Submitted:
16 January 2025
Posted:
16 January 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
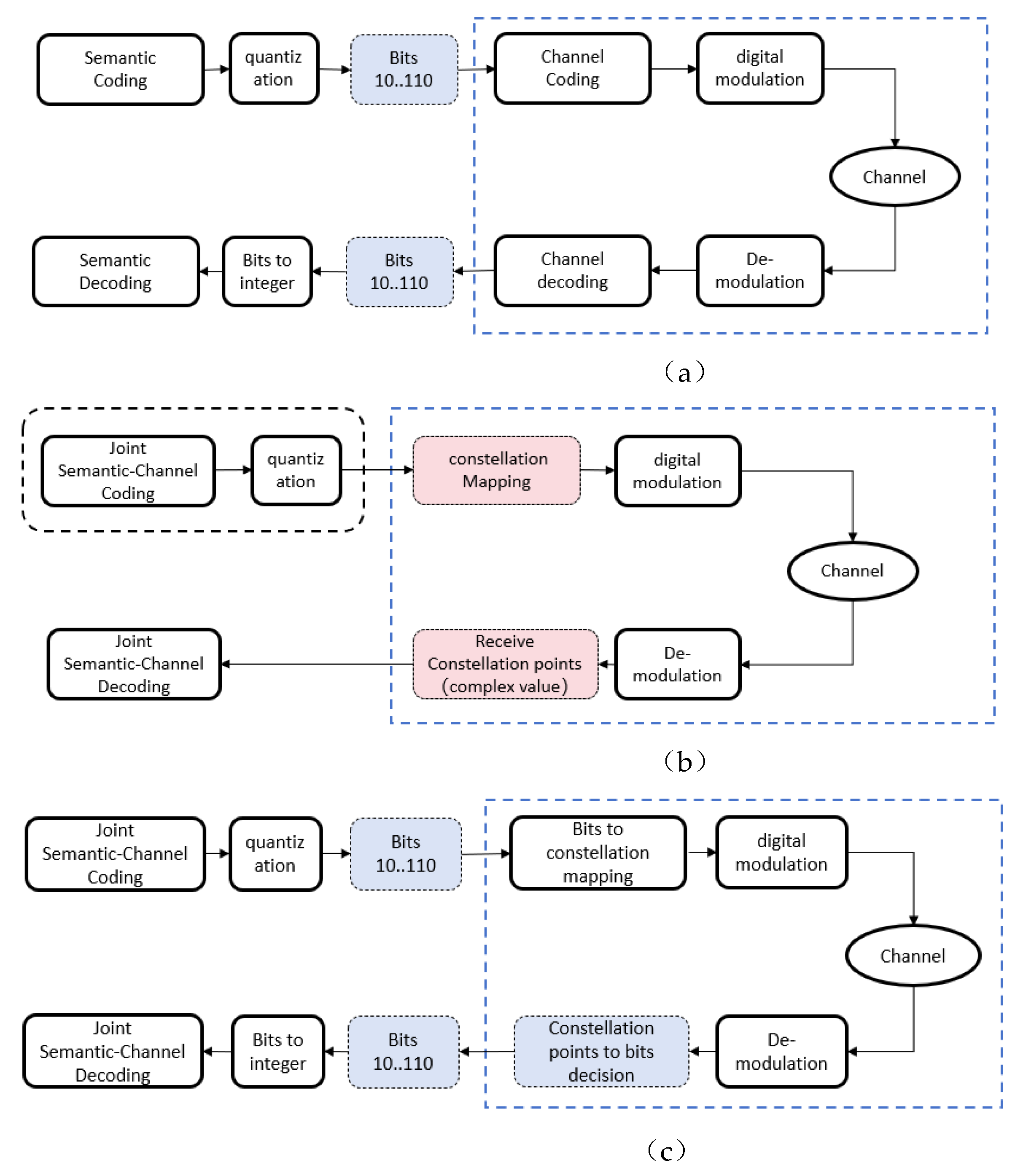
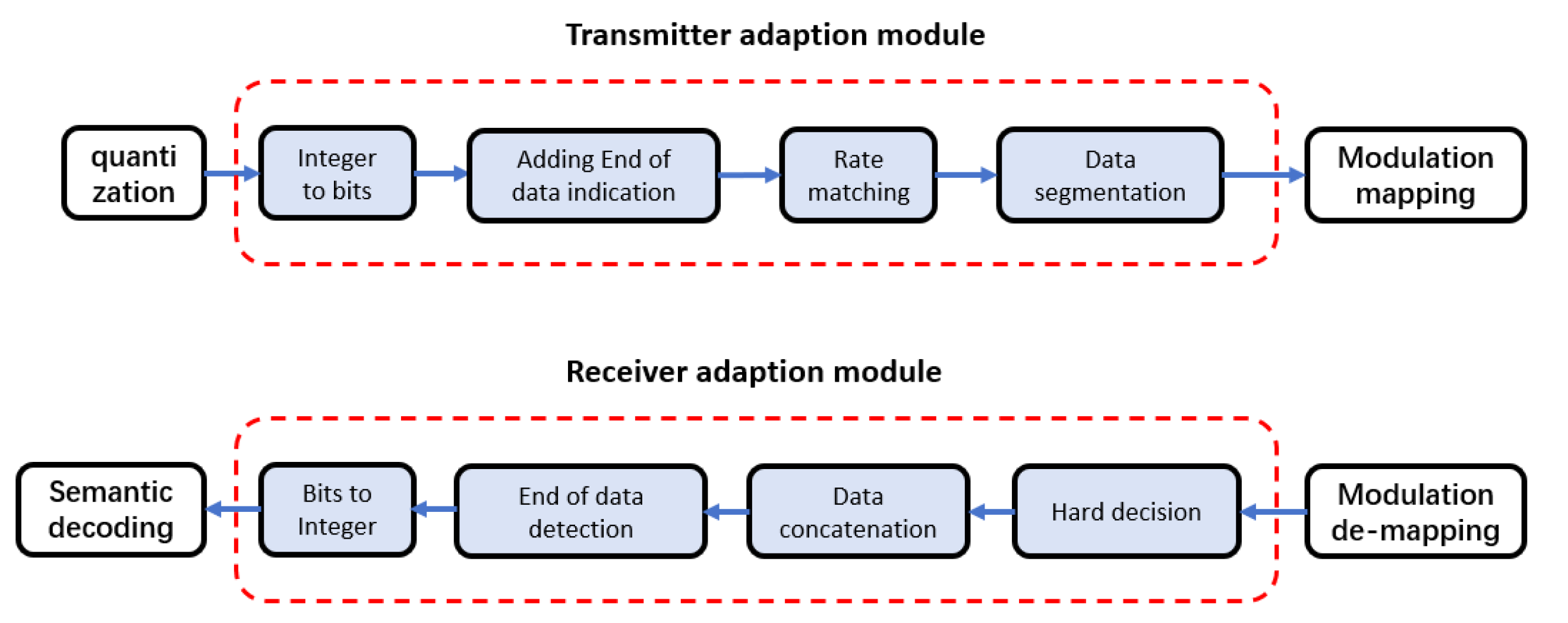
- The specific physical layer procedure of bit-conversion JSCC transmission framework for semantic communication is designed. Furthermore, a semantic communication simulator is developed to implement and verify this transmission framework.
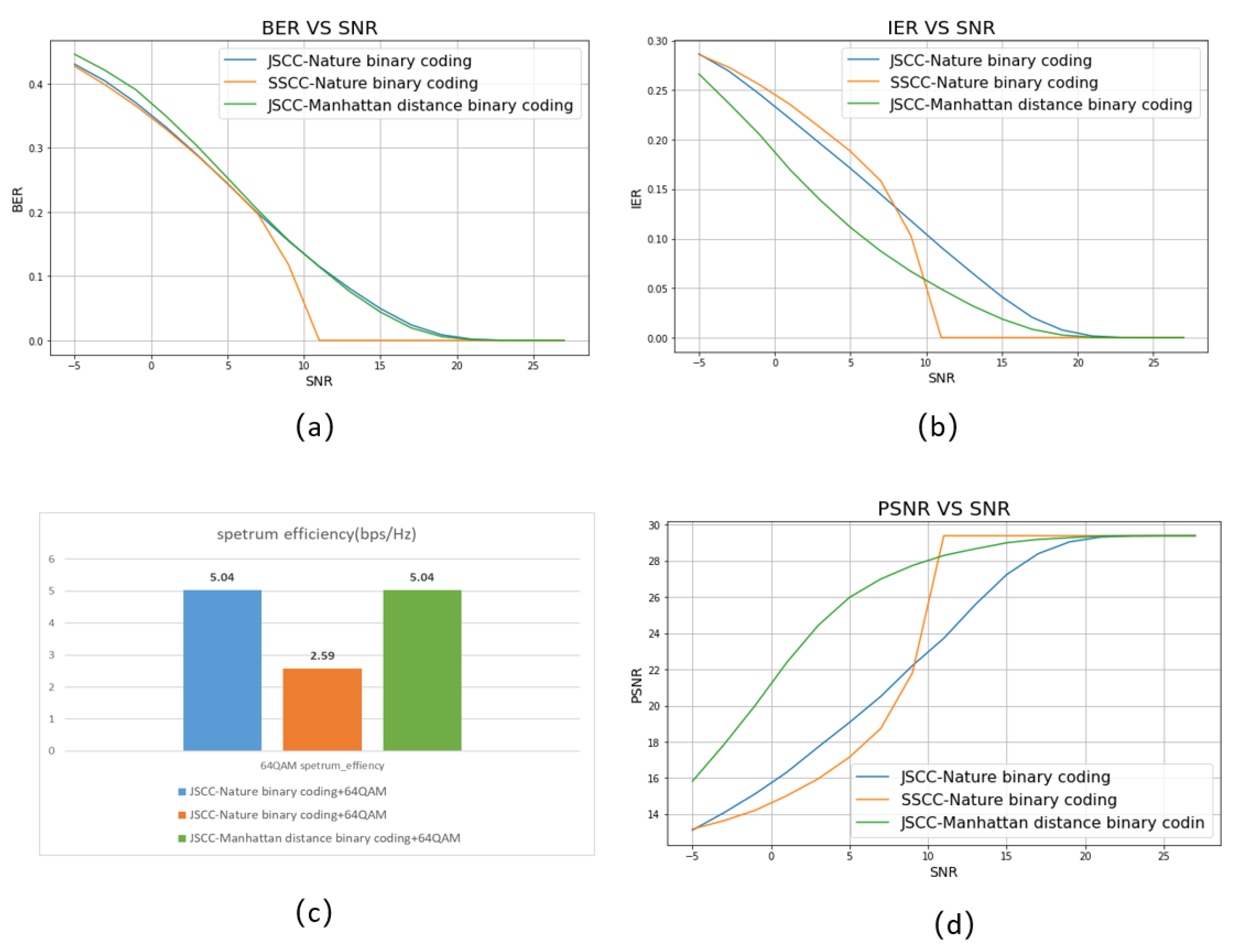
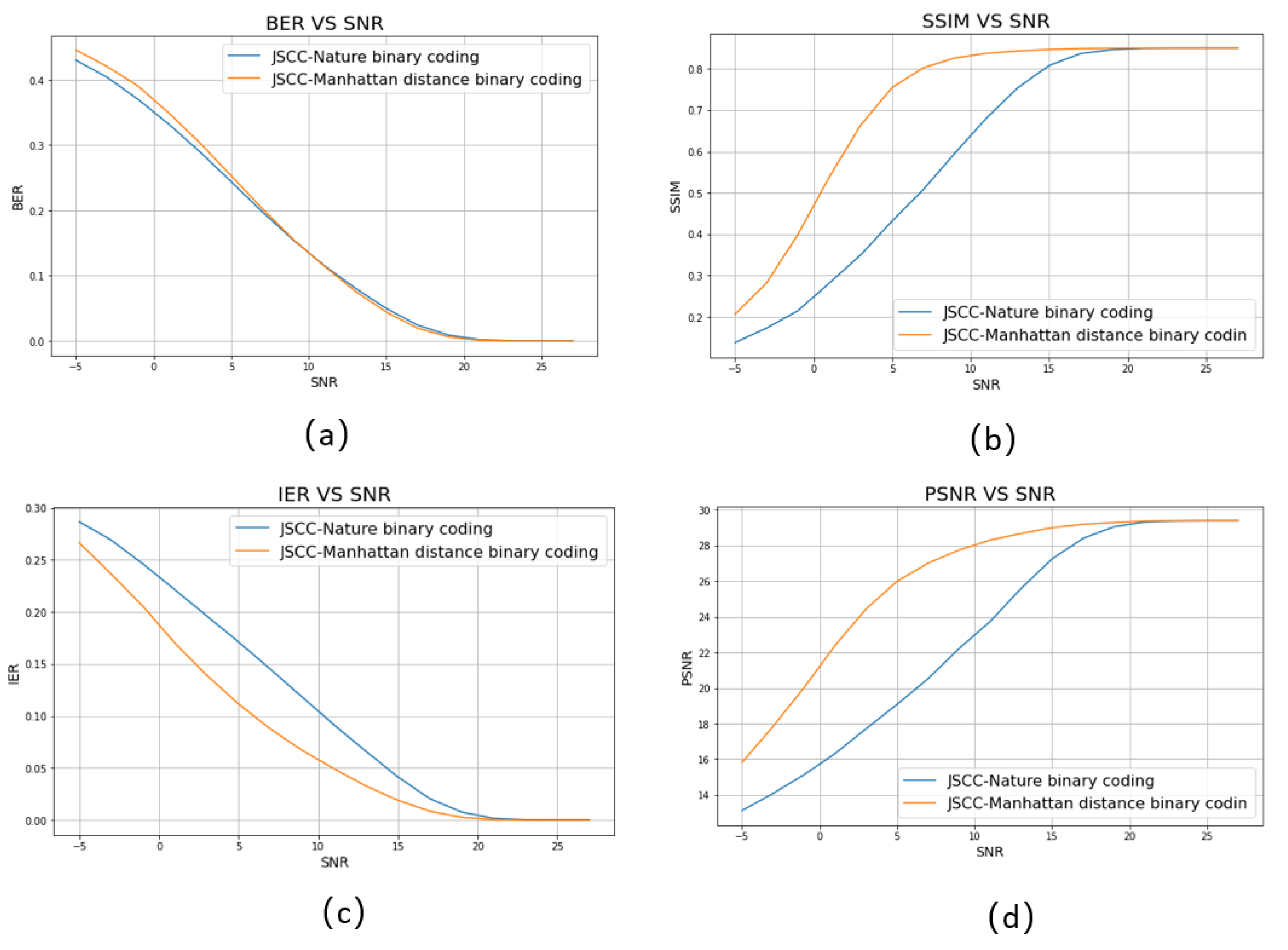
- A novel physical layer metric, IER (Integer Error Rate), is proposed as a physical layer metric for semantic information transmission. And we prove that IER is more suitable than BER for semantic communication by simulation.
- We present a minimum Manhattan distance constellation mapping scheme for m-QAM modulation to optimize the transmission quality in the bit-conversion JSCC transmission framework.
- Lastly, based upon this minimum Manhattan distance constellation mapping scheme, we propose a hybrid transmission scheme to adapt different quantization levels, which can separate the semantic quantization output from the modulation order. Meanwhile, this hybrid transmission scheme can improve the transmission quality of semantic communication at the low SNR range while leveraging the bandwidth-saving advantage of semantic communication.[14,17,18,19]
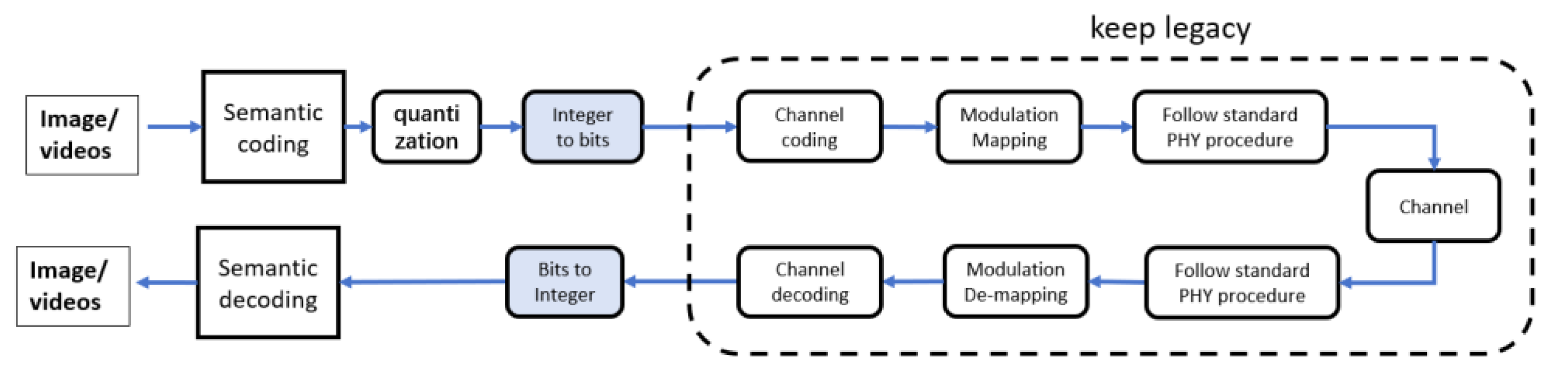
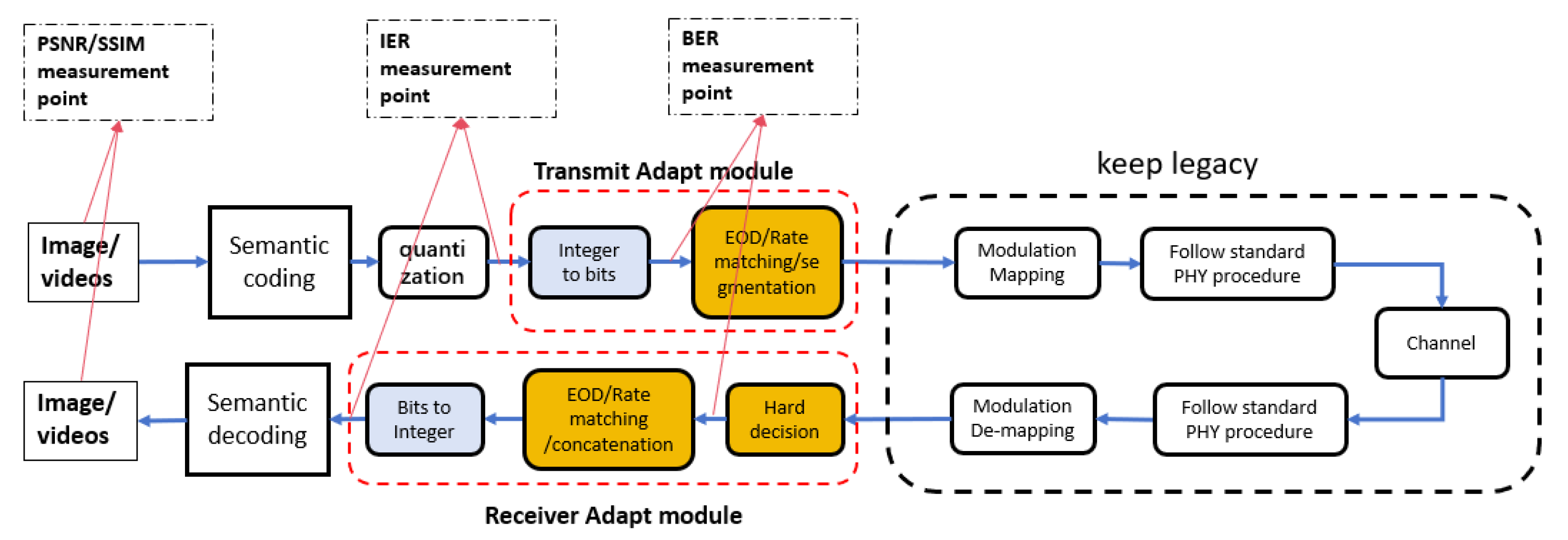
2. Bit-Conversion-Based JSCC Transmission Framework and Simulator
2.1. Bit-Conversion-Based JSCC Transmission Framework
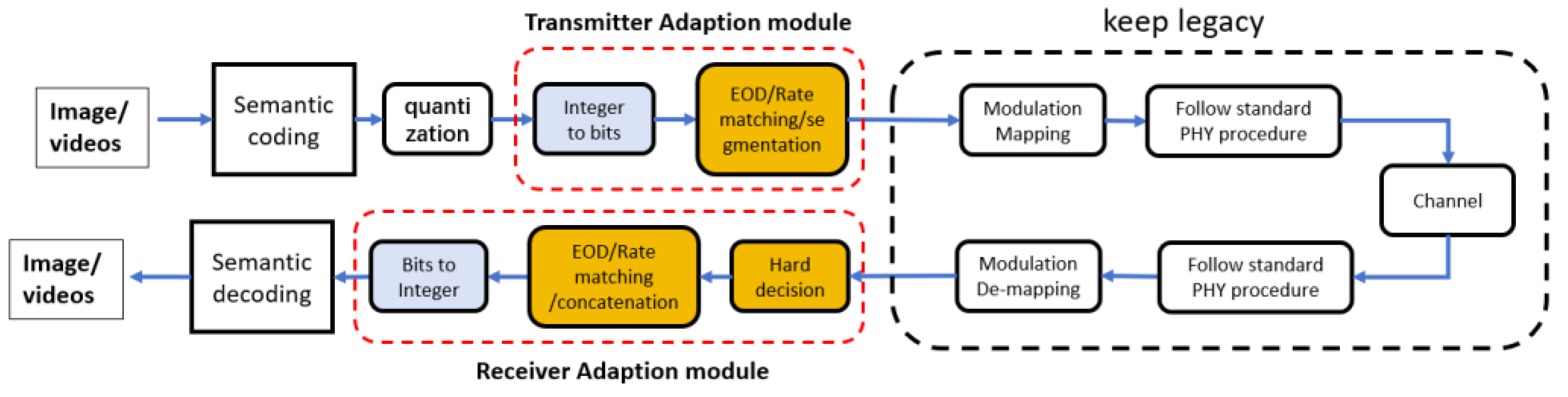
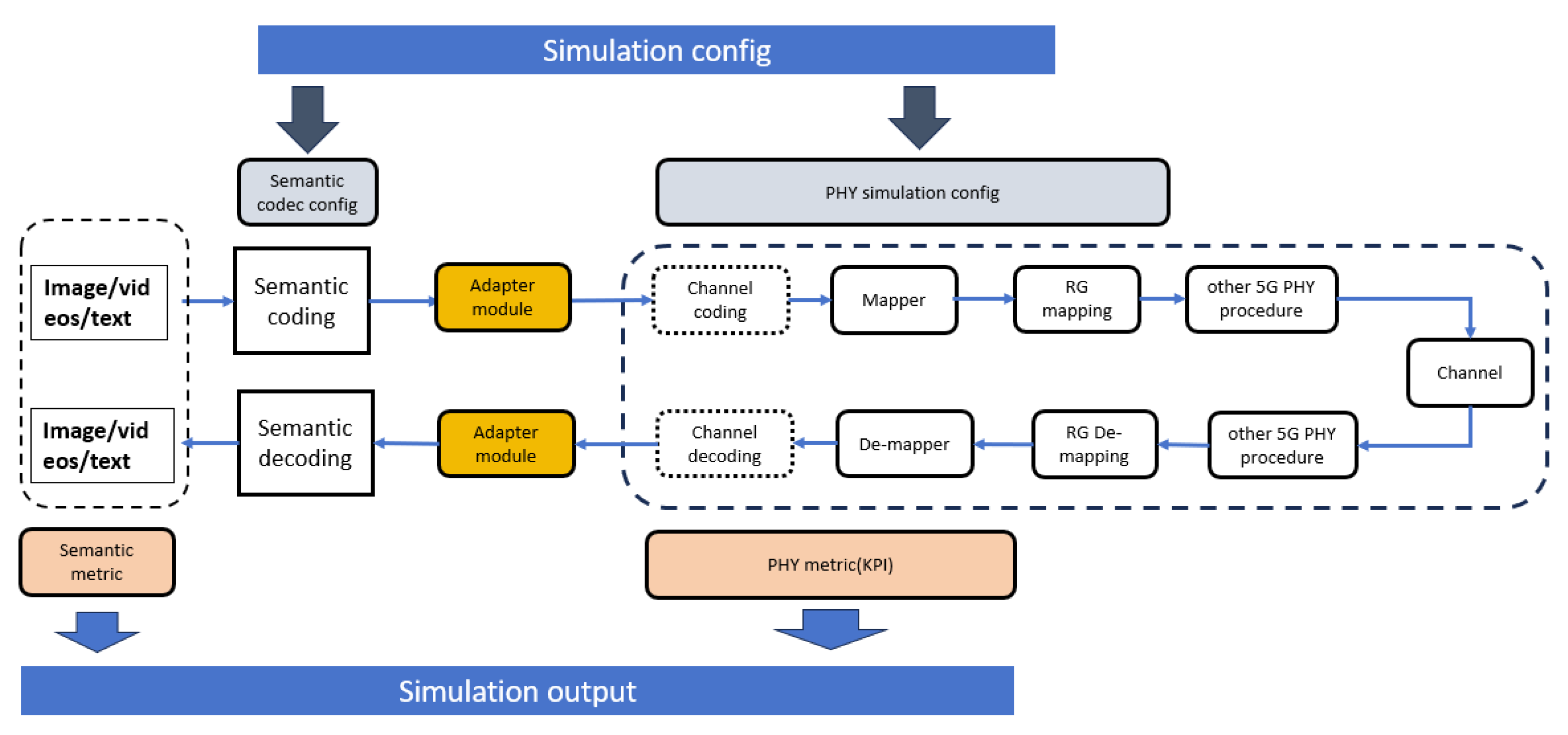
1.2. Simulation Planform for E2E Semantic Communication
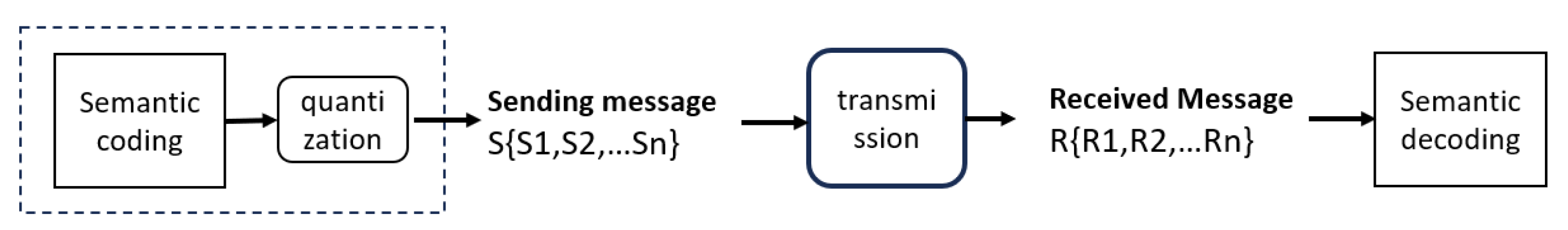
3. IER--A Novel Physical-Layer Semantic Metric
3.1. Definition of IER (Integer Error Rate)
3.2. Relation Between BER and IER
3.3. Relation Between IER BER and Semantic Metric
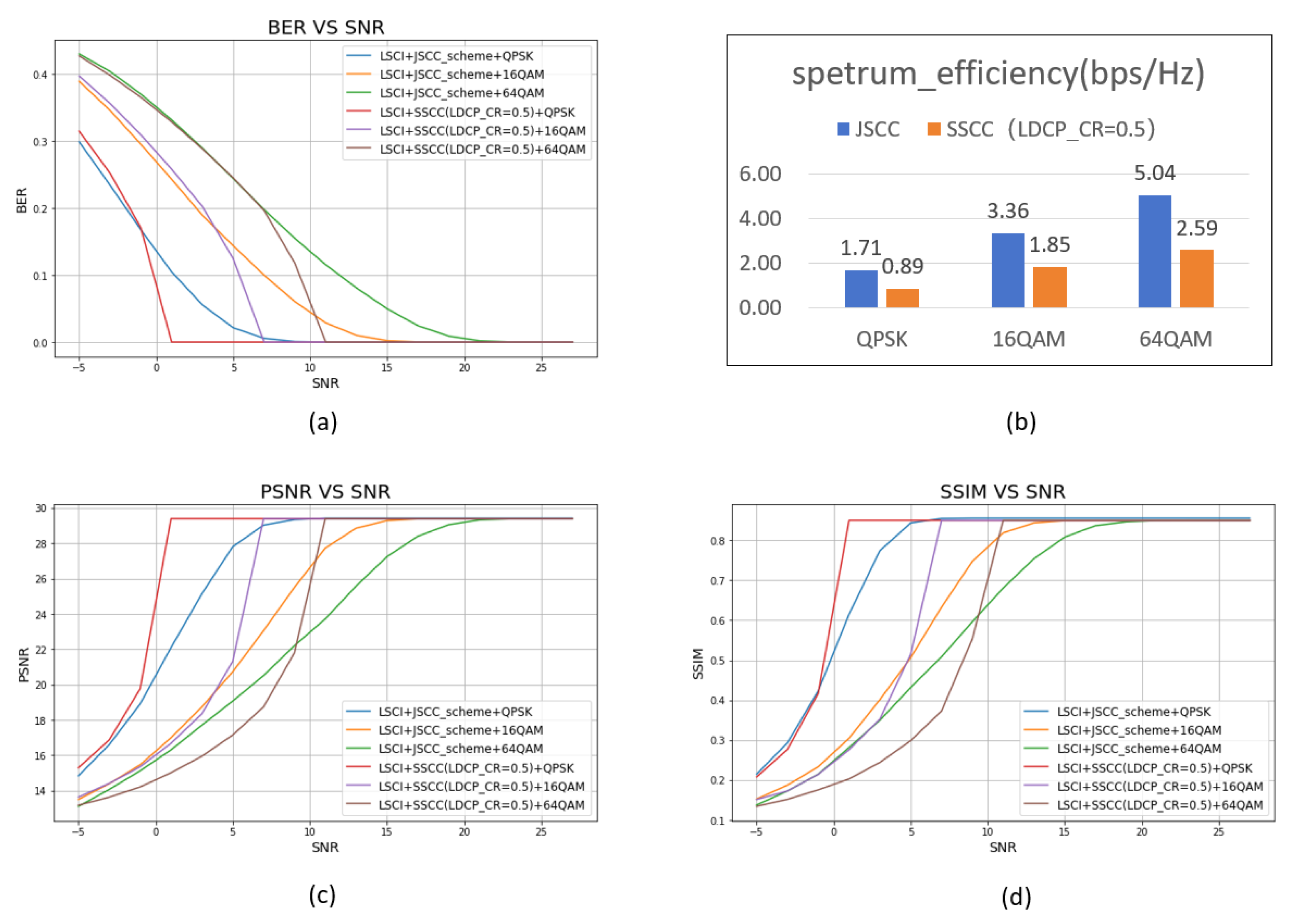
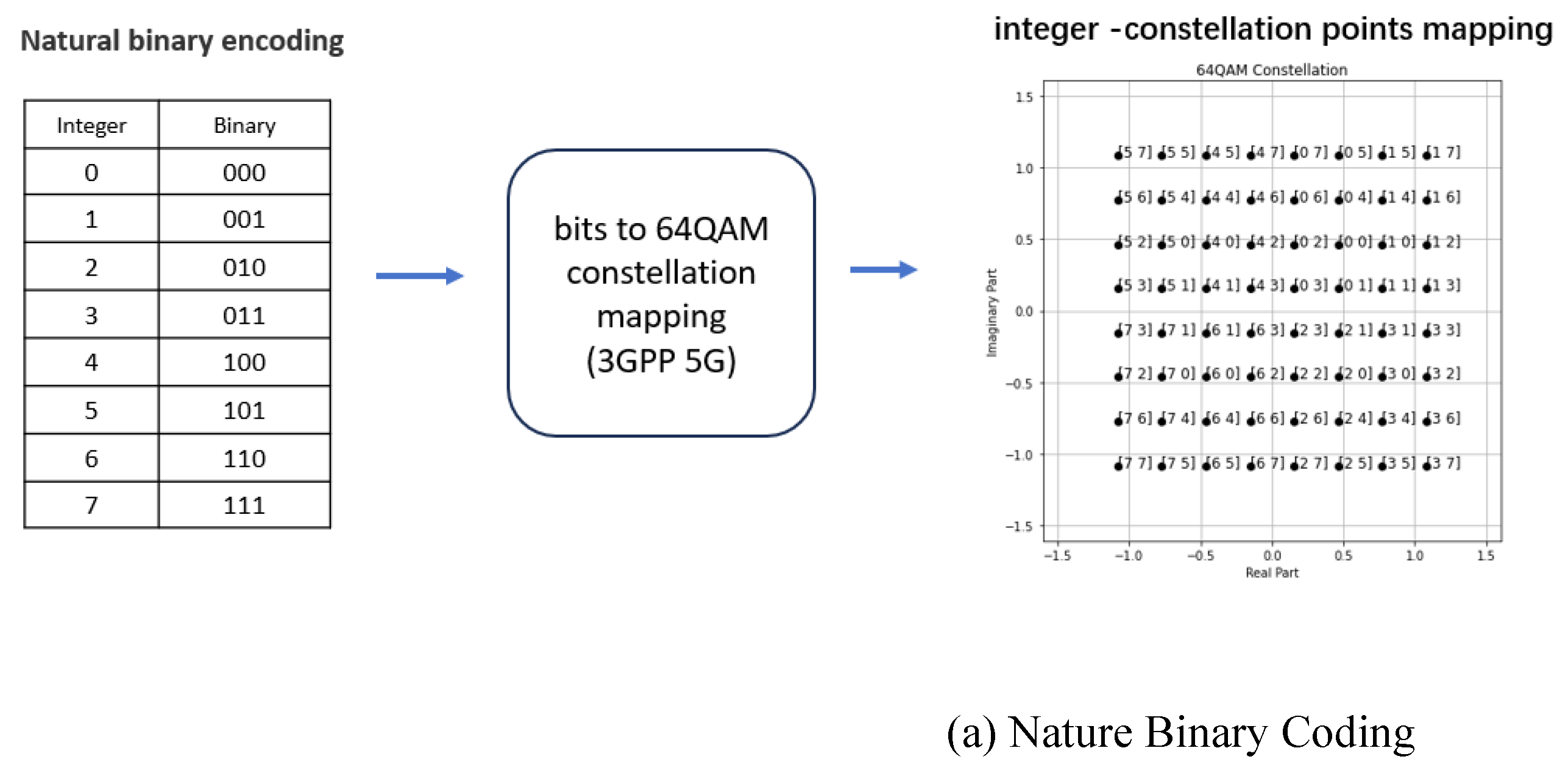
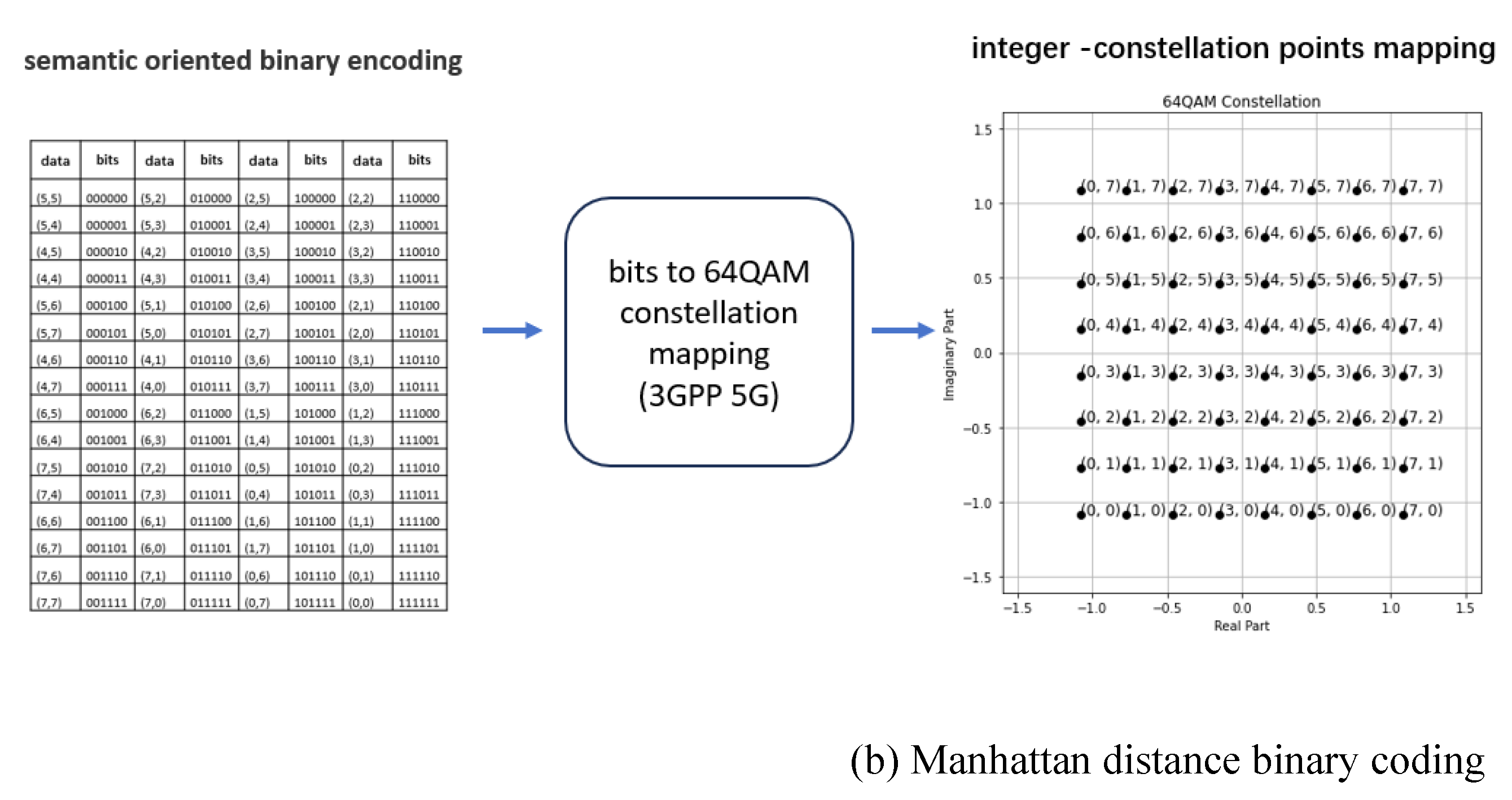
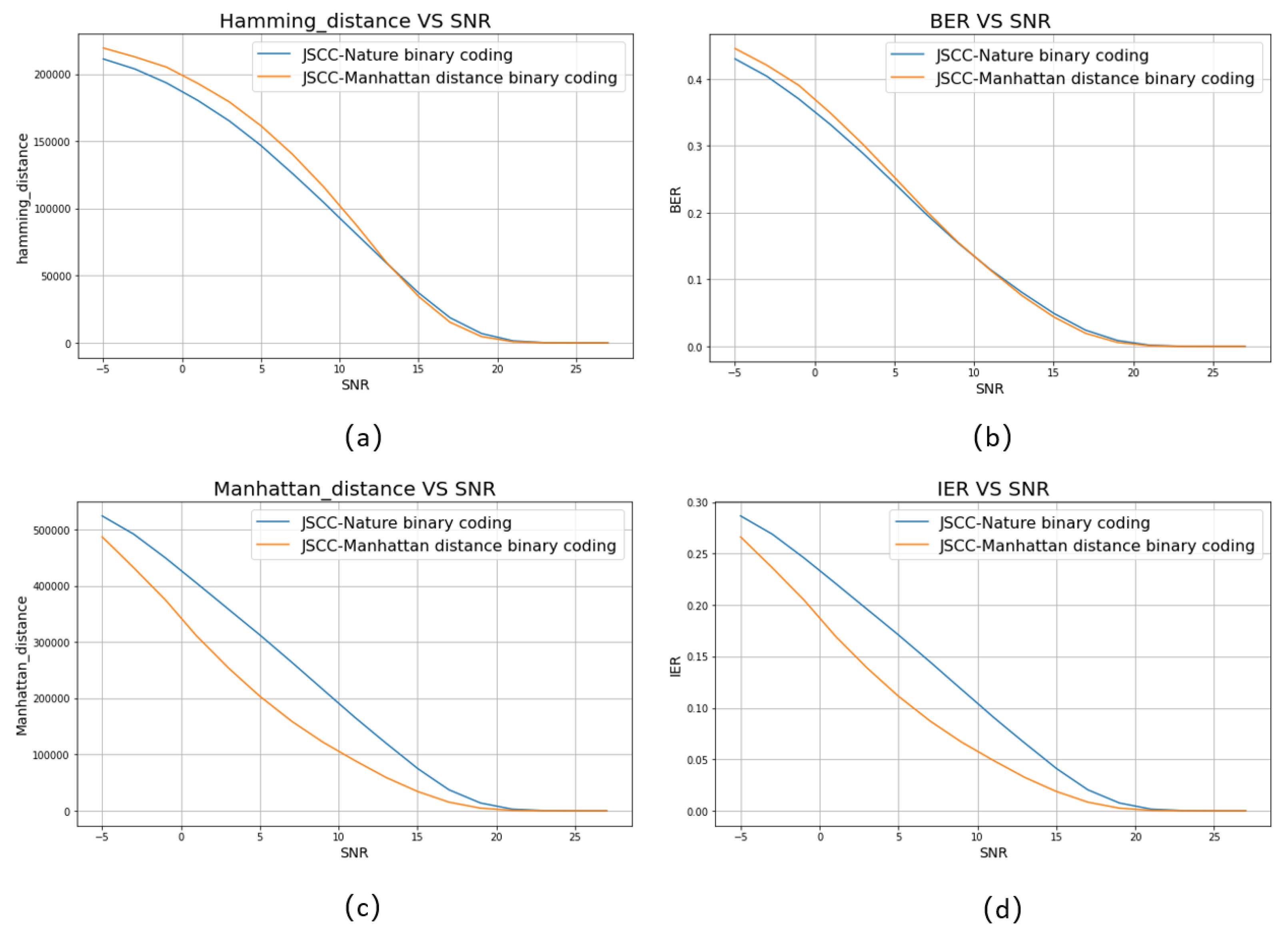
4. Optimization for the Bit Conversion JSCC Scheme
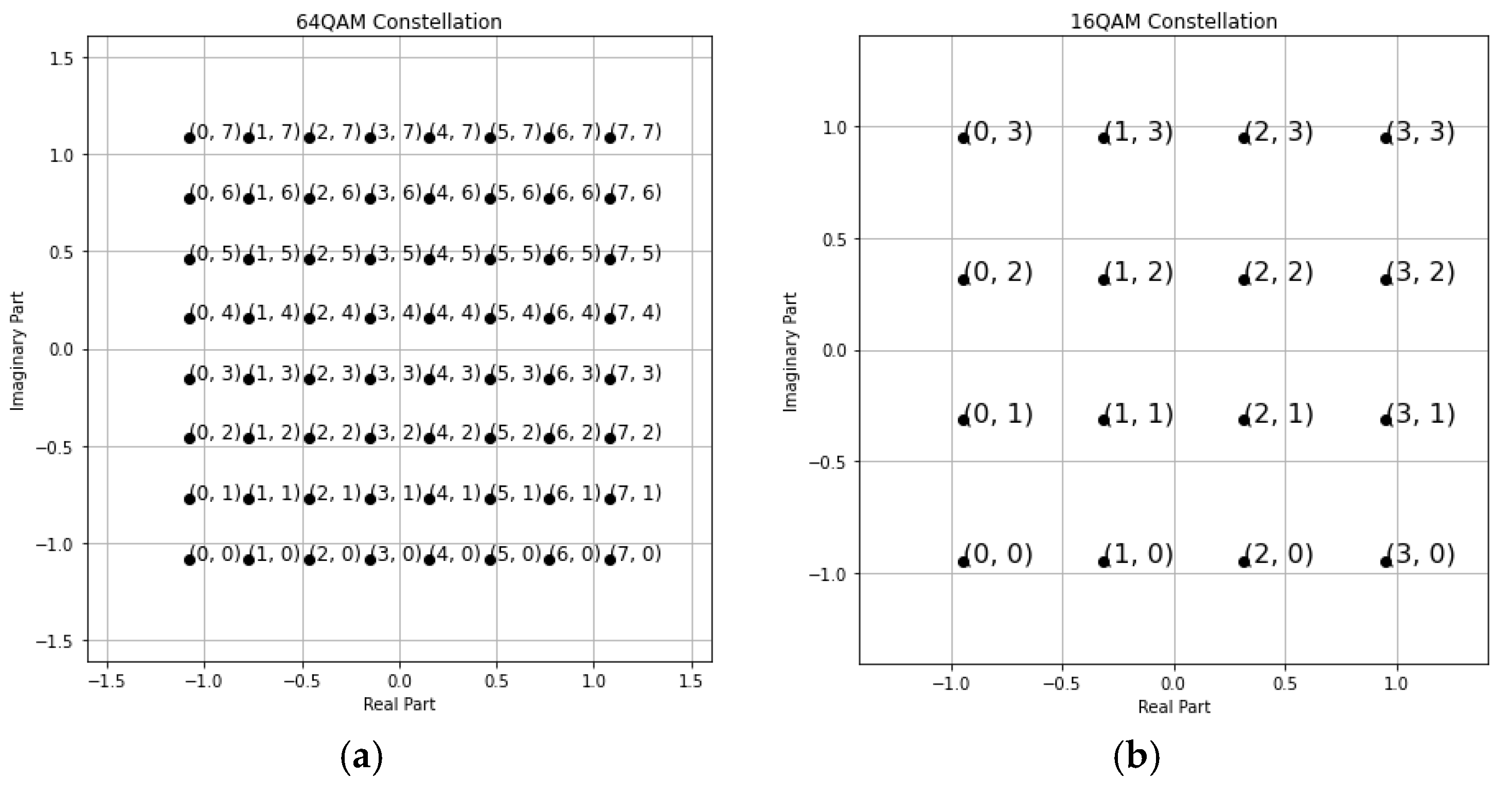
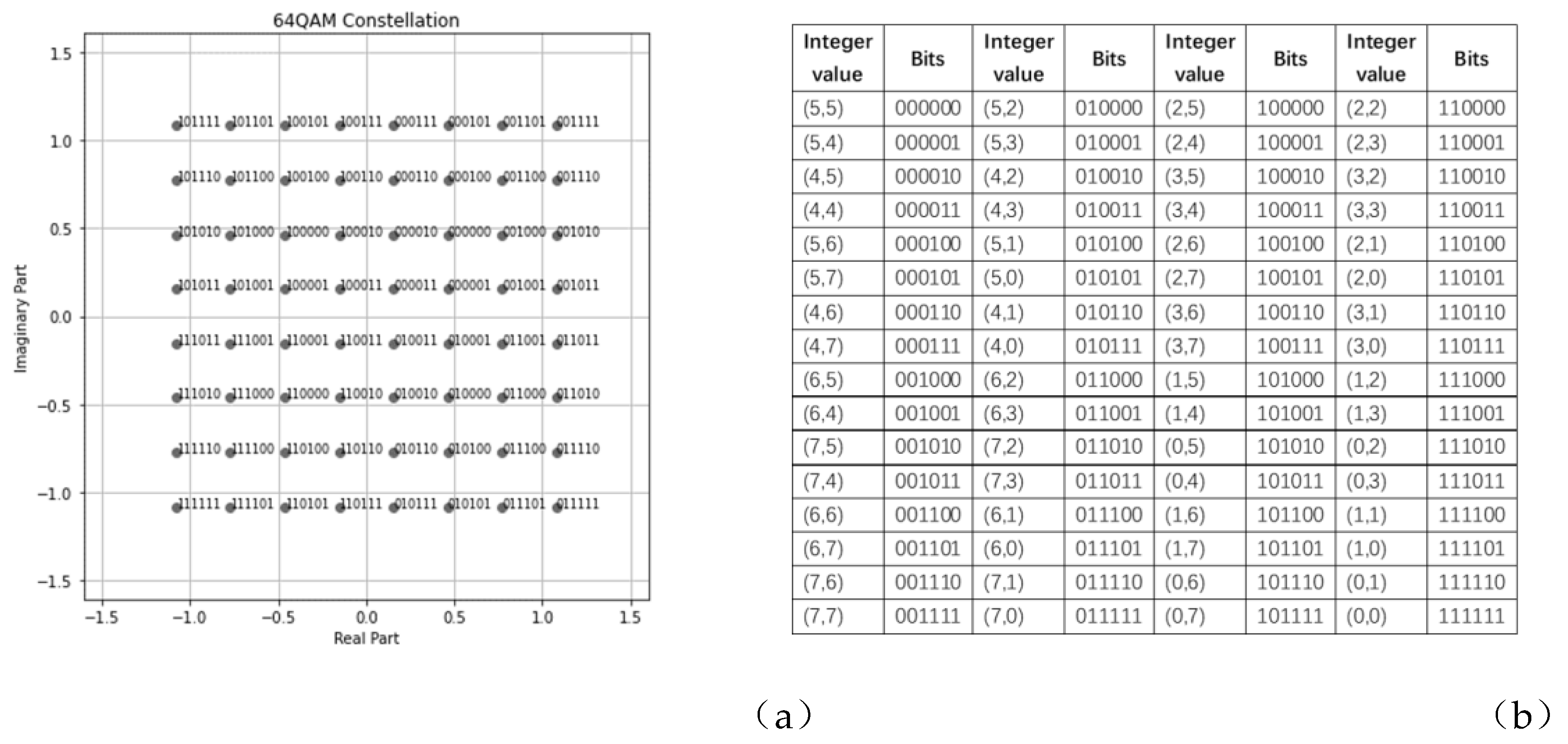
4.1. Minimum Manhattan Distance Constellation Mapping Scheme
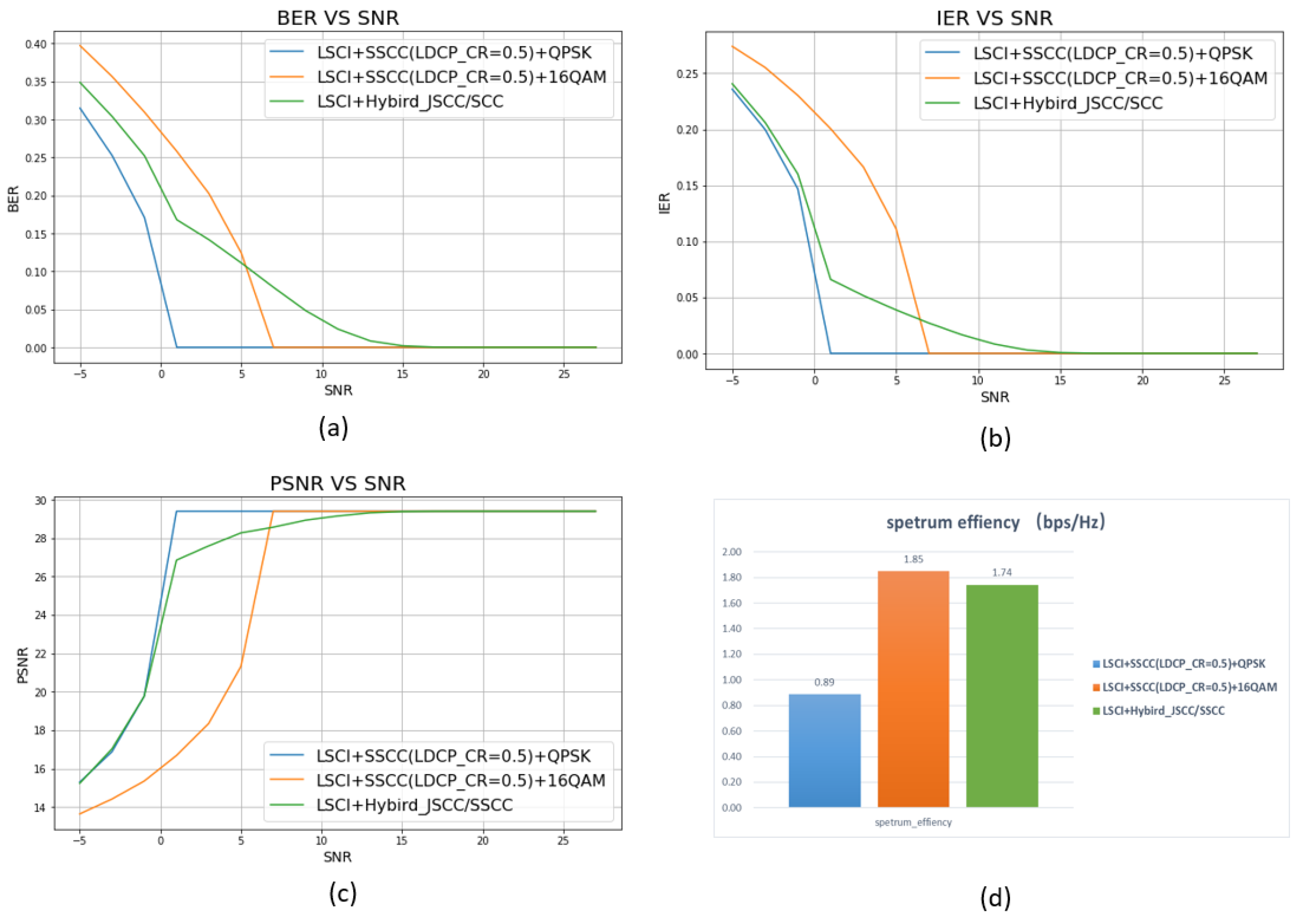
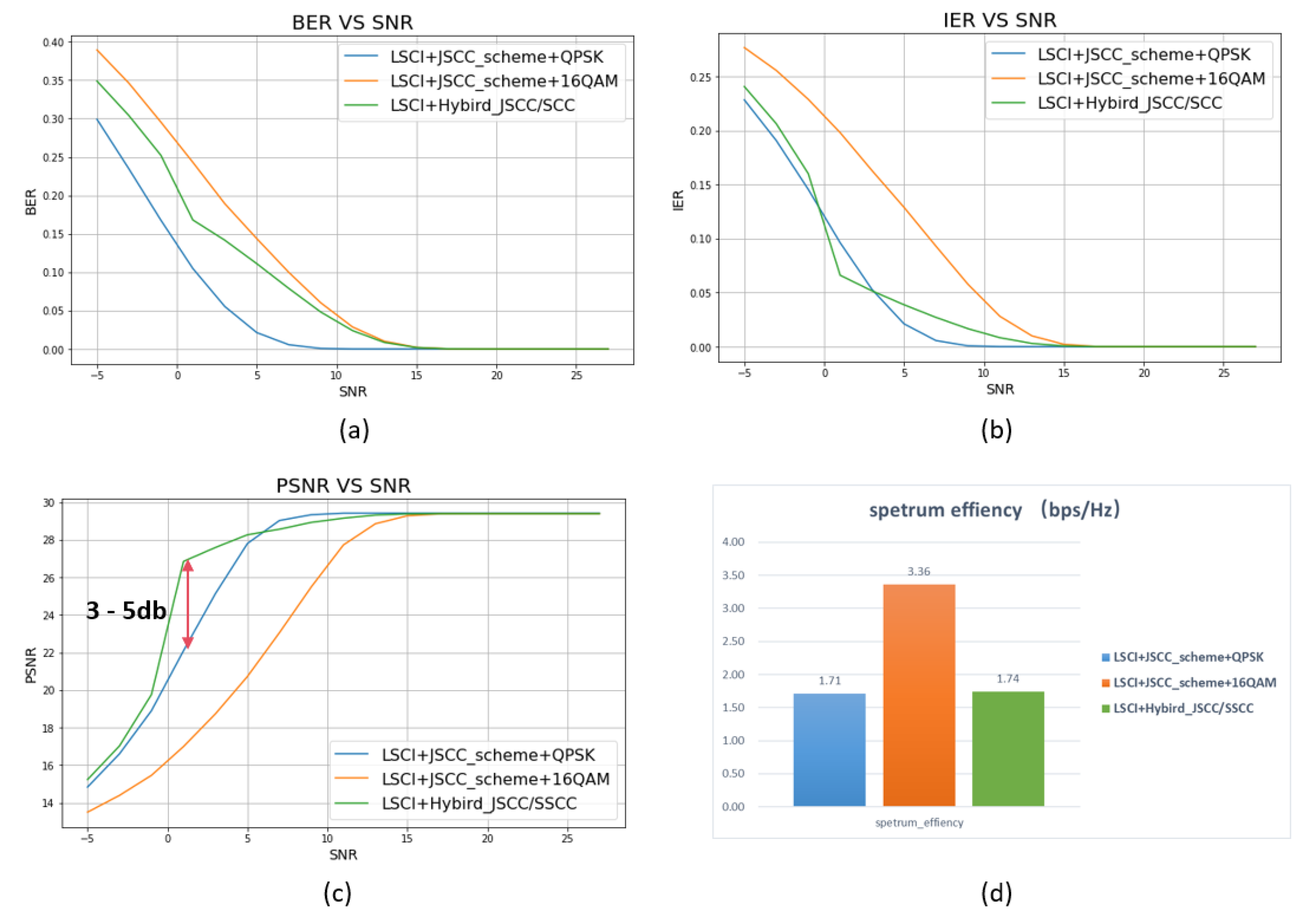
4.2. Hybrid JSCC/SSCC Transmission Scheme
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ping Zhang, Wenjun Xu, Hui Gao, Kai Niu, Xiaodong Xu, Xiaoqi Qin, Caixia Yuan, Zhijin Qin, Haitao Zhao, Jibo Wei, Fangwei Zhang; Toward Wisdom-Evolutionary and Primitive-Concise 6G: A New Paradigm of Semantic Communication Networks, Engineering 2021.
- Y. Wang, Z. Y. Wang, Z. Gao, D. Zheng, S. Chen, D. Gunduz, and H. V. Poor, ‘‘Transformer-empowered 6G intelligent networks: From massive MIMO processing to semantic communication,’’ IEEE Wireless Commun., early access, Nov. 2022; 23. [Google Scholar]
- E. Calvanese Strinati and S. Barbarossa, ‘‘6G networks: Beyond Shannon towards semantic and goal-oriented communications,’’ Comput. Netw., vol. 190, 21, Art. no. 20 May 1079.
- P: Zhang, Jing Gu, Xiaoxian Li, Qimei Cui, and Xiaofeng Tao, "Current Status and Prospects of Semantic Communication Research," China Basic Science, 20 April.
- Yufei Bo, Yiheng Duan, Shuo Shao, Meixia Tao, Joint Coding-Modulation for Digital Semantic Communications via Variational Autoencoder IEEE Transactions on Communications.
- 2023; 12.
- O: Luo,Hsiao-Hwa Chen,Qing Guo,“Semantic Communications, 2022; 29.
- Z. Weng and Z. Qin, “Semantic communication systems for speech transmission,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 2434.
- T. Han, Q. T. Han, Q. Yang, Z. Shi, S. He, and Z. Zhang, “Semantic-preserved communication system for highly efficient speech transmission,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- H. Xie, Z. H. Xie, Z. Qin, G. Y. Li, and B.-H. Juang, “Deep learning enabled semantic communication systems,” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 69, pp. 2663. [Google Scholar]
- Q. Zhou, R. Q. Zhou, R. Li, Z. Zhao, C. Peng, and H. Zhang, “Semantic communication with adaptive universal transformer,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- J. Shao, Y. J. Shao, Y. Mao, and J. Zhang, “Learning task-oriented communication for edge inference: An information bottleneck approach,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- H. Xie, Z. H. Xie, Z. Qin, and G. Y. Li, “Task-oriented multi-user semantic communications for VQA,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- E. Bourtsoulatze, D. B. E. Bourtsoulatze, D. B. Kurka, and D. Gündüz, “Deep joint source channel coding for wireless image transmission,” IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw., vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 567–579, Sep. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- D. B. Kurka and D. Gündüz, "DeepJSCC-f: Deep joint source-channel coding of images with feedback", IEEE J. Sel. Areas Inf. Theory, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 178-193, Dec. 2020.
- T.-Y. Tung, D. B. T.-Y. Tung, D. B. Kurka, M. Jankowski, and D. Gunduz, “DeepJSCC-Q: Constellation constrained deep joint source-channel coding,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- A: Yang,Sixian Wang,Jincheng Dai,Kailin Tan,Kai Niu,Ping Zhang, “WITT, 2023.
- 2023; 41.
- P. Jiang, C.-K. P. Jiang, C.-K. Wen, S. Jin, and G. Y. Li, “Wireless semantic communications for video conferencing,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Z. Weng and Z. Qin, “Semantic communication systems for speech transmission” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 2434.
- 2023.
- Chen Dong, Haotai Liang, Xiaodong Xu, Shujun Han, Bizhu Wang, Ping Zhang, “Semantic Communication System Based on Semantic Slice Models Propagation”, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 2023; 41.
- Michel Deza, Michel Petitjean, Krassimir Markov (eds. 2 July 2012; -5.
- 3GPP TS 38.211 V16.10.0 Physical channels and modulation, chapter5.
- 3GPP TS 38.212 V16.10.


| Message Vector |
integer- valued |
Manhattan distance to vector S | Nature binary coding | Hamming distance to vector S | BER | IER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | [1, 2, 5, 7] | 0 | [001, 010, 101, 111] | 0 | 0% | 0% |
| R1 | [0, 3, 5, 6] | 3 | [000, 011, 101, 110] | 3 | 25% | 9% |
| R2 | [5, 2, 1, 3] | 12 | [101, 010, 001, 011] | 3 | 25% | 37% |
| R3 | [5, 6, 5, 7] | 8 | [101, 110, 101, 111] | 2 | 16% | 13% |
| Test case | binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
|---|---|---|
| transmission Framework: | Bit-conversion JSCC | Bit-conversion JSCC |
| Source file | image | image |
| Semantic codec: | LSCI | LSCI |
| Quantization output range: | [0-7] | [0-7] |
| Data to binary Codec: | Nature binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
| Channel coding | NO | NO |
| Bits constellation Mapping: | 3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G |
| Modulation: | 64QAM | 64QAM |
| Simulation SNR range | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] |
| Channel model | AWGN | AWGN |
| Algorithm Manhattan distance binary coding generation | |
| 1, | Input: |
| 2, | m-QAM modulation order |
| 3, | m-QAM standard bit constellation mapper |
| 4, | Integer constellation mapper |
| 5, | data process: |
| 6, | -> |
| 7, | for i from 0 to : |
| 8, | for integer in range [0, -1]: |
| 9, | find that == |
| 10, | then mapping (): |
| 11, | End for |
| 12, | End for |
| 13, | output: |
| 14, | Manhattan distance binary coding mapping table |
| Test case | JSCC-Nature binary coding | JSCC-Manhattan distance binary coding |
SSCC-Nature binary coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semantic transmission Framework: | Bit-conversion JSCC | Bit-conversion JSCC |
Bit-conversion SSCC |
| Source file | image | image | image |
| Semantic codec: | LSCI | LSCI | LSCI |
| Quantization range: | [0-7] | [0-7] | [0-7] |
| Data to binary Codec: |
Nature binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
Nature binary coding |
| Channel coding | NO | NO | LDPC CR=0.5 |
| Bits constellation Mapping: |
3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G |
| Modulation: | 64QAM | 64QAM | 64QAM |
| Simulation SNR range | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] |
| Channel model | AWGN | AWGN | AWGN |
| test case | modulation | binary codec | channel coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid JSCC/SSCC transmission (QPSK+16QAM) | QPSK (1/3 data) |
nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| 16QAM (2/3 data) |
Manhattan distance binary coding | NO | |
| SSCC-QPSK | QPSK | nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| SSCC-16QAM | 16QAM | nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| test case | modulation | binary codec | channel coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid JSCC/SSCC transmission (QPSK+16QAM) | QPSK (1/3 data) |
nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| 16QAM (2/3 data) |
Manhattan distance binary coding | NO | |
| JSCC-QPSK | QPSK | nature binary coding | NO |
| JSCC-16QAM | 16QAM | nature binary coding | NO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





