Submitted:
26 December 2024
Posted:
27 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Alzheimer's Disease
2. Role of Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases
3. Gut-Brain Axis
4. Bifidobacterium Breve MCC1274 as a Multifaceted Probiotic for Gut and Brain
4.1. Characterization of Bifidobacterium Breve MCC1274 and Its Benefits on Gut Integrity
4.2. Probiotic Properties of B. breve MCC1274
5. Mechanisms of Action of B. breve MCC1274 in Neurodegenerative Disease
5.1. Potential effects of B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation in Modulating Neuroinflammation
5.2. Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Chronic Stress Responses by B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation
5.3. Potential Effects of B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation in Modulating Amyloid and Tau Pathology
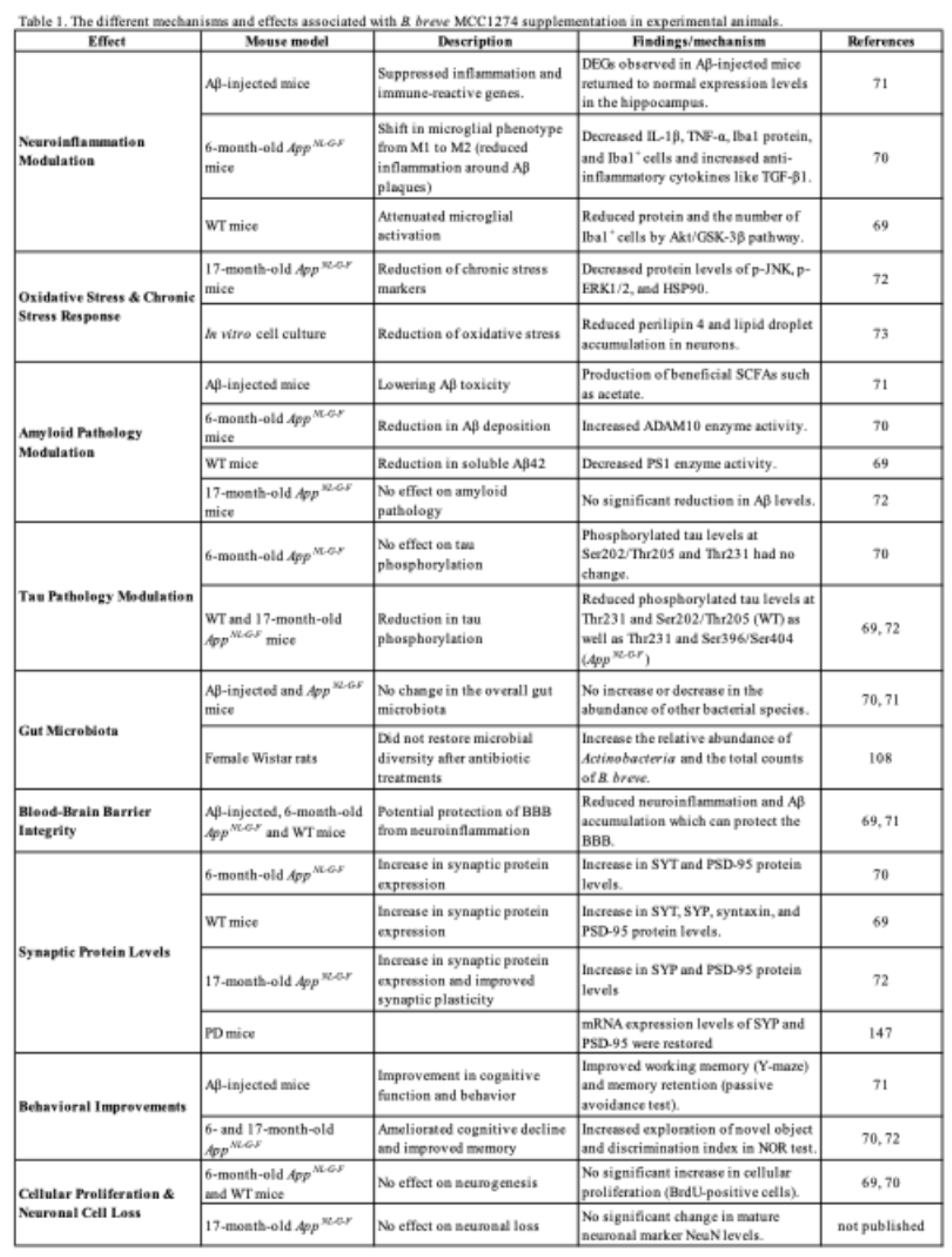
5.4. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Function by Breve MCC1274 Supplementation
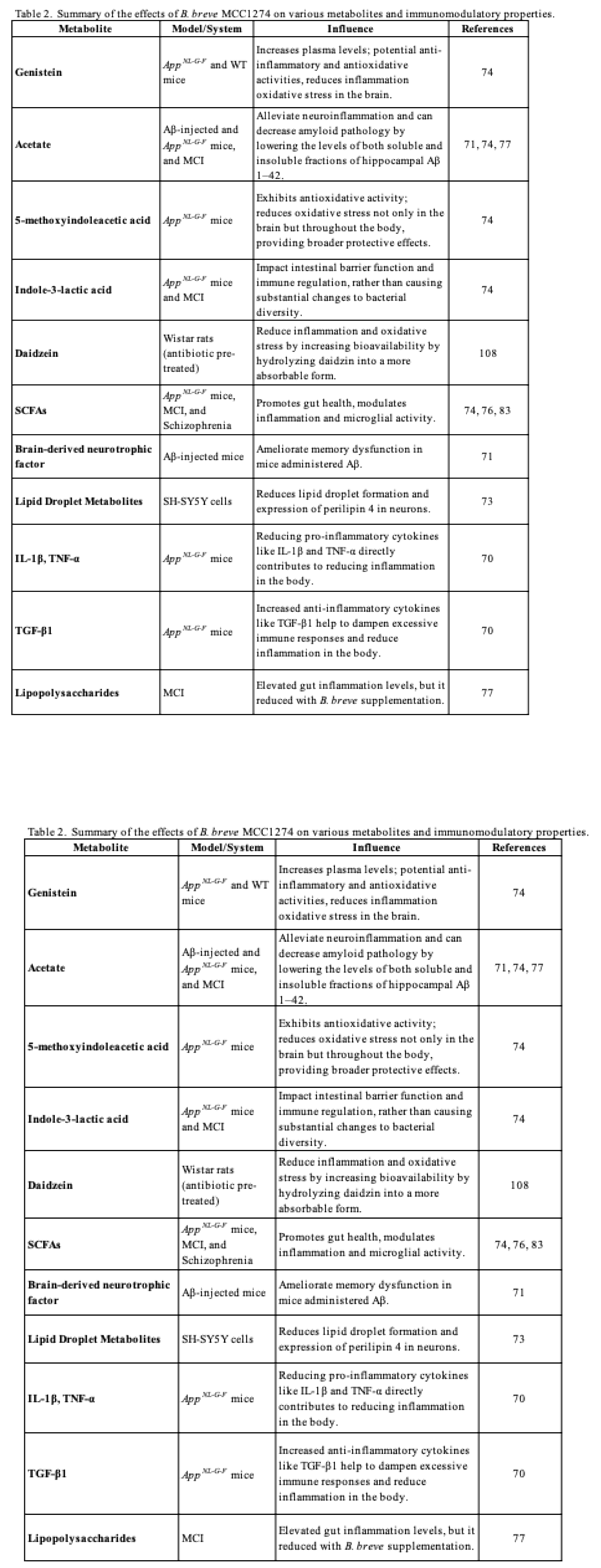
5.5. The impacts of B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation on BBB Integrity
5.6. The Effects of B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation on Cellular Proliferation and Neuronal Cell Loss
5.7. The Effects of B. breve MCC1274 Supplementation on Synaptic Protein Levels
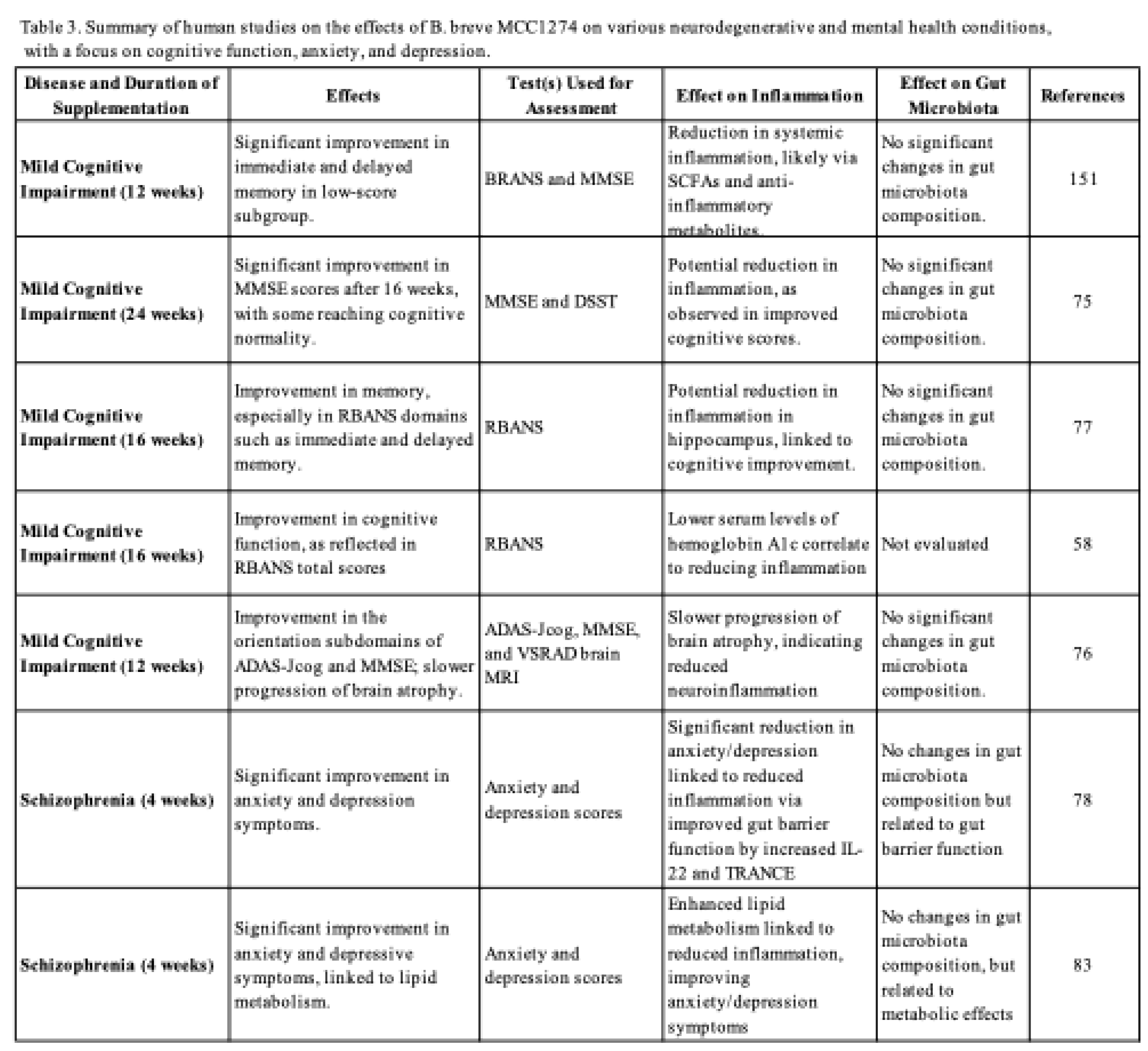
6. B. breve MCC1274 as a Potential Treatment for Cognitive Behavioral Abnormalities in Neurodegenerative Diseases
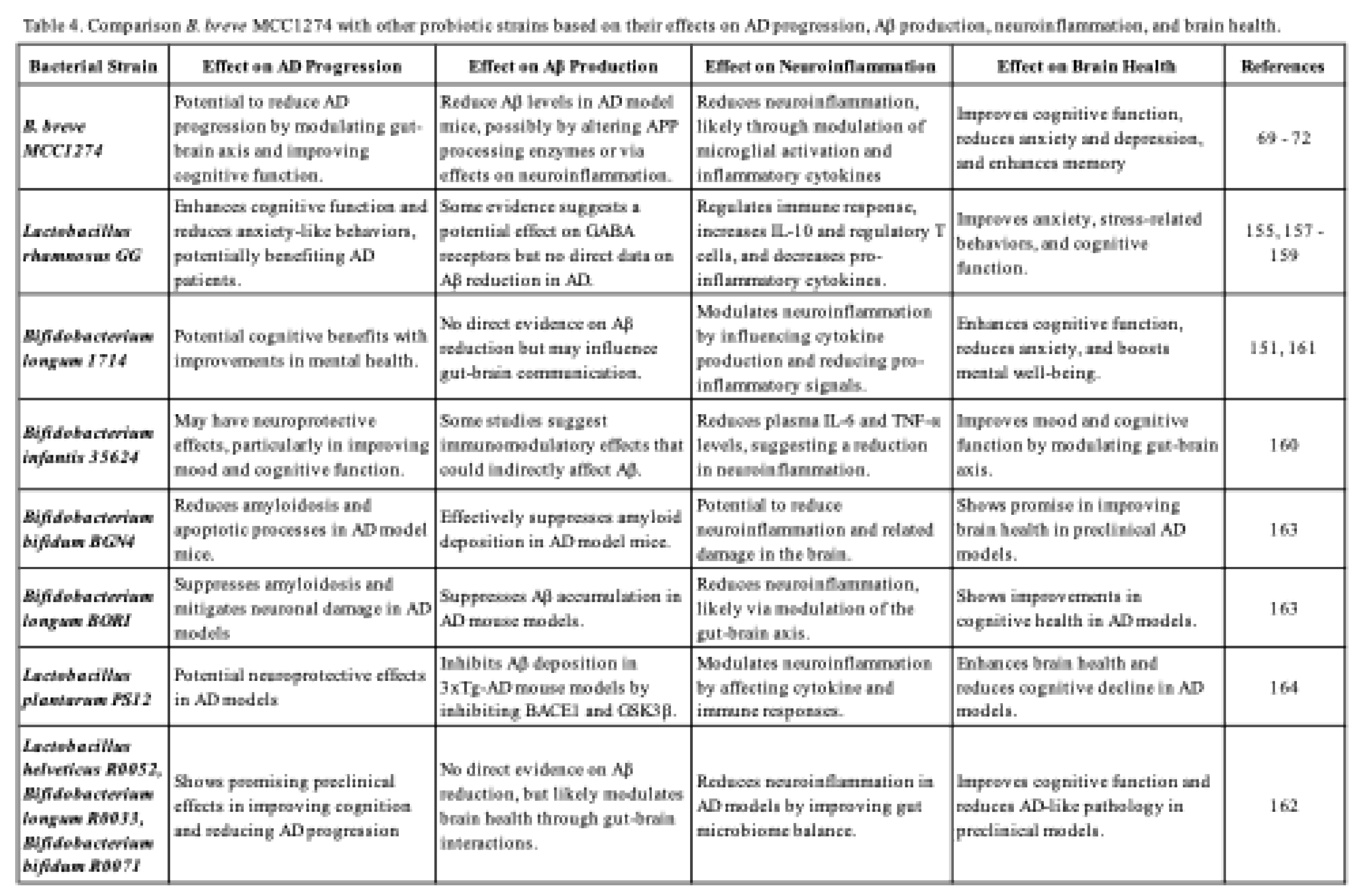
7. Comparison of B. breve MCC1274 with Other Probiotic Strains in AD Progression and Brain Health
8. Future Directions and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubois:, B.; Hampel, H.; Feldman, H.H.; Scheltens, P.; Aisen, P.; Andrieu, S.; Bakardjian, H.; Benali, H.; Bertram, L.; Blennow, K. , et al. Preclinical Alzheimer's disease: Definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement 2016, 12, 292–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Shaw, L.M.; Aisen, P.S.; Weiner, M.W.; Petersen, R.C.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer's pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol 2010, 9, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, M.W.; Veitch, D.P.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Cairns, N.J.; Green, R.C.; Harvey, D.; Jack, C.R.; Jagust, W.; Liu, E. , et al. The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement 2013, 9, e111–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblinsky, N.D.; Power, K.A.; Middleton, L.; Ferland, G.; Anderson, N.D. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diet and Exercise Effects on Cognition: A Review of the Intervention Literature. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A 2022, 78, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza Matute, S.; Iyavoo, S. Exploring the gut microbiota: lifestyle choices, disease associations, and personal genomics. Front Nutr 2023, 10, 1225120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Duffy, A. Factors Influencing the Gut Microbiota, Inflammation, and Type 2 Diabetes. J Nutr 2017, 147, 1468s–1475s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T. , et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecular Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer's Disease: A Central Role for Amyloid. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 1994, 53, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballatore, C.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2007, 8, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M. , et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. The Lancet Neurology 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, R.D.; Masliah, E.; Salmon, D.P.; Butters, N.; DeTeresa, R.; Hill, R.; Hansen, L.A.; Katzman, R. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in alzheimer's disease: Synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Annals of Neurology 1991, 30, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, J.; Budson, A. Current understanding of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and treatment. F1000Res 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappa, S.F. The Quest for an Alzheimer Therapy. Frontiers in Neurology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, T.; Fußer, F.; Schroder, J.; Pantel, J. Pharmacological Treatment of Mild Cognitive Impairment as a Prodromal Syndrome of Alzheimer's Disease. Current Neuropharmacology 2013, 11, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, L.S.; Insel, P.S.; Weiner, M.W.; Initiative, A.s.D.N. Treatment With Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine of Patients in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Archives of Neurology 2011, 68, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutsch, A.; Kantsjö, J.B.; Ronchi, F. The Gut-Brain Axis: How Microbiota and Host Inflammasome Influence Brain Physiology and Pathology. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Transl Med 2015, 3, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Lin, C.; Zheng, J.; Yu, M.; Lan, J. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis, mechanisms, and therapeutic potentials. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J.; Wei, Z. Advances in the study of the effects of gut microflora on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, E.; Parnova, R. Mechanisms of Blood–Brain Barrier Protection by Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Cells 2023, 12, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, G.; Catapano, A.; Trinchese, G.; Cimmino, F.; Penna, E.; Pizzella, A.; Cristiano, C.; Lama, A.; Crispino, M.; Mollica, M.P. Butyrate Improves Neuroinflammation and Mitochondrial Impairment in Cerebral Cortex and Synaptic Fraction in an Animal Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, J.; Zalewska, T.; Sypecka, J.; Ziemka-Nalecz, M. Effect of the HDAC Inhibitor, Sodium Butyrate, on Neurogenesis in a Rat Model of Neonatal Hypoxia–Ischemia: Potential Mechanism of Action. Molecular Neurobiology 2019, 56, 6341–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasén, C.; Beauchamp, L.C.; Vincentini, J.; Li, S.; LeServe, D.S.; Gauthier, C.; Lopes, J.R.; Moreira, T.G.; Ekwudo, M.N.; Yin, Z. , et al. Bacteroidota inhibit microglia clearance of amyloid-beta and promote plaque deposition in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhami, M.; Raj, K.; Singh, S. Relevance of gut microbiota to Alzheimer's Disease (AD): Potential effects of probiotic in management of AD. Aging and Health Research 2023, 3, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, B.; Lou, P.; Dai, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhuge, A.; Yuan, Y.; Li, L. The Relationship Between the Gut Microbiome and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuroscience Bulletin 2021, 37, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V. , et al. Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480.e1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harach, T.; Marungruang, N.; Duthilleul, N.; Cheatham, V.; Mc Coy, K.D.; Frisoni, G.; Neher, J.J.; Fåk, F.; Jucker, M.; Lasser, T.; Bolmont, T. Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 41802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Driscoll, C.M. The blood-brain barrier in aging and neurodegeneration. Molecular Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2659–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Tóth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P. , et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Science Translational Medicine 2014, 6, 263ra158–263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Du, W.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, C.; Jin, X.; Wang, W. Targeting the blood–brain barrier to delay aging-accompanied neurological diseases by modulating gut microbiota, circadian rhythms, and their interplays. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2023, 13, 4667–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bruggeman, A.; De Nolf, C.; Vandendriessche, C.; Van Imschoot, G.; Van Wonterghem, E.; Vereecke, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. Gut microbiota regulates blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier function and Aβ pathology. The EMBO Journal 2023, 42, e111515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.-L. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and Alzheimer’s disease: Implications of the blood-brain barrier as an intervention target. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 2021, 199, 111560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, M.; Imbriani, P.; Bonsi, P.; Martella, G.; Peppe, A. Beyond the Microbiota: Understanding the Role of the Enteric Nervous System in Parkinson’s Disease from Mice to Human. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain–Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Jessica M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, Gregory P.; Shastri, Gauri G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, Cathryn R.; Ismagilov, Rustem F.; Mazmanian, Sarkis K.; Hsiao, Elaine Y. Indigenous Bacteria from the Gut Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Mohanto, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; Mishra, N.; Garg, A.; Chellappan, D.K.; Omara, T.; Iqbal, S.; Kahwa, I. Gut-brain axis: A cutting-edge approach to target neurological disorders and potential synbiotic application. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. , et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooley, K.L. Effects of the Human Gut Microbiota on Cognitive Performance, Brain Structure and Function: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D. , et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Affect Central Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor and Behavior in Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609.e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J. , et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. Microbiota metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Journal of Gastroenterology 2017, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; He, C.; An, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, M.; Shan, Z.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B. The Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Body Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H. Complex regulatory effects of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 2023, 20, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Wang, L.; Huangfu, M.; Li, H. The impact of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids on macrophage activities in disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 165, 115276. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.-T.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, R.-Y.; Wang, F.-X.; Ma, L.-J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H.-D. Neuroprotective Effects of Sodium Butyrate by Restoring Gut Microbiota and Inhibiting TLR4 Signaling in Mice with MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Tillisch, K.; Gupta, A. Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 2015, 125, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhanna, A.; Martini, N.; Hmaydoosh, G.; Hamwi, G.; Jarjanazi, M.; Zaifah, G.; Kazzazo, R.; Haji Mohamad, A.; Alshehabi, Z. The correlation between gut microbiota and both neurotransmitters and mental disorders: A narrative review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2024, 103, e37114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Nguyen, J.C.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, P.P. Influence of Tryptophan and Serotonin on Mood and Cognition with a Possible Role of the Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Violle, N.; Bisson, J.F.; Desor, D.; Javelot, H.; Rougeot, C. Beneficial psychological effects of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in healthy human volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arboleya, S.; Watkins, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Gut Bifidobacteria Populations in Human Health and Aging. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Langa, S.; Martín, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jiménez, E.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. The human milk microbiota: Origin and potential roles in health and disease. Pharmacological Research 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butta, H.; Sardana, R.; Vaishya, R.; Singh, K.N.; Mendiratta, L. Bifidobacterium: An Emerging Clinically Significant Metronidazole-resistant Anaerobe of Mixed Pyogenic Infections. Cureus 2017, 9, e1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, P.H.P.; Grandison, A.S.; Charalampopoulos, D. Bifidobacteria in milk products: An overview of physiological and biochemical properties, exopolysaccharide production, selection criteria of milk products and health benefits. Food Research International 2014, 55, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokusaeva, K.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; van Sinderen, D. Carbohydrate metabolism in Bifidobacteria. Genes Nutr 2011, 6, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Katsumata, N.; Shimizu, T.; Xiao, J. Association of Plasma Hemoglobin A1c with Improvement of Cognitive Functions by Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve Supplementation in Healthy Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 2021, 81, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, Timothy W. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Wasan, A.; Sharma, R.K. Recent developments in probiotics: An emphasis on Bifidobacterium. Food Bioscience 2021, 41, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saturio, S.; Nogacka, A.M.; Alvarado-Jasso, G.M.; Salazar, N.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Gueimonde, M.; Arboleya, S. Role of Bifidobacteria on Infant Health. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melini, F.; Melini, V.; Luziatelli, F.; Ficca, A.G.; Ruzzi, M. Health-Promoting Components in Fermented Foods: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.M.; Tarfeen, N.; Mohamed, H.; Song, Y. Fermented Foods: Their Health-Promoting Components and Potential Effects on Gut Microbiota. Fermentation 2023, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.M.; Guo, H.X.; Cai, J.W.; Meng, X.C. Bifidobacterium breve Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Maintaining the Mucosal and Epithelial Barriers and Modulating Gut Microbes. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzi Cionci, N.; Baffoni, L.; Gaggìa, F.; Di Gioia, D. Therapeutic Microbiology: The Role of Bifidobacterium breve as Food Supplement for the Prevention/Treatment of Paediatric Diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulqadir, R.; Engers, J.; Al-Sadi, R. Role of Bifidobacterium in Modulating the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier: Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Curr Dev Nutr 2023, 7, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics Mechanism of Action on Immune Cells and Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavin, J. Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Zhou, C.; Jung, C.G.; Michikawa, M. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Mitigates Alzheimer's Disease-Related Pathologies in Wild-Type Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Zhou, C.; Ohno, K.; Kuhara, T.; Taslima, F.; Abdullah, M.; Jung, C.-G.; Michikawa, M. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve Prevents Memory Impairment Through the Reduction of Both Amyloid-β Production and Microglia Activation in APP Knock-In Mouse 1. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2022, 85, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Sugahara, H.; Shimada, K.; Mitsuyama, E.; Kuhara, T.; Yasuoka, A.; Kondo, T.; Abe, K.; Xiao, J.-z. Therapeutic potential of Bifidobacterium breve strain A1 for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.; Jung, C.G.; Zhou, C.; Inoue, R.; Chen, Y.; Sento, Y.; Hida, H.; Michikawa, M. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 on Alzheimer's Disease Pathologies in App(NL-G-F) Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, F.; Kuhara, T.; Xiao, J. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Lipid Droplet Formation via PLIN4 Gene Regulation. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Abdelhamid, M.; Zhou, C.; Jung, C.G.; Michikawa, M. Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 Supplementation Increased the Plasma Levels of Metabolites with Potential Anti-Oxidative Activity in APP Knock-In Mice. J Alzheimers Dis 2022, 89, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Yoshino, K.; Saito, I.; Xiao, J.Z. Bifidobacterium Breve A1 Supplementation Improved Cognitive Decline in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: An Open-Label, Single-Arm Study. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2019, 6, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, D.; Xiao, J.; Takeda, T.; Yanagisawa, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Endo, N.; Higa, M.; Kasanuki, K. , et al. Effect of Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Function and Preventing Brain Atrophy in Older Patients with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: Results of a 24-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Alzheimers Dis 2022, 88, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Katsumata, N.; Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Odamaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, K.; Kaneko, T. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Functions of Older Adults with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 77, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, R.; Koga, M.; Katsumata, N.; Odamaki, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Oka, M.; Narita, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Kusumi, I.; Xiao, J.; Matsuoka, Y.J. Effect of bifidobacterium breve A-1 on anxiety and depressive symptoms in schizophrenia: A proof-of-concept study. J Affect Disord 2019, 245, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nature Reviews Neurology 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zong, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z. The effects of microglia-associated neuroinflammation on Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Immunology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong-Guerra, M.; Calfio, C.; Maccioni, R.B.; Rojo, L.E. Revisiting the neuroinflammation hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease: a focus on the druggability of current targets. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1161850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Han, S.; Kwon, J.; Ju, S.; Choi, T.G.; Kang, I.; Kim, S.S. Roles of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, R.; Okubo, R.; Katsumata, N.; Odamaki, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Kusumi, I.; Xiao, J.; Matsuoka, Y.J. Lipid and Energy Metabolism of the Gut Microbiota Is Associated with the Response to Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve Strain for Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2021, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Odamaki, T.; Xiao, J.Z. Production of Indole-3-Lactic Acid by Bifidobacterium Strains Isolated fromHuman Infants. Microorganisms 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.B.; Tanaka, A.; Kuhara, T.; Xiao, J.Z. Potential Effects of Indole-3-Lactic Acid, a Metabolite of Human Bifidobacteria, on NGF-induced Neurite Outgrowth in PC12 Cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Sommella, E.; Salviati, E.; Campiglia, P.; Ganguli, K.; Djebali, K.; Zhu, W.; Walker, W.A. Indole-3-lactic acid, a metabolite of tryptophan, secreted by Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis is anti-inflammatory in the immature intestine. Pediatric Research 2020, 88, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013, 2013, 316523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.S.A.; Oliver, P.L. ROS Generation in Microglia: Understanding Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, K.; Sharma, K.; Tremblay, M. Chronic stress as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease: Roles of microglia-mediated synaptic remodeling, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Stress 2018, 9, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, C.E.; Bartolomucci, A. Stress and Alzheimer's disease: A senescence link? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2020, 115, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, N.J. The relationship between stress and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Stress 2018, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P, S.; Vellapandian, C. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis: Unveiling the Potential Mechanisms Involved in Stress-Induced Alzheimer's Disease and Depression. Cureus 2024, 16, e67595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.-Y.; Lin, T.-K.; Hsu, B.-C. Chapter 25 - Psychopathophysiology and compassion-based cognitive-behavior group therapy for patients with coronary artery disease. In Handbook of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy by Disorder, Martin, C.R., Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Eds. Academic Press: 2023; pp. 307-320. [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.B.; Montgomery, K.; Bale, T.L.; Thompson, S.M. What the hippocampus tells the HPA axis: Hippocampal output attenuates acute stress responses via disynaptic inhibition of CRF+ PVN neurons. Neurobiol Stress 2022, 20, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, V.; Bürgin, D.; Eckert, A.; Kind, N.; Dölitzsch, C.; Fegert, J.M.; Schmid, M. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation in a high-risk sample of children, adolescents and young adults in residential youth care – Associations with adverse childhood experiences and mental health problems. Psychiatry Research 2020, 284, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, C.; Kong, J. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res 2012, 7, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulisano, W.; Maugeri, D.; Baltrons, M.A.; Fà, M.; Amato, A.; Palmeri, A.; D'Adamio, L.; Grassi, C.; Devanand, D.P.; Honig, L.S. , et al. Role of Amyloid-β and Tau Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease: Confuting the Amyloid Cascade. J Alzheimers Dis 2018, 64, S611–s631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hong, F.; Yang, S. Amyloidosis in Alzheimer's Disease: Pathogeny, Etiology, and Related Therapeutic Directions. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azargoonjahromi, A. The duality of amyloid-β: its role in normal and Alzheimer’s disease states. Molecular Brain 2024, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weglinski, C.; Jeans, A. Amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease - front and centre after all? Neuronal Signal 2023, 7, Ns20220086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiek, E.S.; Bennett, D.A. Aducanumab and the "post-amyloid" era of Alzheimer research? Neuron 2021, 109, 3045–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Day, G.S. Anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer disease: finally, good news for patients. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2023, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Day, C.M.; Abdella, S.; Garg, S. Alzheimer's disease current therapies, novel drug delivery systems and future directions for better disease management. Journal of Controlled Release 2024, 367, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Chu, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, J. Impact of Anti-amyloid-β Monoclonal Antibodies on the Pathology and Clinical Profile of Alzheimer's Disease: A Focus on Aducanumab and Lecanemab. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 870517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Day, G.S. Anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer disease: finally, good news for patients. Mol Neurodegener 2023, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Wong, C.B.; Nakamura, K.; Mitsuyama, E.; Tanaka, A.; Kuhara, T.; Odamaki, T.; Xiao, J.Z. Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 with glycosidic activity enhances in vivo isoflavone bioavailability. Benef Microbes 2019, 10, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisio-Santos, D.A.; Karaahmet, B.; Belcher, E.K.; Owlett, L.D.; Trojanczyk, L.A.; Olschowka, J.A.; O'Banion, M.K. Evaluating Effects of Glatiramer Acetate Treatment on Amyloid Deposition and Tau Phosphorylation in the 3xTg Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Front Neurosci 2021, 15, 758677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, R.; Baglietto-Vargas, D.; LaFerla, F.M. The role of tau in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. CNS Neurosci Ther 2011, 17, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Dong, S.; Gu, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Focusing on Tau-Mediated Neurodegeneration. Translational Neurodegeneration 2012, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, E.E.; Ji, C.; Tetlow, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; Sigurdsson, E.M. Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease: current status and future directions. Nature Reviews Neurology 2023, 19, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-X.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Targeting Tau Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease. Drugs & Aging 2010, 27, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafii, M.S. Targeting tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. The Lancet 2016, 388, 2842–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, P.; Sehar, U.; Bisht, J.; Selman, A.; Culberson, J.; Reddy, P.H. Phosphorylated Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, P.; Zejneli, O.; Martinho, M.; Lasorsa, A.; Belle, V.; Smet-Nocca, C.; Tsvetkov, P.O.; Devred, F.; Landrieu, I. Role of Tau as a Microtubule-Associated Protein: Structural and Functional Aspects. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagishi, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Ogura, Y.; Matsuda, S. Dietary regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 2014, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limantoro, J.; de Liyis, B.G.; Sutedja, J.C. Akt signaling pathway: a potential therapy for Alzheimer’s disease through glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta inhibition. The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery 2023, 59, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayas, C.L.; Ávila, J. GSK-3 and Tau: A Key Duet in Alzheimer's Disease. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A.; Nishimura, T.; Yoshimoto, S.; Yoshida, K.; Gotoh, A.; Katoh, T.; Yoneda, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Katayama, T.; Odamaki, T. Comprehensive analysis of metabolites produced by co-cultivation of Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 with human iPS-derived intestinal epithelial cells. Frontiers in Microbiology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Shimomura, Y.; Andoh, A.; Bhan, A.K.; Blumberg, R.S.; Xavier, R.J.; Mizoguchi, A. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest 2008, 118, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenewicz, L.A.; Yin, X.; Wang, G.; Elinav, E.; Hao, L.; Zhao, L.; Flavell, R.A. IL-22 deficiency alters colonic microbiota to be transmissible and colitogenic. J Immunol 2013, 190, 5306–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Nie, K. Gut Microbiota Altered in Mild Cognitive Impairment Compared With Normal Cognition in Sporadic Parkinson's Disease. Front Neurol 2020, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljazovic, A.; Roy, U.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Lesker, T.R.; Zhao, B.; Gronow, A.; Amend, L.; Will, S.E.; Hofmann, J.D.; Pils, M.C. , et al. Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunology 2021, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ou, Z.; Peng, Y. Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in human gastrointestinal tract. Exp Ther Med 2017, 14, 3122–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O'Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V. , et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol Rev 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Han, Z.; Yin, Z.; Ge, X.; Lei, P. Relationship Between Amyloid-β Deposition and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease. Front Cell Neurosci 2021, 15, 695479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Han, J.; Wei, W.; Chen, F. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease: associations, pathogenic mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Front Aging Neurosci 2023, 15, 1258640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, D.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2023, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, A.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xue, G. The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: current understanding and future therapeutic targets. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, S.; Reindl, M. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Neuroinflammation: Current In Vitro Models. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Gage, F.H. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its role in Alzheimer's disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2011, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrup, K. The involvement of cell cycle events in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 2010, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.K.; Monteiro, M.J.; McShea, A.; Smith, M.A. The role of cell cycle-mediated events in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Exp Pathol 1999, 80, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masliah, E.; Terry, R. The role of synaptic proteins in the pathogenesis of disorders of the central nervous system. Brain Pathol 1993, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, C.; Falace, A.; Benfenati, F.; Fassio, A. Synaptic genes and neurodevelopmental disorders: From molecular mechanisms to developmental strategies of behavioral testing. Neurobiology of Disease 2022, 173, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Walsh, D.M. Alzheimer's disease: synaptic dysfunction and Abeta. Mol Neurodegener 2009, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.; Alifragis, P. Synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: the effects of amyloid beta on synaptic vesicle dynamics as a novel target for therapeutic intervention. Neural Regen Res 2018, 13, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Okamoto, S.-i.; Lipton, S.A.; Xu, H. Oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2014, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T. The interplay of neurotransmitters in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Spectr 2005, 10, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Tammineni, P. Mitochondrial Aspects of Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2017, 57, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelucchi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Di Luca, M.; Marcello, E. Chapter 28 - Synaptic dysfunction in early phases of Alzheimer's Disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Quartarone, A., Ghilardi, M.F., Boller, F., Eds. Elsevier: 2022; Vol. 184, pp. 417-438.
- Holz, R.W.; Fisher, S.K. Chapter 12 - Synaptic Transmission and Cellular Signaling: An Overview. In Basic Neurochemistry (Eighth Edition), Brady, S.T., Siegel, G.J., Albers, R.W., Price, D.L., Eds. Academic Press: New York, 2012; pp. 235-257. [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, D.M. Communication networks in the brain: neurons, receptors, neurotransmitters, and alcohol. Alcohol Res Health 2008, 31, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, M.; Bernard, L.P.; Zhang, H. Postsynaptic density 95 (PSD-95) serine 561 phosphorylation regulates a conformational switch and bidirectional dendritic spine structural plasticity. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 16150–16160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coley, A.A.; Gao, W.-J. PSD-95 deficiency disrupts PFC-associated function and behavior during neurodevelopment. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Furuoka, H.; Kaya, M.; Kuhara, T. Oral Administration of Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve Improves Facilitation of Hippocampal Memory Extinction via Restoration of Aberrant Higher Induction of Neuropsin in an MPTP-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiosaka, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Neuropsin—A possible modulator of synaptic plasticity. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 2011, 42, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.-i.; Muroi, Y.; Unno, T.; Ishii, T. Rolipram improves facilitation of contextual fear extinction in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2017, 134, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kuhara, T.; Oki, M.; Xiao, J.Z. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve A1 on the cognitive function of older adults with memory complaints: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Benef Microbes 2019, 10, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, G.; Håkansson, C.; Pereira, J.B.; Palmqvist, S.; Hansson, O.; van Westen, D.; Westman, E. Medial temporal atrophy in preclinical dementia: Visual and automated assessment during six year follow-up. Neuroimage Clin 2020, 27, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.A.; Wichmann, A.K.; Torgerson, B.M.; Ward, M.A.; Schmitz, T.W.; Ries, M.L.; Koscik, R.L.; Asthana, S.; Johnson, S.C. Structural MRI discriminates individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment from age-matched controls: a combined neuropsychological and voxel based morphometry study. Alzheimers Dement 2006, 2, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases. Mol Biomed 2022, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Jin, G.; Pang, X.; Mo, Q.; Bao, J.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Xie, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. , et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG colonization in early life regulates gut-brain axis and relieves anxiety-like behavior in adulthood. Pharmacological Research 2022, 177, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Braun, C.; Murphy, E.F.; Enck, P. Bifidobacterium longum 1714™ Strain Modulates Brain Activity of Healthy Volunteers During Social Stress. Am J Gastroenterol 2019, 114, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, R.; Khosravifar, M.; Abiri, S.; Dashtbin, S.; Alvandi, A.; Nedaei, S.E.; Salimi, Z.; Zarei, F.; Abiri, R. A domestic strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates cognitive deficit and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behavioural Brain Research 2025, 476, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tette, F.M.; Kwofie, S.K.; Wilson, M.D. Therapeutic Anti-Depressant Potential of Microbial GABA Produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strains for GABAergic Signaling Restoration and Inhibition of Addiction-Induced HPA Axis Hyperactivity. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2022, 44, 1434–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharwani, A.; Mian, M.F.; Surette, M.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Forsythe, P. Oral treatment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates behavioural deficits and immune changes in chronic social stress. BMC Medicine 2017, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, D.; O'Mahony, L.; Murphy, E.F.; Bourke, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Kiely, B.; Shanahan, F.; Quigley, E.M. Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 modulates host inflammatory processes beyond the gut. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbuhn, A.F.; Reynolds, S.M.; Campbell, C.W.; Bradford, L.A.; Deckert, J.A.; Kreutzer, A.; Fry, A.C. Effects of Probiotic (Bifidobacterium longum 35624) Supplementation on Exercise Performance, Immune Modulation, and Cognitive Outlook in Division I Female Swimmers. Sports 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Tompkins, T.A.; Matera, M.G. Immunomodulatory impact of a synbiotic in T(h)1 and T(h)2 models of infection. Ther Adv Respir Dis 2010, 4, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-j.; Park, G.; Shin, H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J. Administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and Bifidobacterium longum BORI Improves Cognitive and Memory Function in the Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-J.; Chen, J.-L.; Liao, J.-F.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chieu, M.-W.; Ke, Y.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Hsieh-Li, H.M. Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 prevents cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease mice by modulating propionic acid levels, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta activity, and gliosis. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies 2021, 21, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




