2. Equations
These laws want to explain the results of the final derivation process of this research and what this research wants to prove.
(1)
Where Gµν represents the Einstein tensor, G is the universal gravitational constant, Tµν is the energy-momentum tensor,
is the wavelength is (nm),
is the photon energy is in electron volt, n is the energy level.
Where k represents the wave vector.
Where
represents the reduced Planck constant, rn is the Bohr radius, En is the photon energy is in joules,
is the Planck time,
is the Planck length. This law explains the final result of the derivation. This law proves the creation of a relationship that links the photon energy and curvature of space-time.
Where
represents the Planck energy.
(5)
The precise structure constant links the speed of the electron to the speed of light through this law.
Likewise, it affects energy in relativity and makes it the total energy of the photon.
(6)
Where E represents the energy, h( a) is the atomic constant, KE is the kinetic energy, P is the momentum,
is the angular velocity, C is the speed of light,
is the Phase Velocity, and
is the fine-structure constant. This law explains the final result of the derivation. This law proves the creation of a relationship that links energy and kinetic energy. That the lost kinetic energy comes out in the form of radiant energy.
(7)
Where
represents the Planck acceleration,
is the Planck energy. This law explains the final result of the derivation. This law proves the creation of a relationship that links the Planck energy and curvature of space-time.
(8)
Where ε0 represents the vacuum permittivity,
is the Vacuum permeability,
is the electron charge. This law works to link the constants ( gravity, electron charge and Planck constant ) into one law.
(9)
This is a law that links the constants ( gravity, electron charge and speed ) into one law.
(10)
Where
represents the multiverse constant,
is the fine-structure constant. This law wants to prove is the creation of a relationship that links the curvature of space-time and the energy of the total photon.
This law affects the Planck constant and the charge of the electron.
Where
Vacuum permeability,
is the Planck length.
(13)
Where
represents the Planck constant,
is the frequency.
(14)
Where
represents the Planck mass.
(15)
These equations represent the energy of a photon in electron volts.
These equations represent the modification of Bragg’s law.
k is the wave vector,
is the momentum,
is the Phase Velocity
k is the wave vector
These equations represent some of the laws that can represent the energy of a photon in relativity in joules.
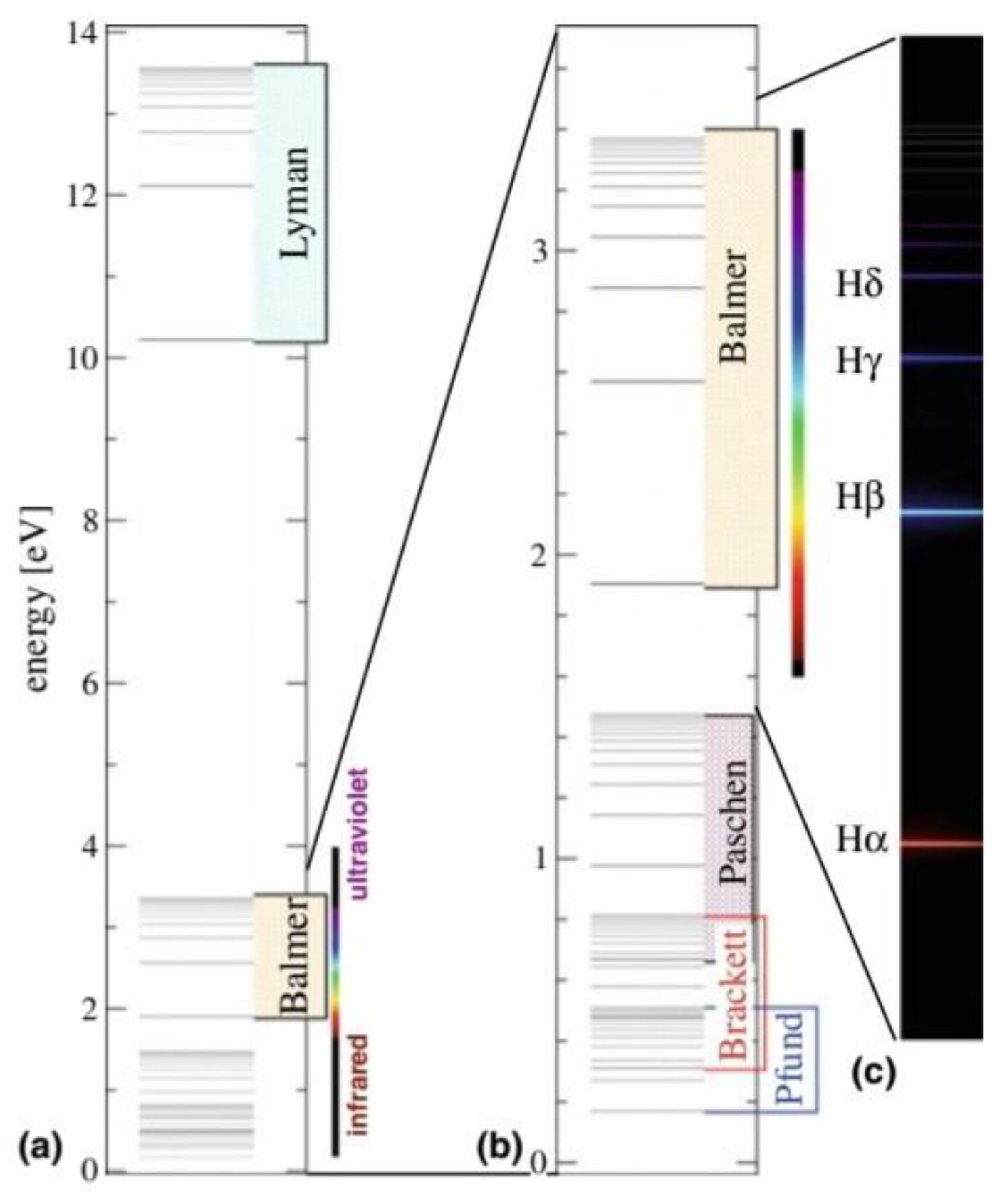
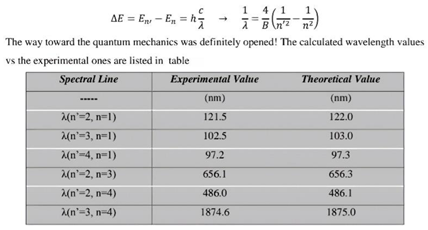
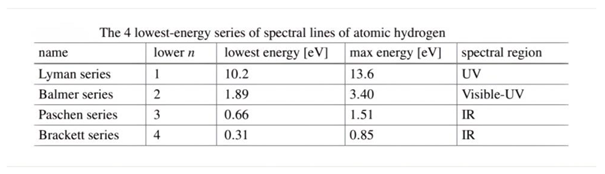
These equations represent some laws that can represent the Bohr energy, wavelength laws, and Rydberg constant, where the electron energy is in volts and the wavelength is in nanometers.
4. Derivation of equations
Completing the derivation of the laws resulting from quantum relativity ( quantum world )
This is derivation number 1
This is derivation number 2
k is the wave vector
is the Phase Velocity
This is derivation number 3
This is derivation number 4
This is derivation number 5
k is the wave vector
is the Phase Velocity
This is derivation number 6
k is the wave vector
This is derivation number 7
is the wavelength is (nm),
is the photon energy is in electron volt
This is derivation number 8
This is derivation number 9
This is derivation number 10
kE
This is derivation number 11
k is the wave vector
This is derivation number 12
This is derivation number 13
Where
represents the Planck mass.
This is derivation number 14
This is derivation number 15
Dirac equation
Ratio of electron mass to Planck mass ( David mass )
Where
represents the affine derivative,
is the connection coefficients,
is the partial derivative
This is derivation number 16
This is derivation number 17
This is derivation number 18
This is derivation number 19
Where
represents the Planck force
This is derivation number 20
This is derivation number 21
This is derivation number 22
This is derivation number 23
This is derivation number 24
This is derivation number 25
This is derivation number 26
This is derivation number 27
This is derivation number 28
This is derivation number 29
This is derivation number 30
This is derivation number 31
This is derivation number 32
This is derivation number 33
Bragg’s law
This is derivation number 34
This is derivation number 35
This is derivation number 36
This is derivation number 37
This is derivation number 38
This is derivation number 39
is the Phase Velocity
This is derivation number 40