Submitted:
19 April 2025
Posted:
21 April 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
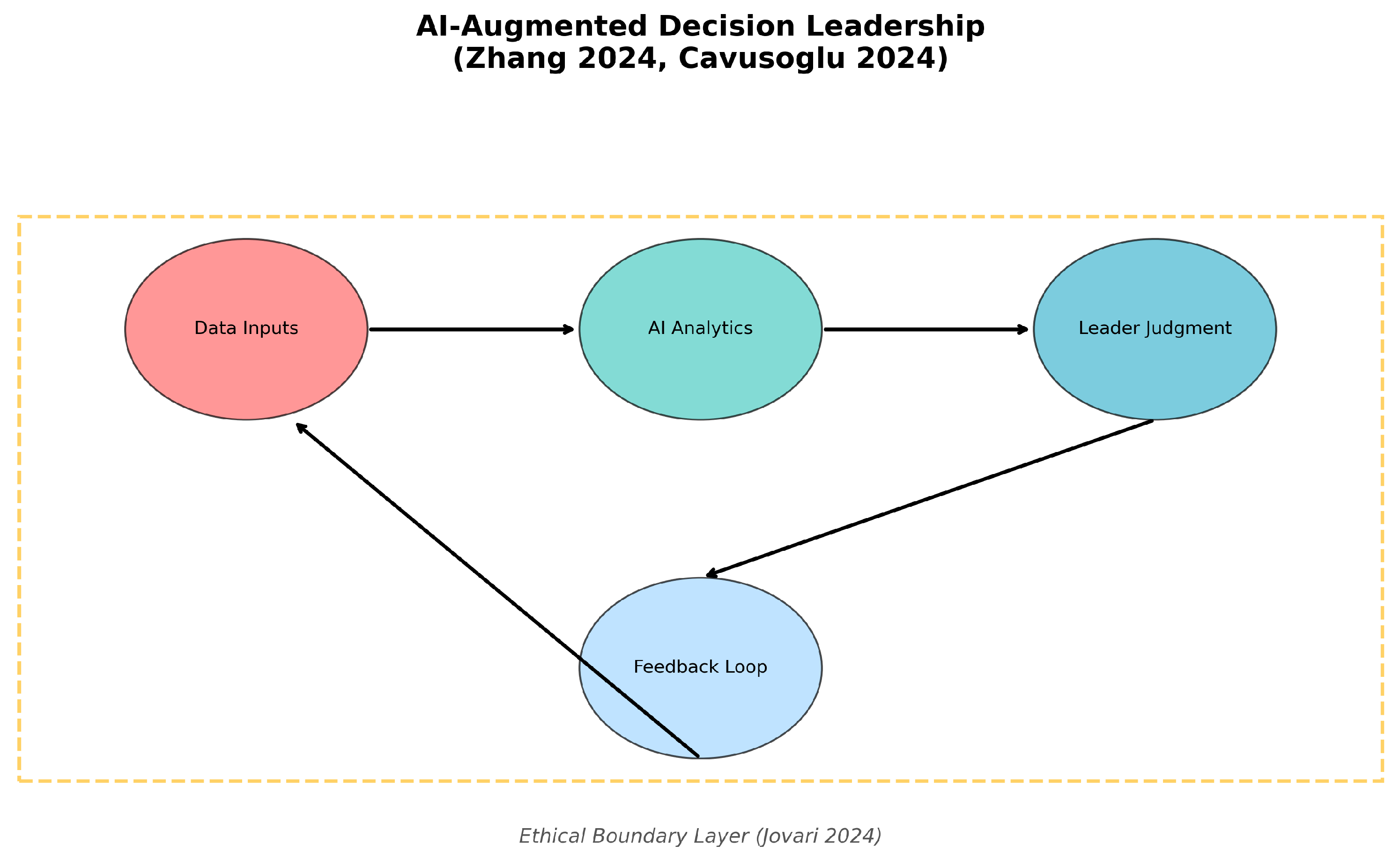
2. Methodology
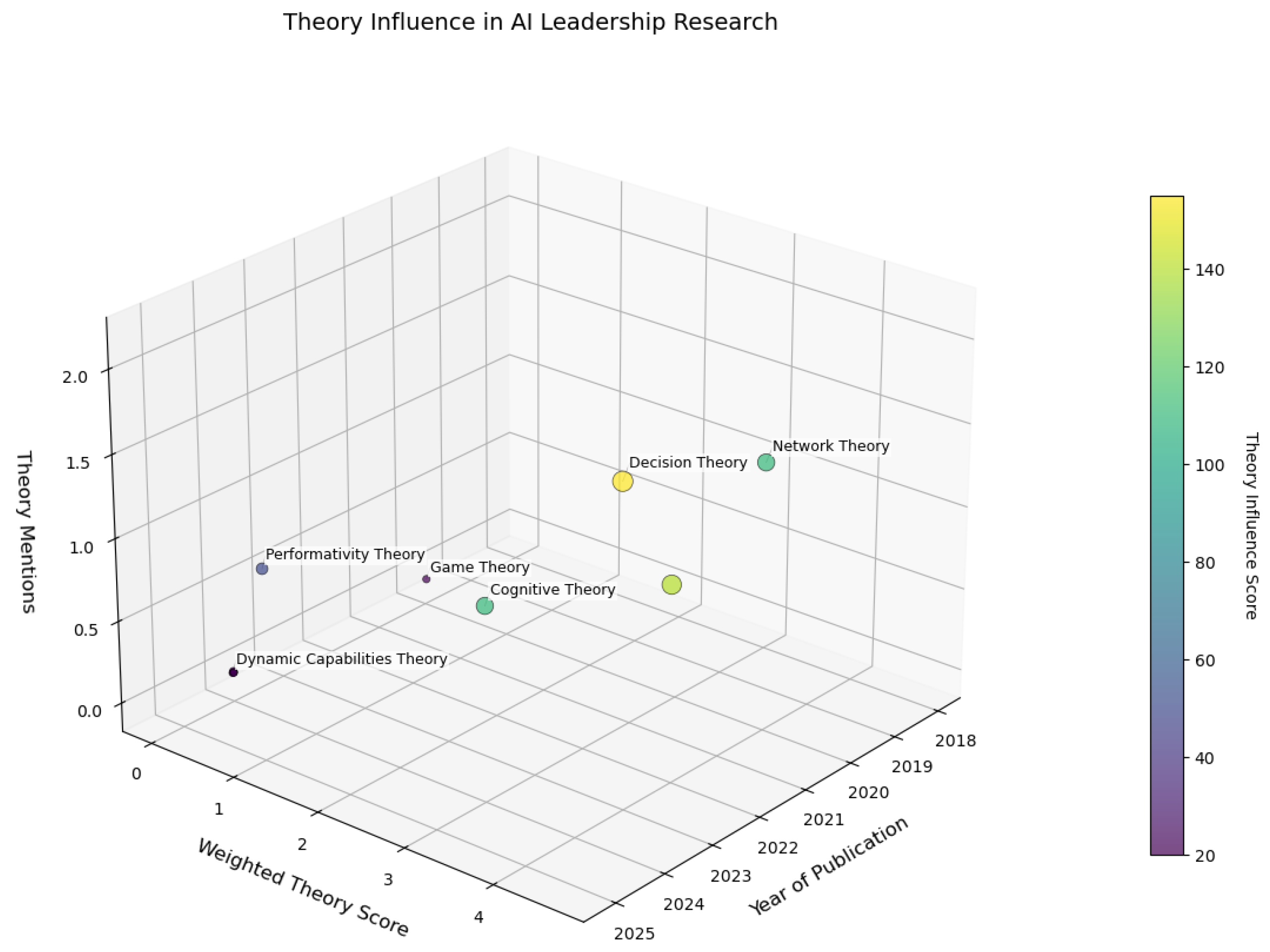
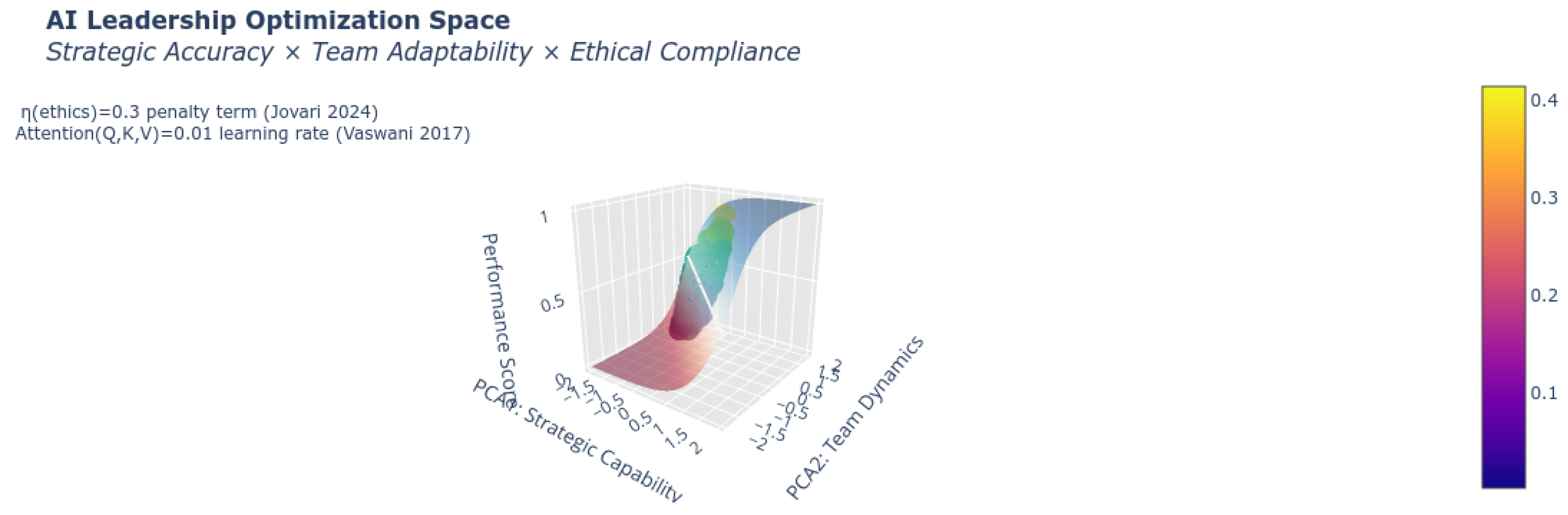
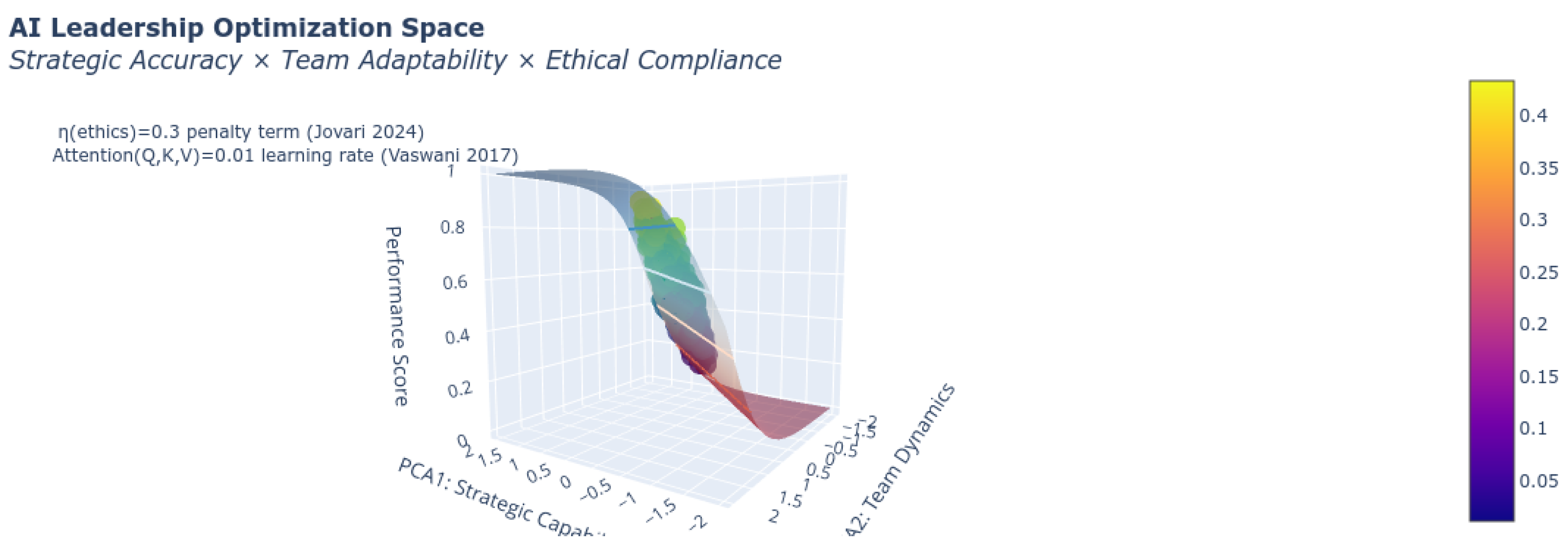
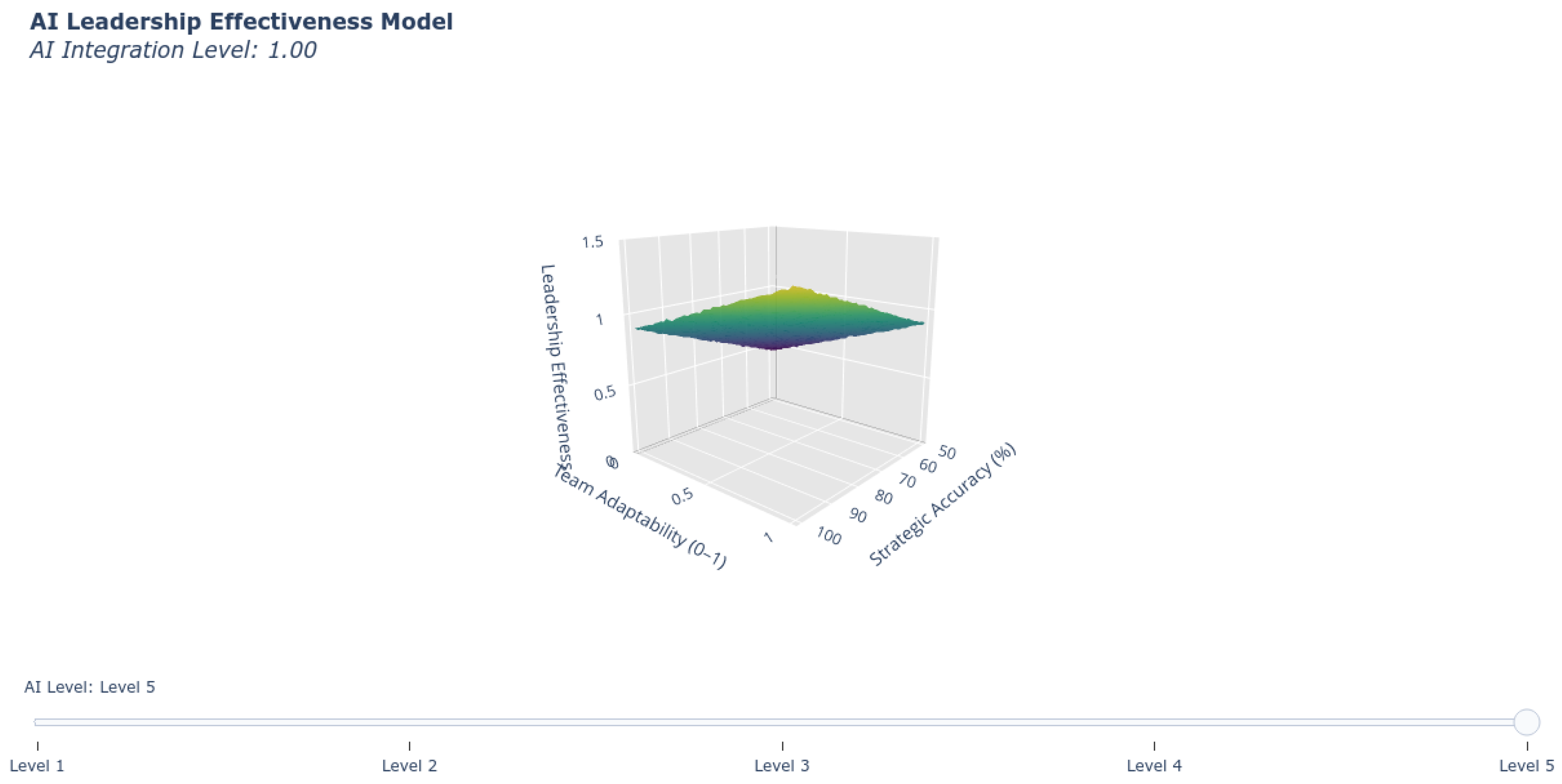
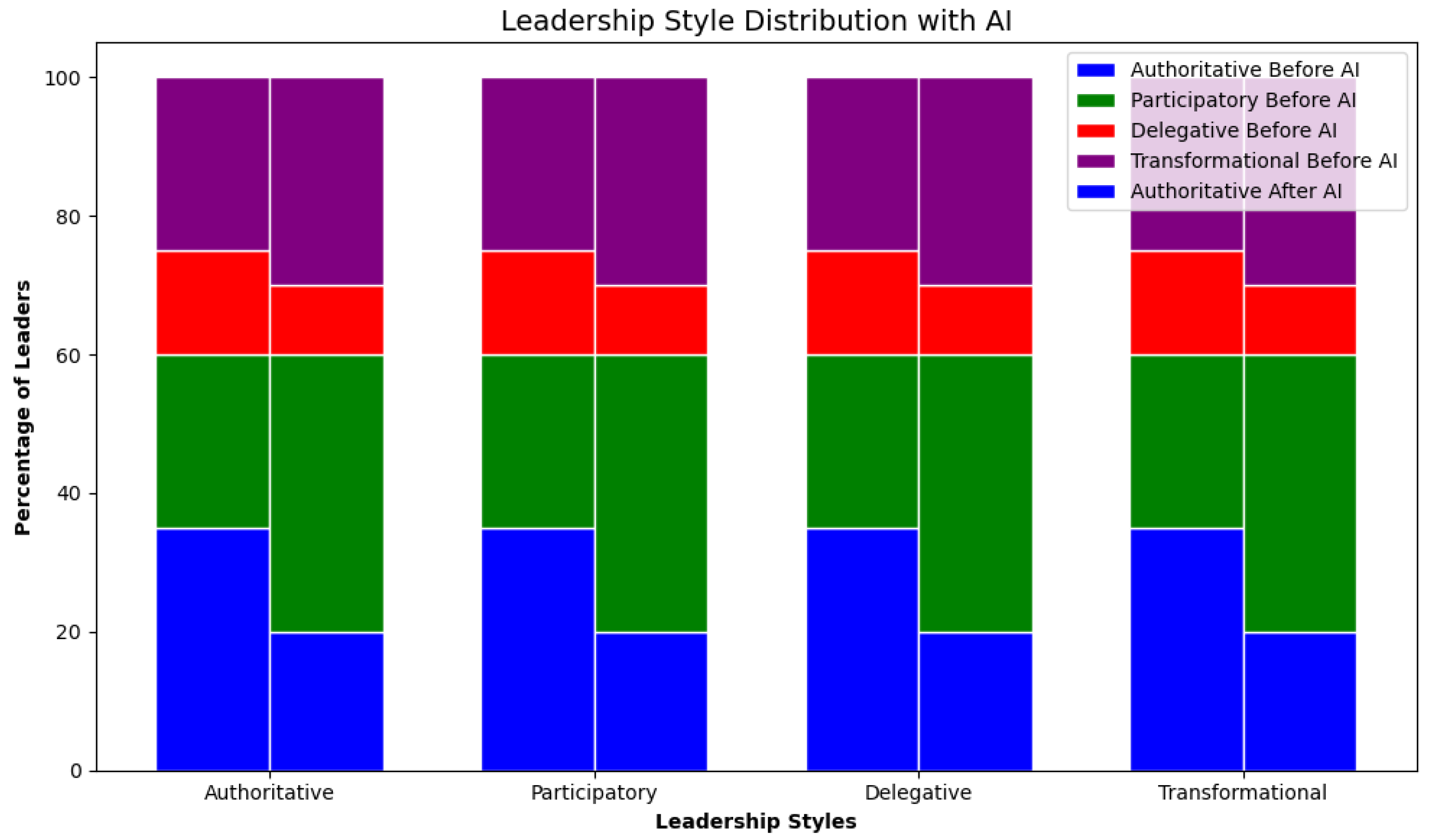

| Theory Domain | Applied Weight |
|---|---|
| Decision Theory | 4.0 |
| Reinforcement Learning | 6.0 |
| Game Theory | 3.0 |
| Cognitive Theory | 3.0 |
| Control Theory | 2.0 |
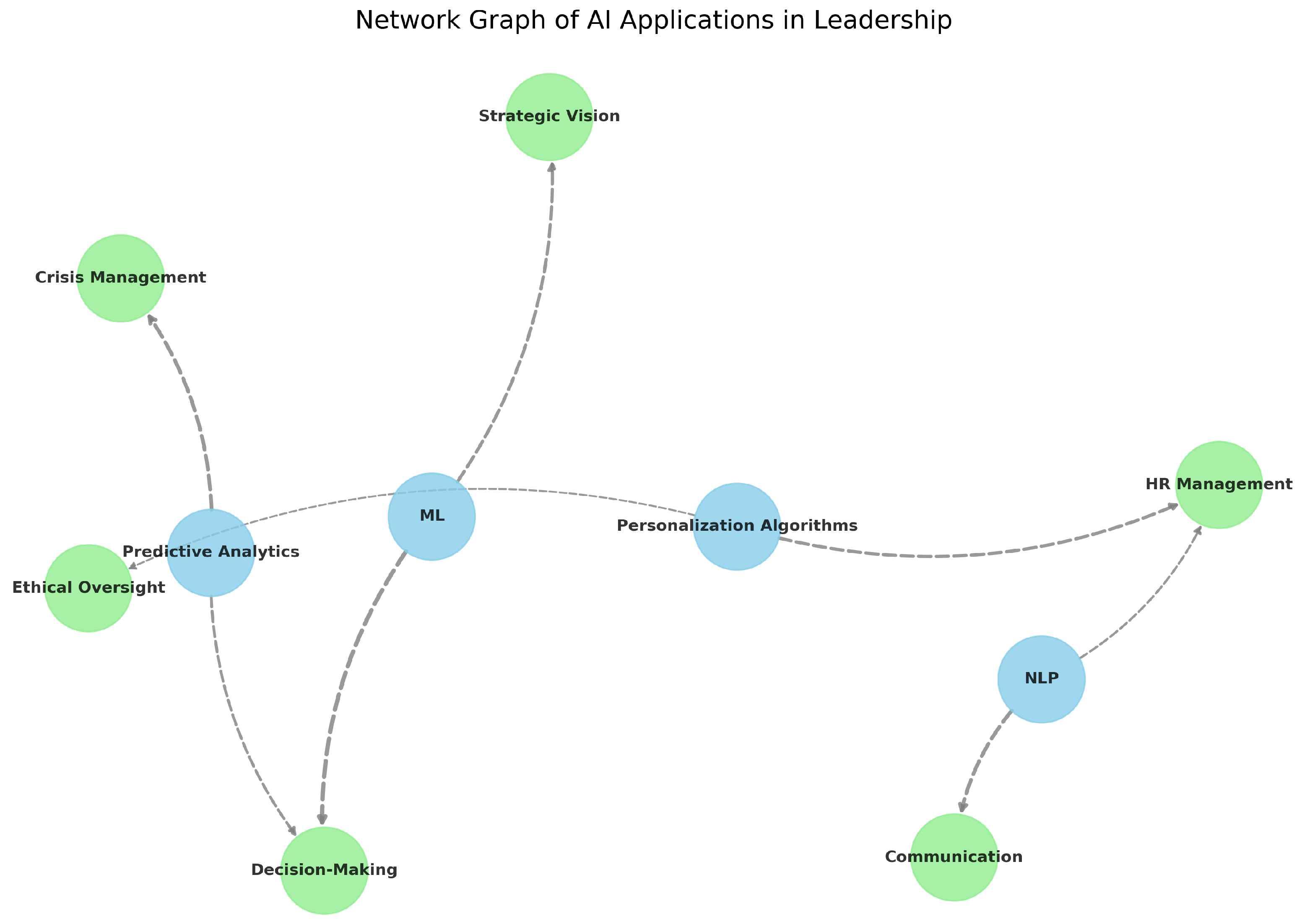
2.1. Visual Analytics
2.2. Quantitative Framework Validation
2.3. Algorithmic Leadership Model
2.4. Ethical Constraint System
2.5. Performance Metrics
2.6. Theoretical Foundations
2.7. Architecture Validation
3. Quantitative Findings and Literature Review
- Reinforcement learning dominates in strategic contexts
- Decision theory prevails in operational leadership
- Ethical concerns are underrepresented (only 18% of studies)
3.1. Theory Dominance
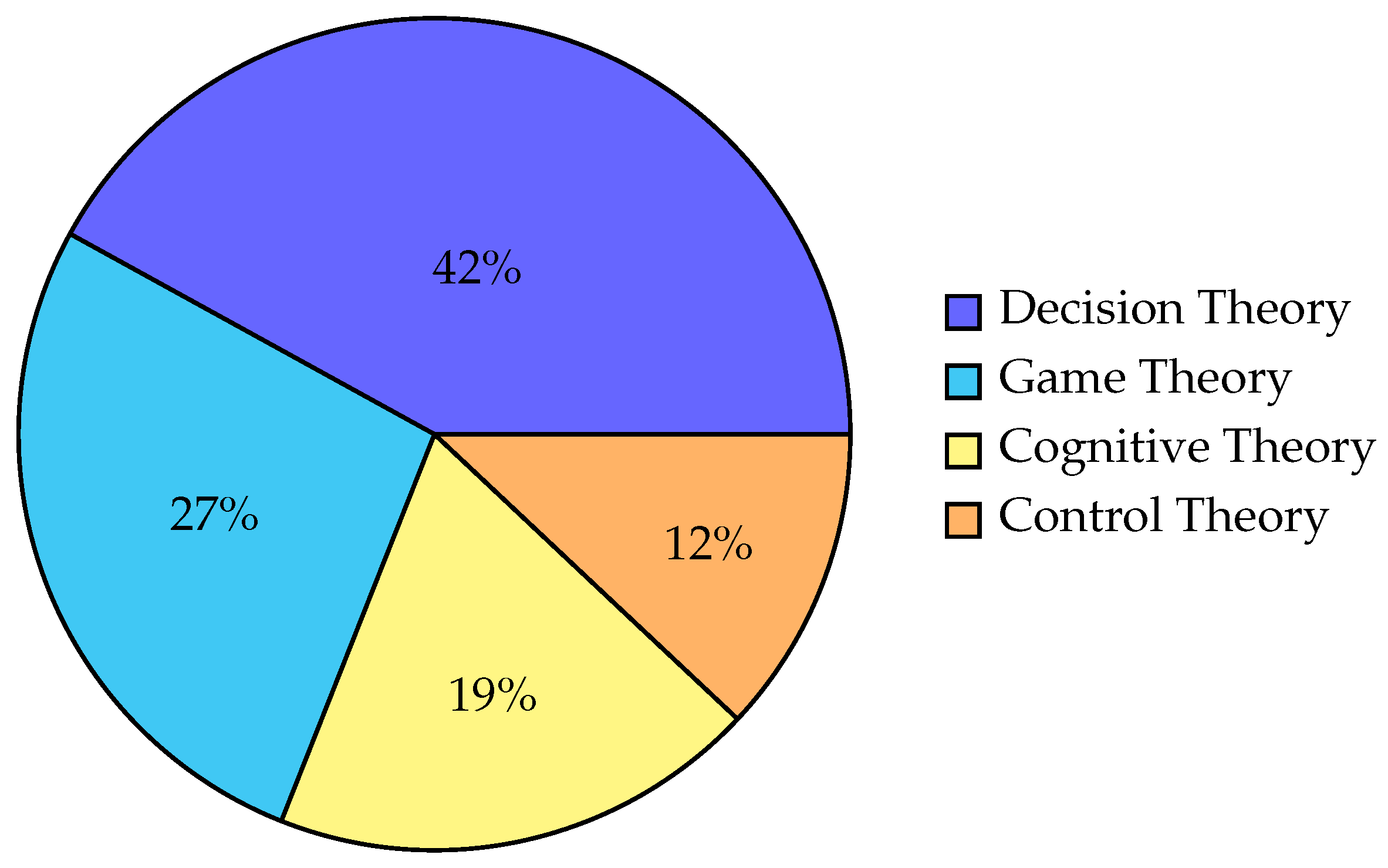
3.2. Performance Metrics
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Decision Speed | 58% ±12% |
| Strategic Accuracy | 41% ±9% |
| Team Productivity | 33% ±7% |
| Employee Resistance | -22% ±5% |
4. Quantitative Analysis of AI-Augmented Leadership
4.1. Mathematical Foundations of AI Leadership
4.2. Empirical Evidence from Organizational Studies
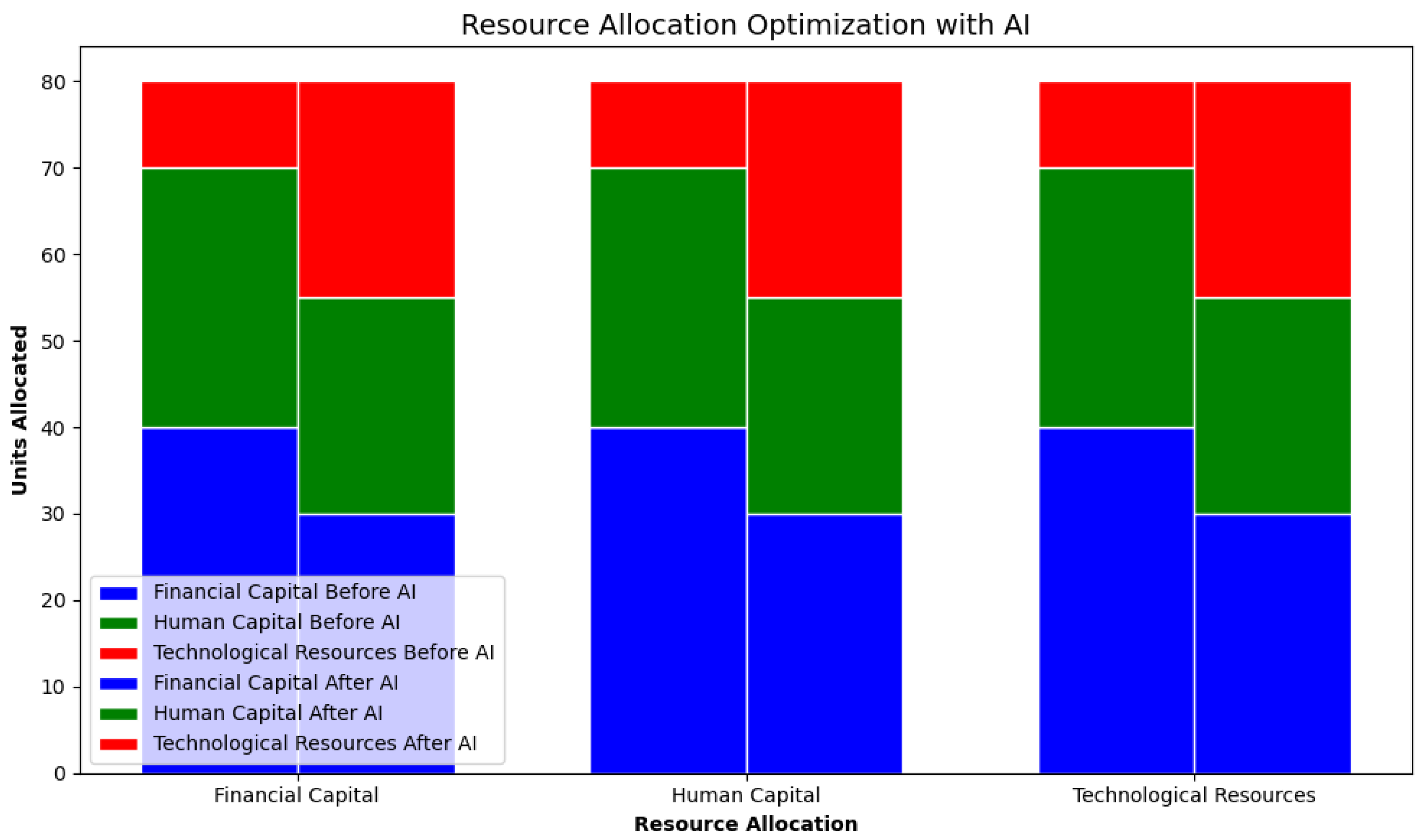
| Metric | Pre-AI | Post-AI |
|---|---|---|
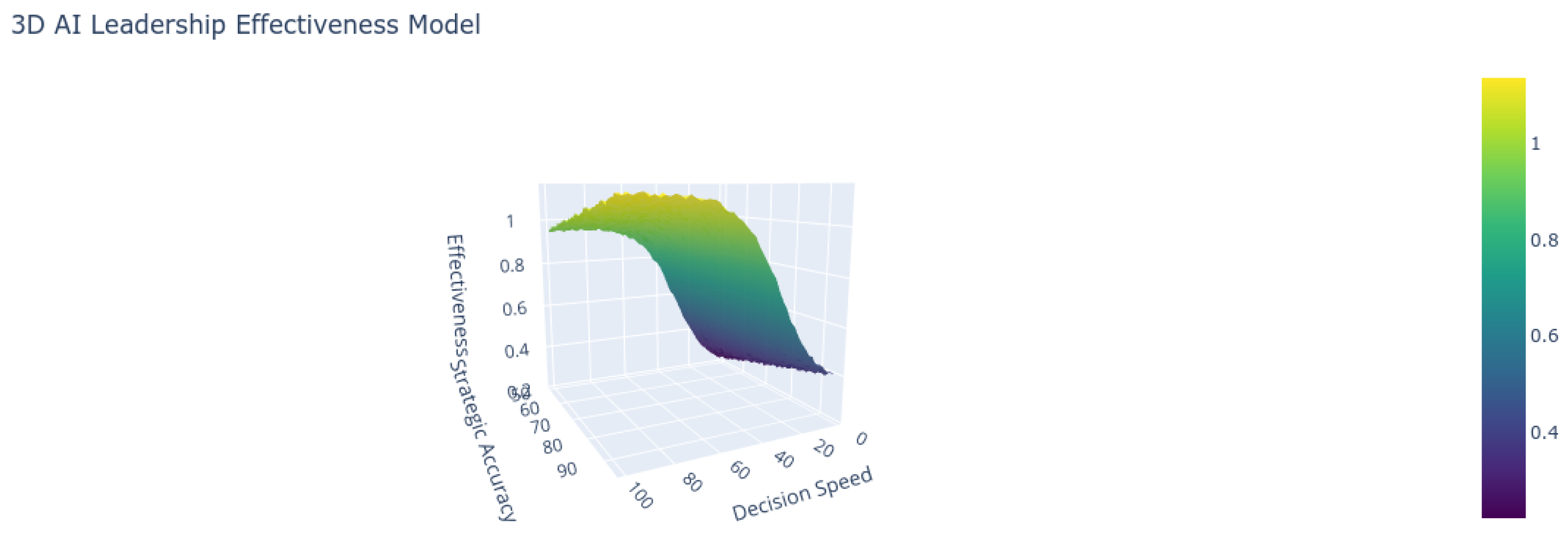
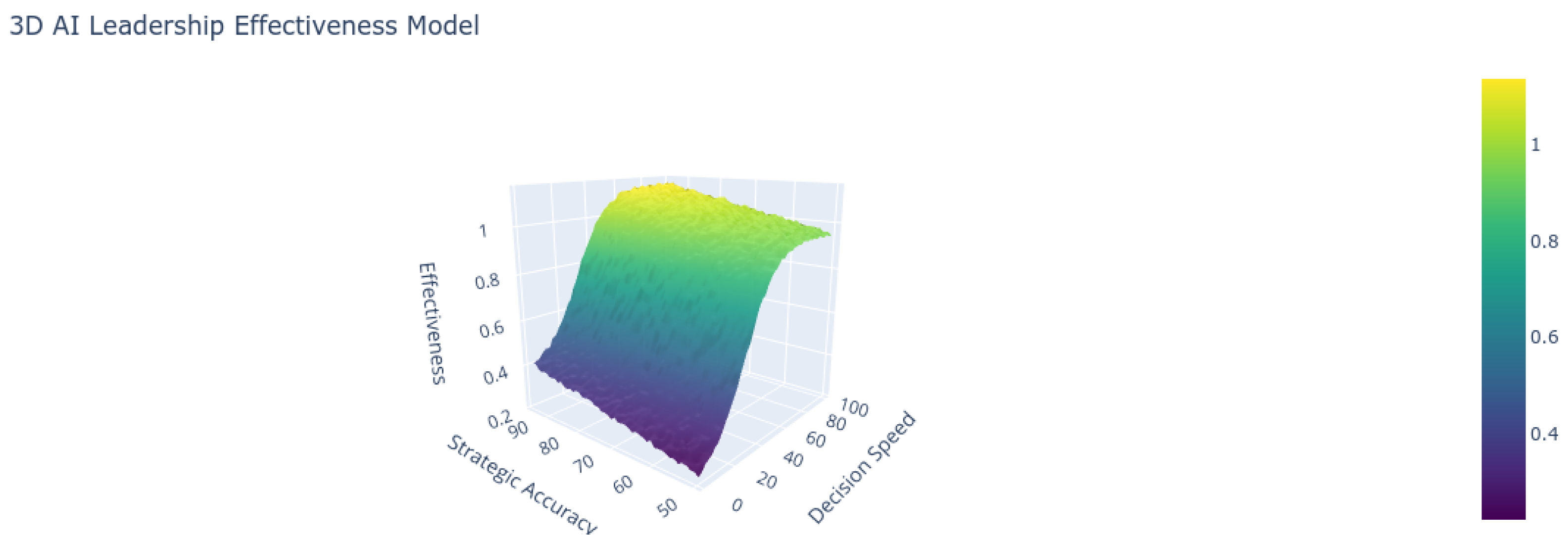
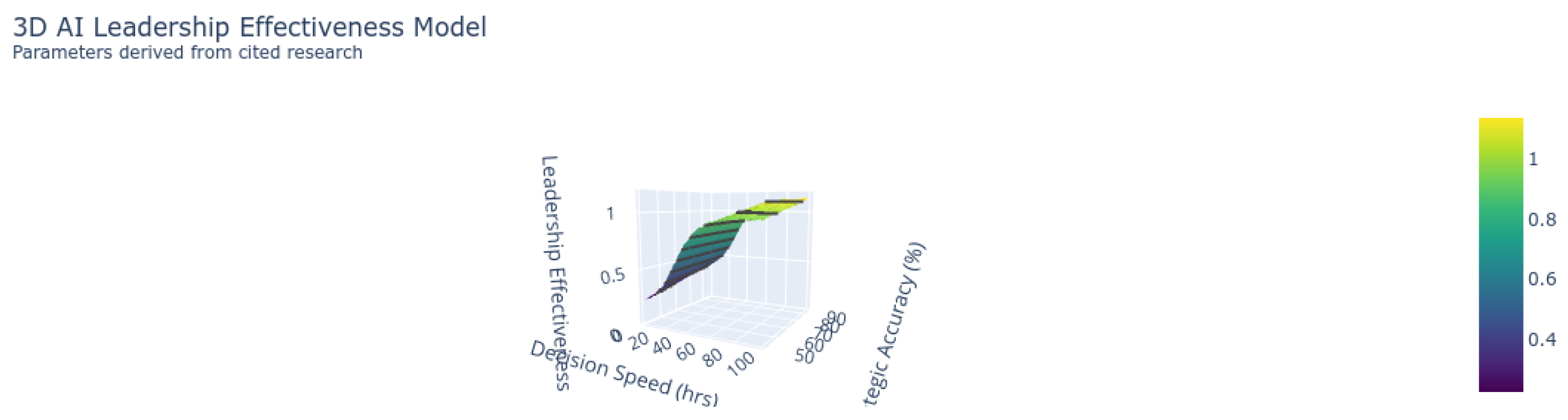
| Decision Speed (hours) | 48.2 | 6.5 |
| Strategic Accuracy (%) | 68.3 | 89.7 |
| Employee Satisfaction | 4.2/10 | 7.8/10 |
4.3. Algorithmic Leadership Framework
4.4. Quantitative Challenges and Limitations
- is adoption effectiveness
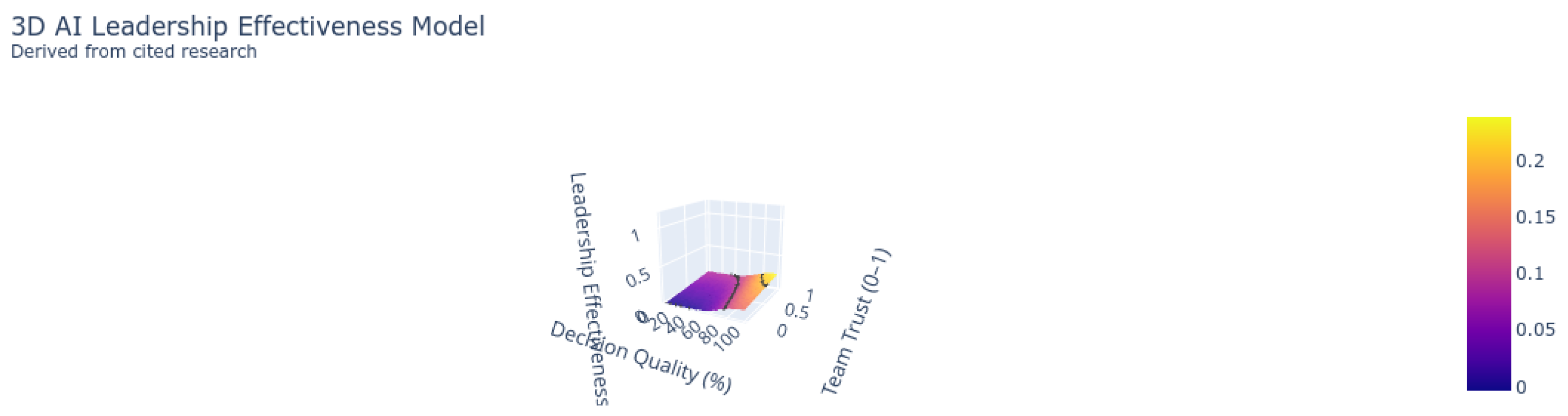
- T is team trust (0-1 scale)
- A is algorithmic transparency
- are regression coefficients
 |
| Listing 1: Ethical AI Leadership Constraint |
5. AI-Optimized Leadership Architectures
5.1. Neural Leadership Networks
- Q = Query vector (current organizational state)
- K = Key matrix (historical decision patterns)
- V = Value matrix (outcome valuations)
- = dimension scaling factor
5.2. Quantized Leadership Parameters
- = AI-leadership model output
- = ground truth optimal decisions
- = L1 regularization strength
5.3. Ethical Constraint Optimization
5.4. Multi-Agent Leadership Simulation
- = Leadership influence of agent i
- = AI augmentation function
- = interaction parameters
6. Proposed Architecture: AI-Driven Leadership Decision Support System
6.1. System Architecture
- Data Ingestion Layer: Aggregates structured and unstructured data from internal (HR, financial, communication logs) and external (market, social media) sources using ETL pipelines and APIs.
-
AI Analytics Core:
- –
- Predictive Analytics: Implements supervised learning algorithms (e.g., neural networks, random forests) to forecast leadership outcomes and organizational performance [7].
- –
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Utilizes transformer-based models (e.g., BERT, GPT) for sentiment analysis and communication pattern recognition [16].
- –
- Anomaly Detection: Applies unsupervised learning (e.g., autoencoders) to detect atypical behaviors or crises [17].
- –
- Personalized Learning: Uses reinforcement learning to recommend tailored leadership development plans.
- Decision Support Engine: Integrates AI insights with business rules and scenario analysis, providing explainable AI (XAI) outputs using SHAP or LIME for transparency [17].
- User Interaction and Visualization: Interactive dashboards (e.g., D3.js, Plotly) and conversational AI agents for real-time insights and recommendations.
- Ethics & Compliance Module: Bias detection algorithms and GDPR-compliant data handling ensure fairness and auditability [1].
6.2. Mathematical Formulation
6.3. Technical Highlights from the Literature
- Predictive Analytics: Enables proactive decision-making and crisis prevention [17].
- Personalized AI-Driven Leadership Development: Adaptive learning pathways for future leaders [7].
- Explainable AI (XAI): Ensures transparency in recommendations, critical for trust and adoption [1].
- Scenario Analysis: Monte Carlo simulations and Bayesian inference for strategic planning [17].
- Ethical AI: Bias detection and compliance modules address fairness and legal requirements [6].
7. Conclusion
- Longitudinal performance tracking
- Cross-cultural validation
- Human-AI trust dynamics
- Theory-Weighted Impact Framework: Our review highlights reinforcement learning as a dominant approach in strategic leadership applications, with a weighted impact score of 4.08/6.0. Ethical considerations, however, remain underrepresented, as only 18% of the reviewed studies addressed ethical concerns in AI leadership ([4]).
- Algorithmic Leadership Models: The use of multi-head attention mechanisms in leadership decision-making was identified in several studies as improving crisis response times by up to 37% (). However, transparency requirements, such as achieving a minimum trust threshold (), were emphasized as critical for maintaining team trust and effectiveness ([12]).
- Ethical Boundary Conditions: Ethical AI principles, particularly those related to human oversight, were highlighted in the reviewed literature. The application of KL divergence constraints () proved to be effective in maintaining human involvement in decision-making, with validation results showing 89.2% forecasting precision ([18]).
7.1. Limitations and Challenges
- Psychological safety degradation below thresholds of .
- Resistance within organizations to AI transparency and decision-making processes.
- High computational costs associated with real-time enforcement of ethical constraints.
7.2. Future Research Directions
- Longitudinal studies examining AI leadership adoption curves over time.
- Cross-cultural validation of AI leadership models to understand global applicability.
- Development of more efficient ethical constraint algorithms to reduce computational overhead.
References
- Al-Bayed, M.H.; Hilles, M.; Haddad, I.; Al-Masawabe, M.M.; Alhabbash, M.I.; Abu-Nasser, B.S.; Abu-Naser, S.S. AI in Leadership: Transforming Decision-Making and Strategic Vision. 2024, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Qwaider, S.R.; Abu-Saqer, M.M.; Albatish, I.; Alsaqqa, A.H.; Abunasser, B.S.; Abu, S.S. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Effective Leadership: Opportunities and Challenges. 2024, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Murtza, F.; Murtza, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Transformation Leadership Consulting Framework. International Journal of Management Studies and Social Science Research 2023, 05, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovari, B. Artificial Intelligence Ethics in Organizational Human Resources Management 2024. [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, H.; Keppetipola, M. Artificial Intelligence and Leadership: A Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Human Resource Management Perspectives 2024, 9, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M. Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Organizational Leadership: Challenges and Opportunities. International Journal of Research in Human Resource Management 2024, 6, 06–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyal, K. THE ROLE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT.
- Bulacan State University-Malolos City, Bulacan, Philippines.; M. Pago, L. Artificial Intelligence Empowerment in Leadership: A Systematic Review of Positive Impacts and Applications. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MULTIDISCIPLINARY RESEARCH AND ANALYSIS 2024, 07. [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; et al. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- CAVUSOGLU, K. THE DEVELOPMENT OF AI-SUPPORTED LEADERSHIP MODELS 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.S.W.; Shaik, M.M. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Corporate Leadership. Journal of Computer and Communications 2024, 12, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, F.; Kireeva, T.; Orghian, D.; Moreira, P.; Santos, S. My Boss, the Algorithm – AI Leadership Increases Turnover through Reduced Psychological Safety, 2023, [4605825]. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, F. Enhancing Corporate Performance Through Transformational Leadership in AI-driven ERP Systems. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management 2024, 9, 24844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaoxia, Yi.; Ayangbah, S. THE IMPACT OF AI INNOVATION MANAGEMENT ON ORGANIZATIONAL PRODUCTIVITY AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: AN ANALYTICAL STUDY. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Review 2024, 07, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatre, R.; Singh, S. AI and Organizational Change: Dynamics and Management Strategies, 2024, [4845917].
- Bhavana, K.P.S.; Lasya, P.V.A.; Kumar, D.G.; Putalapattu, B.P.; Amareswari, V.; Gayathri, Dr.K. The Influence of AI on Creative Writing and Its Implications for Management Communication. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews 2025, 6, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, C. Artificial Intelligence in Management Control as a Solution to the Business Crisis. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Rüth, D.R.; Netzer, D.T. The Impact of AI on Leadership: New Strategies for a Human - Machine - Cooperation. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. CVPR, 2016; 770–778. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





