynamics of Horizons, Phys. Rept. 406 (2005), 49.
- T. Padmanabhan, Thermodynamical Aspects of Gravity: New insights, Rept. Prog. Phys. 73 (2010), 046901.
- S. A. Hayward, Unified first law of black-hole dynamics and relativistic thermodynamics, Class. Quant. Grav. 15 (1998), 3147-3162.
- M. Akbar and R. G. Cai, Thermodynamic Behavior of Friedmann Equation at Apparent Horizon of FRW Universe, Phys. Rev. D 75 (2007), 084003.
- R. G. Cai and L. M. Cao, Unified First Law and Thermodynamics of Apparent Horizon in FRW Universe, Phys. Rev. D 75 (2007), 064008.
- A. Paranjape, S. Sarkar and T. Padmanabhan, Thermodynamic route to Field equations in Lanczos-Lovelock Gravity, Phys. Rev. D 74 (2006), 104015.
- A. Sheykhi, B. Wang and R. G. Cai, Thermodynamical Properties of Apparent Horizon in Warped DGP Braneworld, Nucl. Phys. B 779, (2007) 1.
- R. G. Cai and N. Ohta, Horizon Thermodynamics and Gravitational Field Equations in Horava-Lifshitz Gravity, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010), 084061.
- M. Jamil, E. N. Saridakis and M. R. Setare, The generalized second law of thermodynamics in Horava-Lifshitz cosmology, JCAP 1011 (2010), 032.
- Y. Gim, W. Kim and S. H. Yi, The first law of thermodynamics in Lifshitz black holes revisited, JHEP 1407 (2014), 002.
- Z. Y. Fan and H. Lu, Thermodynamical First Laws of Black Holes in Quadratically-Extended Gravities, Phys. Rev. D 91 (2015), 064009.
- R. D’Agostino, Holographic dark energy from nonadditive entropy: cosmological perturbations and observational constraints, Phys. Rev. D 99 (2019), 103524.
- L. M. Sanchez and H. Quevedo, Thermodynamics of the FLRW apparent horizon, Phys. Lett B 839 (2023), 137778.
- S. Wang, Y. Wang and M. Li, Holographic Dark Energy, Phys. Rept. 696 (2017) 1.
- C. Tsallis, Possible generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs statistics, J. Stat. Phys., 52 (1-2) (1988), 479-487; C. Tsallis, The Nonadditive Entropy Sq and Its Applications in Physics and Elsewhere: Some Remarks, Entropy 13, 1765 (2011).
- J. Ren, Analytic critical points of charged Renyi entropies from hyperbolic black holes, JHEP 05 (2021), 080.
- A. R´enyi, Proceedings of the Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematics, Statistics and Probability, University of California Press (1960), 547-56.
- A. Sayahian Jahromi et al, Generalized entropy formalism and a new holographic dark energy model, Phys. Lett. B 780 (2018), 21-24.
- J. D. Barrow, The Area of a Rough Black Hole, Phys. Lett. B 808 (2020), 135643.
- G. Kaniadakis, Statistical mechanics in the context of special relativity II, Phys. Rev. E 72 (2005), 036108.
- K. Mejrhit and S. E. Ennadifi, Thermodynamics, stability and Hawking–Page transition of black holes from non-extensive statistical mechanics in quantum geometry, Phys. Lett. B 794 (2019), 45-49.
- S. Nojiri, S. D. Odintsov and Tanmoy Paul, Different aspects of entropic cosmology, Phys. Lett. B 835 (2022), 137553.
- D. Pavon and W. Zimdahl, Holographic dark energy and cosmic coincidence, Phys. Lett. B 628 (2005) 206.
- R. C. G. Landim, Holographic dark energy from minimal supergravity, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 25 (2016), 1650050.
- S. I. Kruglov, Universe inflation and nonlinear electrodynamics, Eur. Phys. J. C 84 (2024), 205.
- Sofia Di Gennaro, Hao Xu, Yen Chin Ong, How barrow entropy modifies gravity: with comments on Tsallis entropy, Eur. Phys. J. C 82 (2022), 1066.
- M. Roos, Introduction to Cosmology (John Wiley and Sons, UK, 2003).
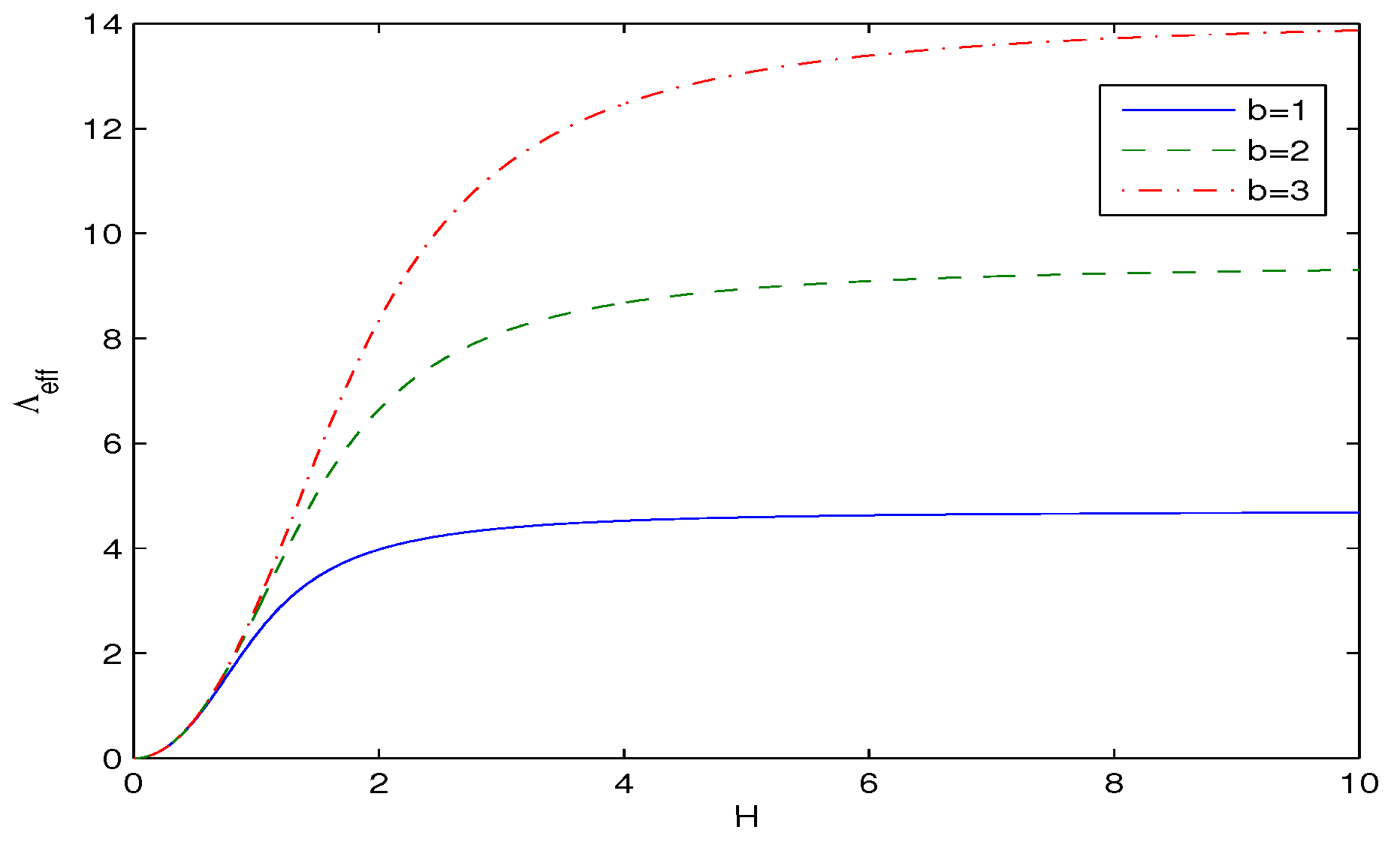
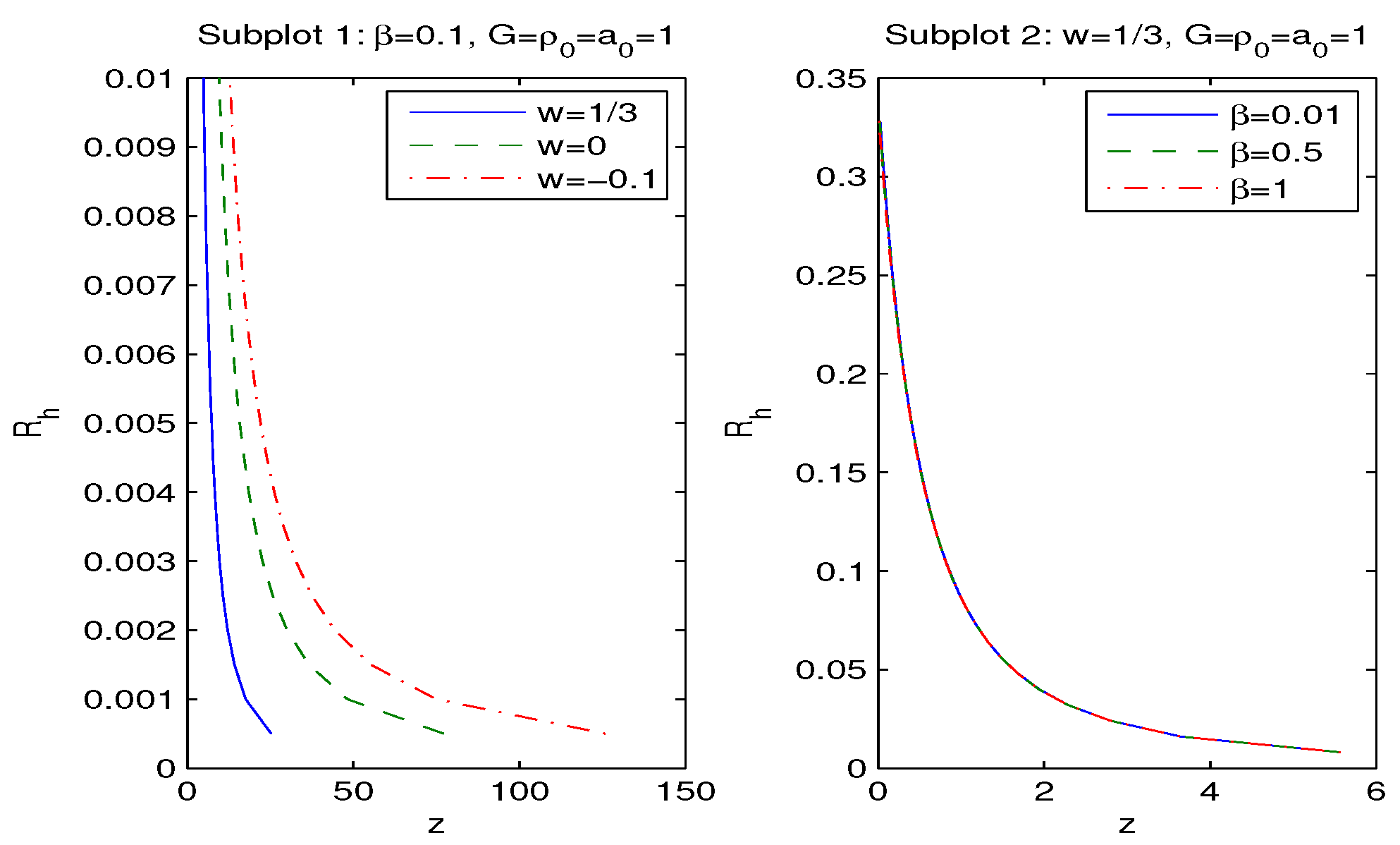
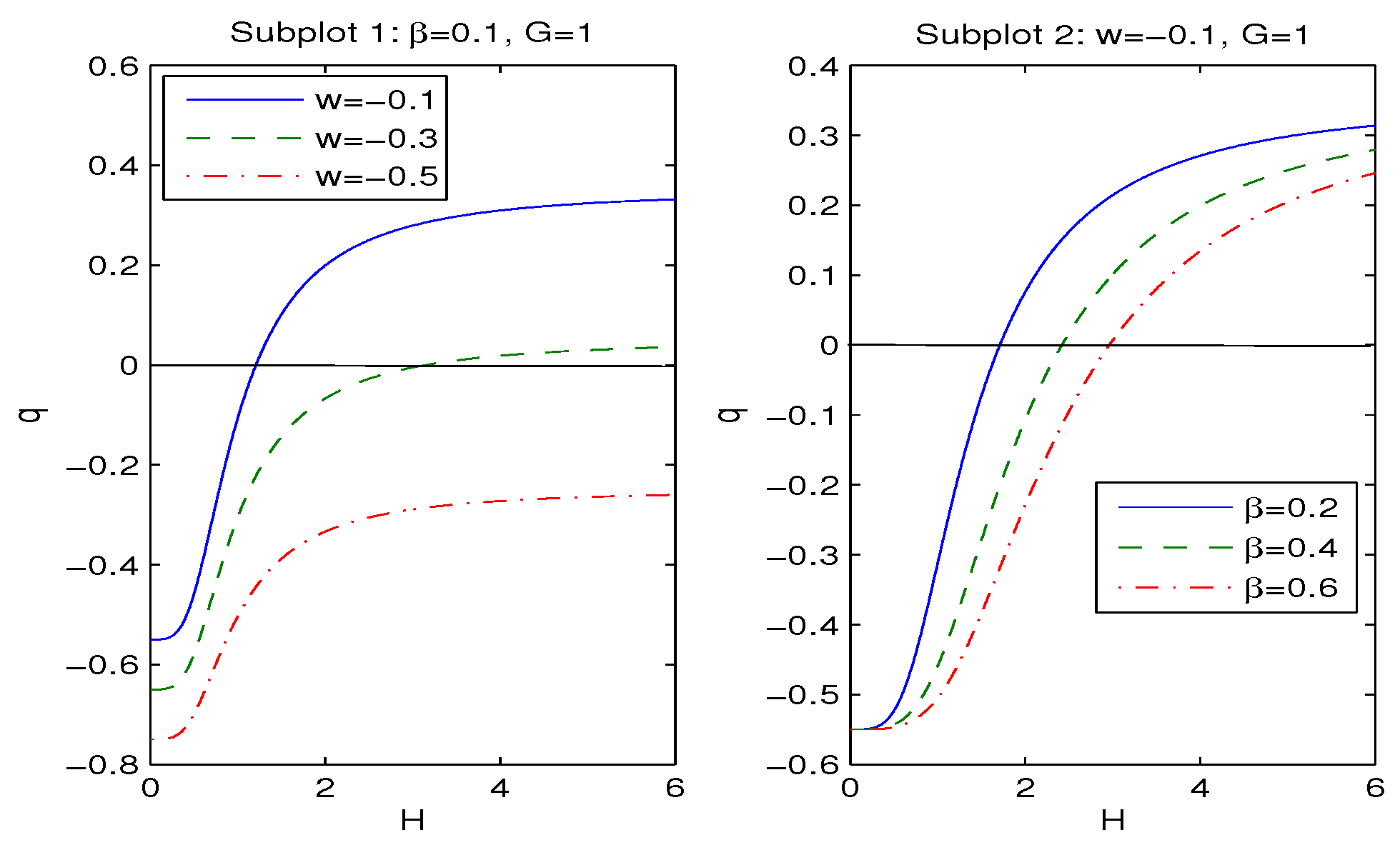
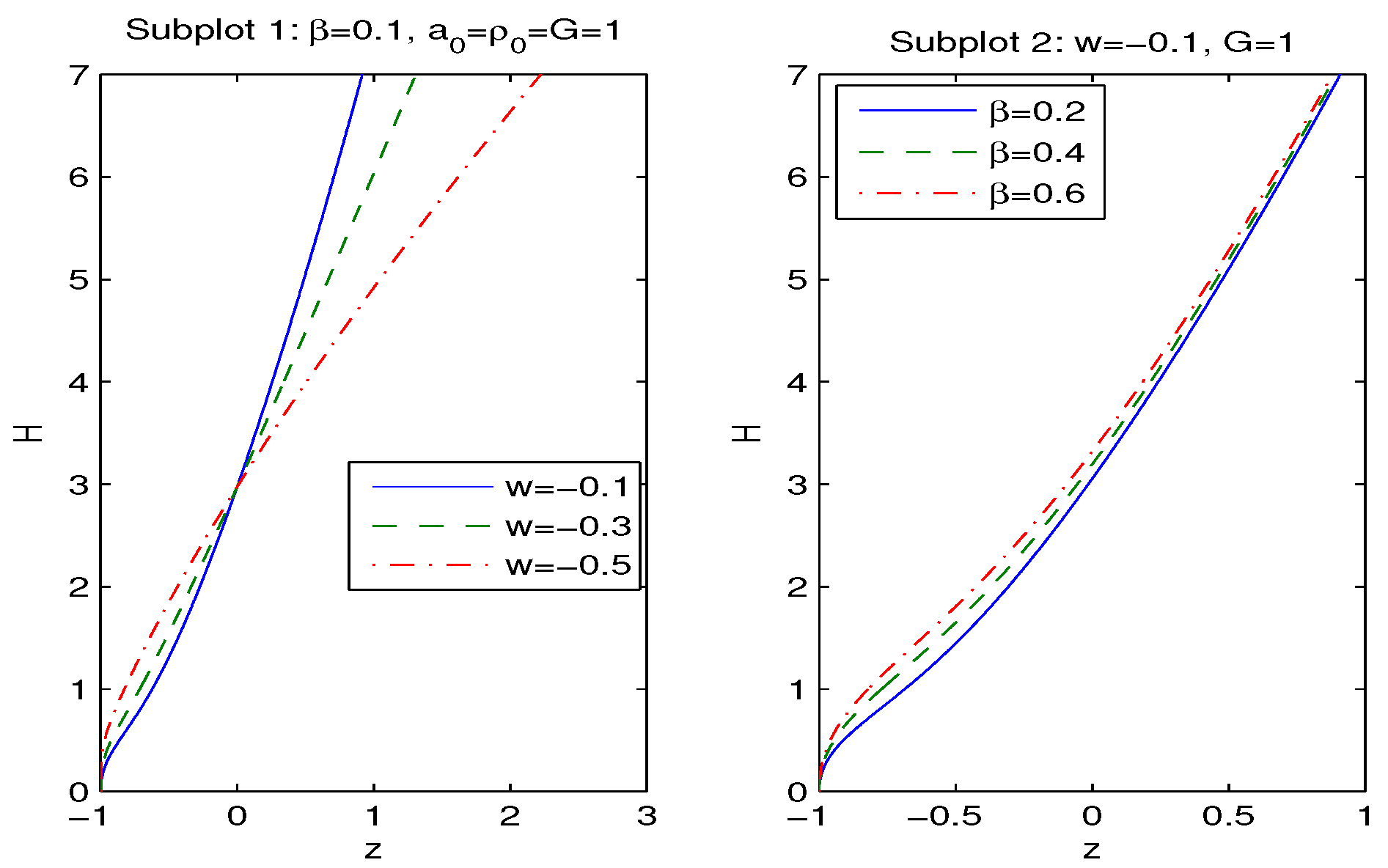
| 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | |
| H | 3.20 | 3.42 | 3.63 | 3.82 | 4.01 | 4.19 | 4.36 | 4.53 | 4.68 | 4.84 | 4.99 |
| -0.05 | -0.004 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.32 |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |
| H | 2.977 | 3.053 | 3.125 | 3.193 | 3.258 | 3.320 | 3.378 | 3.435 | 3.489 |
| 0.527 | 0.549 | 0.567 | 0.583 | 0.597 | 0.609 | 0.619 | 0.629 | 0.637 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




